Functional nausea
Functional nausea refers to unpleasant nausea that occurs at a minimum every week, over a period of more than two months that is not always associated with vomiting and is not caused by a medical issue.
Nausea typically is a distinct feeling of discomfort that can precede vomiting but can be experienced even for a child who does not vomit. It’s often linked to changes in the autonomic system, such as salivation, an increase in respiration and heart rate, and a decrease in mucosal and gastric blood flow
Vomiting (emesis) is the forceful expulsion from the mouth of gastric contents triggered by contraction of the chest and abdominal musculature. Vomitus usually has a mild yellow hue, caused by the reflux of tiny amounts of bile into the stomach. Vomitus is considered to be bilious when it is a bright yellow or green color which indicates greater amounts of bile present in the stomach. Bilious vomiting is typically due to intestinal obstruction as explained below.
Signs that could indicate an issue with vomiting that is serious.
 Other symptoms that are not specific:
Other symptoms that are not specific:
- Prolonged vomiting
- An extreme lethargy
- Significant weight loss
The signs of gastrointestinal obstruction or illness:
- Bilious vomiting
- Projectile vomiting for infants between three and six weeks of age
- Hematemesis
- Hematochezia (rectal bleeding)
- The tenderness and abdominal distension are marked.
The presence of neurologic symptoms could indicate systemic diseases
- Fontanelle swelling in neonates or an infant
- Headache, triggers of position for vomiting or nausea upon the first awakening, or lack of nausea
- Seizures, altered consciousness, or neurologic anomalies that are focal
- History of head injuries
- Hypotension in proportion to the obvious illness, or hyponatremia and hyperkalemia¶
Mechanisms of functional nausea
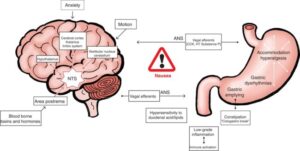
There are a variety of types of impulses that can trigger the cerebral cortex. These impulses can be related to anxiety, motion artifacts changes in the balance of chemicals in the body. These impulses could cause a change in the Area Postremam and transmit impulses via the vagus nerve. causing stomach muscles to tighten.¶
When should you call the doctor Concerning Nausea?
Consult a physician regarding vomiting and nausea:
If nausea persists for more than a couple of days or when there is a chance of becoming pregnant. If the home remedy isn’t working, there is dehydration or a recognized injury is present (such as a head injury or infection) which could be the cause of nausea.
Adults should seek out a doctor when vomiting lasts for longer than a single day, or if diarrhea and vomiting last longer than 24 hours and are indicators of dehydration. Bring a child or infant younger than 6 years old to a doctor if vomiting persists for longer than a couple of hours, there is diarrhea or signs of dehydration appear or there is fever, or in the event that the child hasn’t peed for more than 4-6 hours.
If your child is over six years to a doctor if vomiting persists for more than a day, diarrhea that is accompanied by vomiting continues for more than 24 hours. there are indications of dehydration, the fever is higher than 101 ° and the kid hasn’t had a bowel movement for at least six hours.
It is important to seek medical attention when any of these scenarios occur:
The vomit contains blood (bright blood as “coffee ground” to be precise)
Headache severe or stiff neck
The feeling of drowsiness, confusion, or a loss of alertness
Extreme abdominal pain
Diarrhea
rapid pulse or breathing, chest pain
Treatment for functional nausea
Drinking gradually greater amounts of clear fluids
Do not eat solid foods until the vomiting has stopped
If diarrhea and vomiting last longer than 24 hours an oral rehydrating drink like Pedialyte is recommended to treat and prevent dehydration.
Women who are pregnant and experiencing morning sickness may eat a few crackers prior to getting up from the bed, or consume a high-protein snack prior to getting ready to go to sleep (lean cheese or meat).
In the case of cancer treatment, vomiting can be addressed by a different type of medication. There are prescription and nonprescription medicines which can be employed to treat vomiting that is caused by motion sickness, pregnancy, and other forms of dizziness. However, you should consult your doctor prior to using any of these remedies.
How can I prevent functional nausea?
There are many ways to stop nausea from developing
Take small bites throughout the day, instead of three big meals.
Take your time eating.
Avoid hard-to-digest foods.
Consume food items that are cold or at room temperature if you’re feeling sickened by the smell of warm or hot foods.
Relax after eating, with your head raised approximately 12 inches higher than your feet.
Drink fluids in between meals instead of during meals.
Try eating at a time when you feel less feeling ill.
How can I prevent vomiting if feeling nauseated?
If you feel nauseated, you might be able to stop vomiting by:
Drinking small quantities in clear sweetened beverages like soda or juices of fruit (except grapefruit and grapefruit juices since they are acidic enough)
Relieving in an upright position or an upright lying position activities can aggravate nausea and can cause vomiting.
To prevent nausea and vomiting in children:
To alleviate nausea in the car place your child in a position where they face the front of the car (watching rapid movements out of the side windows may cause nausea to become more severe). Additionally, playing or reading video games while driving can cause motion sickness.
Additional details
Always consult your doctor to confirm that the information provided on this site is appropriate to your specific situation.

Wow, amazing weblog structure! How long have you
been running a blog for? you make blogging look easy.
The entire glance of your website is magnificent,
let alone the content! You can see similar here sklep online
I have fun with, result in I discovered just what I used to be taking a look for.
You have ended my four day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day.
Bye I saw similar here: Sklep online
Hey there! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with Search Engine Optimization? I’m
trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords
but I’m not seeing very good gains. If you know of any please share.
Thanks! You can read similar art here: Sklep online
It’s very interesting! If you need help, look here: ARA Agency
Good day! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with SEO?
I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not
seeing very good results. If you know of any please share.
Kudos! You can read similar text here: Sklep internetowy
Hello there! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with SEO?
I’m trying to get my website to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good success.
If you know of any please share. Cheers! I saw similar art
here: List of Backlinks
Good day! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with SEO?
I’m trying to get my website to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good success.
If you know of any please share. Many thanks! I
saw similar blog here: AA List
Hi! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search
Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for
some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very
good gains. If you know of any please share.
Cheers! I saw similar article here: GSA List
Hi there! Do you know if they make any plugins to
help with SEO? I’m trying to get my site to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very
good success. If you know of any please share. Thank you! I saw
similar blog here: Scrapebox AA List
northern pharmacy canada
Wow, incredible blog structure! How long have you ever been running
a blog for? you make blogging look easy. The full glance of your site is magnificent, as neatly as the content!
You can see similar here sklep online
metformin pills 500 mg
online pharmacy search
Informative Site… Hello guys here are some links that contains information that you may find useful yourselves. It’s Worth Checking out 급전
I’m sharing this with my friends and colleagues.대출
This post resonated with me deeply. Thank you for sharing your insights.급전
I’ve learned so much from reading your blog. Thank you for the education.대출
Your post resonated with me on so many levels, thanks!급전
canada happy family pharmacy
I found your article really insightful and thought-provoking. Thank you!급전
200 mg prednisone daily
Thanks for sharing this insightful post!대출
I enjoyed reading this post. It gave me a lot to think about.dashdome
darknet market lists https://mydarkmarket.com/ – darknet search engine dark web websites
Thanks for the valuable information. This is very helpful.nexusnook
Thanks for the valuable information. This is very helpful.nexusnook
darknet drug links https://mydarknetmarketlinks.com/ – tor markets 2024 dark web sites
darknet sites https://mydarknetmarketlinks.com/ – deep web links deep web links
You have a real gift for writing. Your posts are always so engaging and full of valuable information. Keep up the great work!nexusnook
https://goldengoosecanada.ca/
I love how you present information in such a clear and engaging way. This post was very informative and well-written. Thank you!peakpulsesite
best online canadian pharcharmy
best canadian pharmacy cialis
geinoutime.com
Zhang Mao는 말을 타고 그의 병사들을 전차 진형의 뒤쪽으로 이끌었습니다.
hi, thanks!: click here
I love how you present information in such a clear and engaging way. This post was very informative and well-written. Thank you!peakpulsesite
geinoutime.com
이번에는 Fang Jifan이 혼란스러워 할 차례 였고 감히이 놈을 사랑할 수 있을까요?
hi, thanks!: Peranox
hi, thanks!: Peranox
hi, thanks!: zone porn
Your blog is a wealth of information. I always learn something new from your posts. This one was particularly enlightening. Great job!blogpulse
I love how you present information in such a clear and engaging way. This post was very informative and well-written. Thank you!peakpulsesite
hi, thanks!: zone porn
Your passion for the subject matter is evident in every post you write. This was another outstanding article. Thank you for sharing!coinsslot
propecia for sale uk
I always look forward to your new posts. You have a way of making even the most complex topics easy to understand. Excellent job!swiftnook
geinoutime.com
하지만 Fang Jifan은 여전히 걱정이 있었기 때문에 서둘러 출발하여 청중을 위해 궁전에 들어갔습니다.
北斗の拳-ボクシング王(V2.2)
この記事には心から共感しました。とても感動しました。
This post was incredibly informative and well-organized. I learned so much from reading it. Thank you for your hard work and dedication!rendingnicheblog
geinoutime.com
그런데 문득 더블 월간 패스 기간 동안 모두가 지원해야 한다는 생각이 떠올랐습니다.
Good post! We are linking to this particularly great post
on our site. Keep up the great writing.
My site: web site
I simply needed to thank you very much all over again. I’m not certain the things I might have made to happen without the creative concepts shown by you over my topic. It has been a very scary case in my opinion, however , noticing this specialised strategy you treated the issue forced me to jump for joy. Now i’m grateful for this information and even expect you find out what a powerful job you were putting in educating others with the aid of your web blog. I am sure you haven’t encountered any of us.
There are a few fascinating points with time in the following paragraphs but I do not know if I see every one of them center to heart. There may be some validity but I’m going to take hold opinion until I look into it further. Great write-up , thanks and that we want much more! Added to FeedBurner likewise
when i am downloading stuffs over the internet, psp game downloads are always my priority;;
Have you already setup a fan page on Facebook ?~’-”;
irritable bowel is really bad, this disease can really crap your digestive system,.
Thanks for this excellent. I was wondering whether you were planning of writing similar posts to this one. .Keep up the excellent articles!
geinoutime.com
Wang Jinyuan은 Fang Jifan을 믿을 수 없다는 표정으로 바라보았지만 Fang Jifan의 결정에 겁을 먹었습니다.
Man you legend. return see my website, you must get pleasure from it.
Sewing Machines… […]any time to read or go to the content or perhaps internet sites we certainly have associated with[…]…
There is noticeably a bundle to know about this. I assume you made sure nice points in options also.
Wonderful blog! I found it while surfing around on Yahoo News. Do you have any suggestions on how to get listed in Yahoo News? I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there! Many thanks
very good post, i surely adore this fabulous website, persist in it
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you design this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz answer back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to find out where u got this from. many thanks
‘Thank you for this blog. That’s all I can say. You most definitely have made this blog into something that’s eye opening and important. You clearly know so much about the subject, youve covered so many bases. Great stuff from this part of the internet. Again, thank you for this blog.”
Wonderful goods from you, man. I have understand your stuff previous to and you’re just extremely wonderful. I really like what you’ve acquired here, really like what you’re stating and the way in which you say it. You make it enjoyable and you still care for to keep it wise. I can not wait to read much more from you. This is really a great site.
Hiya, I simply hopped over to your website by way of StumbleUpon. No longer one thing I’d generally learn, however I preferred your feelings none the less. Thank you for making one thing worth reading.
I’d must check with you here. Which is not something I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a put up that can make people think. Additionally, thanks for allowing me to comment!
You’ve really written a very good quality article here. Thank you very much
Thank you spending some time to talk about the following, I’m boldy a lot and even true love studying more to do with now this topic. However, if future, when you realize know-how, do you ever thoughts bringing up-to-date all your webpage that have a lot more stuff? This is useful for my family.
This looks absolutely perfect. All these tinny details are made with lot of background knowledge. I like it a lot. This was a useful post and I think it is rather easy to see from the other comments as well that this post is well written and useful
Nicely We definitely liked studying it. This particular topic procured by you is extremely efficient for correct preparing.
You completed several good points there. I did specific searches on the issue and found many people go in conjunction with along with your blog.
Thank you for any other great article. Where else may anybody get that type of info in such a perfect manner of writing? I’ve a presentation next week, and I am at the search for such information.
Youre so cool! I dont suppose Ive read anything similar to this prior to. So nice to find somebody with original thoughts on this subject. realy appreciate beginning this up. this excellent website are some things that is required on-line, an individual after a little originality. helpful job for bringing new things towards web!
When I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new surveys are added- checkbox and from now on when a comment is added I receive four emails with the exact same comment. Possibly there is in any manner you’ll be able to eliminate me from that service? Thanks!
I like what you guys are up also. Such intelligent work and reporting! Carry on the excellent works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my web site
well, i would say that infertility can be a thing of the past because of modern advancements in medicine”
You ought to actually take into consideration engaged on developing this blog into a serious authority on this market. You evidently have a grasp deal with of the subjects everyone seems to be searching for on this website in any case and you may certainly even earn a buck or two off of some advertisements. I’d discover following recent matters and raising the amount of write ups you place up and I assure you’d start seeing some wonderful targeted site visitors within the close to future. Just a thought, good luck in no matter you do!
We’re a gaggle of volunteers and starting a brand new scheme in our community. Your site provided us with useful info to work on. You’ve done a formidable process and our entire neighborhood might be thankful to you.
very nice post, i absolutely adore this web site, keep on it
Chaga mushroom dinner might have been taught a lot of globally by means of Euro contributor Alexandr Solzhenitsyn michael’s narrative ‘Cancer Ward’ exactly where the large person could alleviated linked with types of cancer among help from this specific coffee. Chaga Mushroom
After study a handful of the blog articles on the web site now, and I truly as if your technique of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and are checking back soon. Pls have a look at my site at the same time and told me what you consider.
Hey there guys, newbie here. I’ve lurked about here for a little while and thought I’d take part in! Looks like you’ve got quite a good place here
You completed several nice points there. I did a search on the subject and found a good number of persons will consent with your blog.
Appreciate it to get a incredibly apparent and very helpful publish. I’m positively a violator of many of these rules. I generally uncover personally conflicted when producing a blog posting because I see myself personally creating more than people prefer to read, but I feel that I have got to do the subject matter proper rights by completely protecting it. I think that by pursuing some of these policies I finish up cutting out critical factors to the dialogue. I guess you could have to acquire a stability.
Wow , Your blog has some great information on there. Glad i come across it. I have now bookmarked and shared your blog on social platforms. Thanks alot
Strange this put up is totaly unrelated to what I used to be searching google for, but it surely was indexed at the first page. I guess your doing one thing right if Google likes you sufficient to put you at the first web page of a non similar search.
This is a lot of information to take in, but I am enjoying the thought process. I really am impressed with your article. Thank you.
This site was… how do I say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve found something which helped me. Appreciate it.
Hi there! Do you know if they make any plugins to help
with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my website to rank for some targeted
keywords but I’m not seeing very good results.
If you know of any please share. Appreciate it! You can read similar art here:
Escape rooms
Inquire into various other publisher’s information sites. In the event you communicate insurance jacksonville fl with all the posting local community, anyone are more likely to have the web site go through more regularly. All over again, visitors.
I believe this site has very good written subject matter content .
One of the things I enjoy regarding reading websites such as this, is that there aren’t any spelling or lexical errors! Causes it to be tough about the readers sometimes. Very good work upon that and also the subject of this website. Many thanks!
I’ve been exploring for a little for any high-quality articles or blog posts on this sort of area . Exploring in Yahoo I ultimately stumbled upon this website. Studying this information So i’m satisfied to convey that I’ve a very excellent uncanny feeling I found out exactly what I needed. I most unquestionably will make certain to don’t omit this website and provides it a glance a continuing.
This is my first time i visit here. I found so many informative stuffs on your blog, especially its discussion. Form the tons of comments and posts, I guess I am not the only one having all enjoyment here. Keep up the good work.
Some truly nice and useful information on this site, also I believe the pattern holds superb features.
one of the best addition to a home garden is of course a garden fountain. it also cools down the temperature of the garden::
Your blog is so informative … keep up the good work!!!! online casino
What would be your next topic next week on your blog.*,*’*
It’s rare knowledgeable individuals on this topic, and you appear to be what happens you are referring to! Thanks
It?? hard to find experienced people about this topic, however, you seem like you know what you??e discussing! Thanks
I conceive this site has some rattling excellent information for everyone : D.
Admiring the time and energy you put into your blog and in depth information you offer. It’s good to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same old rehashed material. Fantastic read! I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m adding your RSS feeds to my Google account.
Perhaps you should also a put a forum site on your blog to increase reader interaction.;*,”,
Can I just now say thats a relief to find someone that truly knows what theyre speaking about on the web. You certainly learn how to bring a problem to light and earn it critical. The best way to should check out this and can see this side from the story. I cant think youre no more common since you absolutely possess the gift.
What your stating is absolutely correct. I know that everybody need to say the identical thing, but I just assume that you put it in a way that everybody can fully grasp. I also really like the photos you set in here. They suit so effectively with what youre hoping to say. Im confident youll attain so many folks with what youve received to say.
I really appreciate your piece of work, Great post.
Just wish to say your article is as astonishing. The clarity
in your post is simply spectacular and i could assume you’re an expert on this
subject. Well with your permission allow me to grab your feed to keep
updated with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please carry on the rewarding
work.
My page :: seo services
This is a topic which is near to my heart… Cheers! Where can I find the contact details for questions?
our coffee tables have a top part that is made of high strength glass,`
I would like to consider the ability of thanking you for the professional advice I have often enjoyed going to your site. I will be looking forward to the actual commencement of my college research and the general prep would never have been complete without coming to your website. If I could be of any help to others, I would be glad to help by means of what I have gained from here. Kosova Airlines
I visited a lot of website but I believe this one has got something extra in it in it
Well, this Tuesday I read through a couple of your posts and this is probably one of your better ones. Have a nice day!
It’s amazing in support of me to have a site, which is
beneficial designed for my knowledge. thanks admin
Feel free to visit my webpage … SEO Hawk
excellent issues altogether, you simply received a brand
new reader. What would you suggest in regards to your publish that you simply made some days ago?
Any positive?
Here is my web blog – Best Rated Seo Agency
Hello! I simply would wish to make a huge thumbs up for the fantastic info you have here with this post. We are coming back to your website for further soon.
The following time I learn a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as a lot as this one. I mean, I do know it was my option to read, however I really thought youd have one thing attention-grabbing to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about one thing that you would fix in the event you werent too busy on the lookout for attention.
I really like reading through an article that will make people think. Also, thank you for allowing for me to comment.
You can certainly see your enthusiasm in the work you write. The world hopes for even more passionate writers like you who are not afraid to say how they believe. Always go after your heart.
i think that gay marriage should be allowed in certain states but not in other states .
Thank you for another fantastic article. Where else may just anybody get that type of info in such an ideal manner of writing? I have a presentation subsequent week, and I am at the search for such information.
Aw, it was a very good post. In idea I must invest writing such as this additionally – spending time and actual effort to produce a excellent article… but what can I say… I procrastinate alot by no means often get something carried out.
I’ll immediately seize your rss feed as I can’t in finding your email subscription hyperlink or newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Please allow me understand in order that I may just subscribe. Thanks!
Can I just say what a relief to discover somebody that truly knows what theyre speaking about online. You certainly discover how to bring a difficulty to light making it crucial. Workout . should ought to see this and understand why side of the story. I cant believe youre not more well-liked since you also certainly develop the gift.
This is great! I think reading this, I loved every word. Seriously, keep posting the good information, bloggers like myself need it.
chiropractors are heaven sent when i got a very bad sprain after playing football’
Great articles and great layout. Your blog post deserves all of the positive feedback it’s been getting.
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your weblog and in accession capital to assert that I acquire in fact enjoyed account your blog posts. Anyway I will be subscribing to your augment and even I achievement you access consistently quickly.
I am curious to find out what blog system you have been using? I’m having some minor security problems with my latest site and I’d like to find something more safeguarded. Do you have any recommendations?
I enjoy this website, will certainly arrive back. Make sure you carry on writing high quality posts.
Love the blog here. Nice colors. I am definitely keeping up on the comments here. I hope to see more from you in the near future.
Thank you for sharing with us, I believe this website really stands out : D.
Perhaps you should also a put a forum site on your blog to increase reader interaction.`-`:.
I enjoy the efforts you have put in this, regards for all the great blog posts.
In a similar fashion, determine this particular.. might a male exactly who says he has gaining many trillion us dollars annually, take the time to be able to local seo create plus current market a great booklet expounding on the best way he / she would the item? There’s no doubt that not necessarily! Opt for a person’s very first instincs, they’re usually rather appropriate!
Hello! I just would like to give you a large thumbs up for your wonderful information you’ve here on this post. We are returning to your blog to get more soon.
This post post made me think. I will write something about this on my blog. x
Thanks , I have recently been searching for info about this topic for a while and yours is the greatest I’ve came upon till now. However, what concerning the bottom line? Are you sure concerning the source? rentacar kosova
Hello! I merely would wish to supply a massive thumbs up with the excellent info you’ve got here with this post. We are coming back to your site to get more detailed soon.
I’ve also been meditating on the identical idea personally lately. Happy to see somebody on the same wavelength! Nice article.
F*ckin’ remarkable things here. I’m very glad to see your post. Thanks so much and i am taking a look ahead to touch you. Will you please drop me a mail?
I enjoy you because of all of the effort on this web page. My daughter loves carrying out research and it’s really easy to see why. Almost all know all regarding the dynamic means you convey both interesting and useful steps through your web site and as well as invigorate participation from other individuals on this area of interest so our favorite girl has been being taught so much. Have fun with the remaining portion of the year. You are always doing a superb job.
théme est correctement écrit. Et-il possible de reprendre du billet
vjw4e7
I found your weblog web site on google and verify just a few of your early posts. Proceed to maintain up the superb operate. I just additional up your RSS feed to my MSN Information Reader. Searching for forward to studying more from you afterward!? I am typically to running a blog and i actually admire your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I am going to bookmark your website and hold checking for brand spanking new information.
i would like to replace our bathroom lighting with light emitting diodes to save electricity-
Fantastic site. Lots of useful information here. I am sending it to a few pals ans also sharing in delicious. And certainly, thank you to your effort!
I have been surfing online more than three working hours today, however I never found any kind of interesting document like your own. It is quite worth enough to me. Personally, if all web owners and blog writers created great articles as you did, the internet will be a lot more useful than previously.
I’m always looking for these kinds of posts but its not easy to find such good information.
I’m not sure why but this web site is loading very slow for me. Is anyone else having this issue or is it a issue on my end? I’ll check back later on and see if the problem still exists.
I wan’t going to comment as this posts a bit old now, but just wanted to say thanks.
Awesome document! I¡¯ll rss fix nowadays wth the little feedreader software application!¡
very nice publish, i definitely love this web site, carry on it
After I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now every time a comment is added I get four emails with the identical comment. Is there any way you’ll be able to remove me from that service? Thanks!
Enjoyed examining this, very good stuff, thankyou .
I adore your website.. excellent colours & theme. Did an individual design this site oneself or maybe have you actually rely on someone else to do it for you personally? Plz answer while I!|m planning to design and style my very own blog site as well as want to learn where by u became this specific through. thanks
After study many of the content for your web site now, i truly as if your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark site list and are checking back soon. Pls have a look at my site also and figure out how you feel.
i always make sure that our kitchen appliances are very clean and shiny before using them;
I will right away take hold of your rss as I can not in finding your e-mail subscription link or e-newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Kindly permit me recognise in order that I could subscribe. Thanks.
Good day, i am doing research right now and your blog really helped me,
What others have stated and in some uncommon cases, suicide might occur.
I think other web site owners should take this site as an model – very clean and excellent style and design, as well as the content. You are an expert in this topic!
Simply wish to say your article is as astonishing. The clarity in your post is just cool and i could assume you are an expert on this subject. Well with your permission allow me to grab your RSS feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please continue the gratifying work. insurance guides
I discovered your blog post site on the internet and check many of your early posts. Keep the good operate. I merely additional your Rss to my MSN News Reader. Looking for forward to reading more on your part down the road!…
Have you tried twitterfeed on your blog, i think it would be cool.**~..
Hey there, I think your blog might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your website in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, superb blog!
Heya i’m for the first time here. I came across this board and I in finding It truly useful & it helped me out much. I’m hoping to give one thing back and help others such as you aided me.
Youre so cool! I dont suppose Ive read anything like this prior to. So nice to seek out somebody by original applying for grants this subject. realy i
I impressed, I must say. Actually not often do I encounter a blog that both educative and entertaining, and let me tell you, you have hit the nail on the head. Your idea is excellent; the problem is one thing that not enough people are talking intelligently about. I’m very pleased that I stumbled across this in my seek for one thing relating to this.
Spot on with this write-up, I truly assume this web site wants much more consideration. probably be again to learn rather more, thanks for that info.
Way cool! Some very valid points! I appreciate you writing this article plus the rest of the site is really good.
Thank you, I have just been looking for info approximately this subject for ages and yours is the greatest I’ve came upon till now. However, what concerning the bottom line? Are you certain concerning the source?
After exploring a handful of the articles on your blog, I honestly like your way of blogging. I saved as a favorite it to my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back soon. Please visit my website too and tell me how you feel.
I discovered your blog post site on google and check a few of your early posts. Always keep in the great operate. I simply extra the RSS feed to my MSN News Reader. Looking for toward reading much more on your part at a later date!…
I enjoy reading through a post that can make people think. Also, many thanks for allowing for me to comment.
geinoutime.com
Fang Jifan은 떨고 돌아서 뛰었지만 Zhang Mao는 어깨에 팔을 얹었습니다!
This is a topic that’s near to my heart… Take care! Exactly where are your contact details though?
mail order pharmacy list
zithromax
Howdy! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with SEO?
I’m trying to get my website to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very
good results. If you know of any please share.
Thank you! I saw similar text here
Hello to all, for the reason that I am really eager of reading this website’s post to
be updated on a regular basis. It includes good material.
canadian online pharmacies ratings
This is the perfect website for anyone who would like to understand this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I personally will need to…HaHa). You certainly put a fresh spin on a topic that has been written about for decades. Excellent stuff, just wonderful.
Thank you for the good writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it. Look advanced to more added agreeable from you! However, how can we communicate?
This will be the right blog for everyone who is would like to discover this topic. You recognize a great deal its virtually tricky to argue along with you (not that I really would want…HaHa). You certainly put a brand new spin using a topic thats been discussed for several years. Wonderful stuff, just wonderful!
Incredible this kind of guideline is incredible it truly helped me and also my family, cheers!
Thanks for this wonderful post! It has long been very helpful. I wish that you’ll carry on posting your wisdom with us.
This site is really a walk-through for all of the data you wanted about it and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse here, and you’ll undoubtedly discover it.
Hello! I would wish to give a enormous thumbs up to the wonderful information you may have here about this post. I will be returning to your blog site to get more detailed soon.
I discovered your website internet site on the internet and appearance a few of your early posts. Maintain inside the top notch operate. I additional up your Rss to my MSN News Reader. Seeking toward reading a lot more by you later on!…
You’re probably thinking since this is a studio comedy, everything will be wrapped up in a nice little package.
I’d must check with you here. Which isn’t some thing It’s my job to do! I enjoy reading an article that should make people think. Also, thanks for permitting me to comment!
I admire the valuable information and facts you offer inside your posts. Ill bookmark your weblog and also have my children examine up right here typically. Im fairly positive theyll discover a lot of new things here than anybody else!
This is a very informative article. It really sparked my interest on several points. I agree with most of the points and am currently pondering the rest. Thank you for keeping your information so engaging.
Aw, this was an exceptionally nice post. Spending some time and actual effort to create a great article… but what can I say… I hesitate a whole lot and don’t seem to get nearly anything done.
This was a good read. Thanks for the post.
I appreciate your time and effort allocated to this article, bad i had to spend this long to find it but as they say top quality is hard to locate. Continue the good work.
The when I just read a weblog, Hopefully who’s doesnt disappoint me as much as brussels. Come on, man, It was my method to read, but I just thought youd have some thing intriguing to express. All I hear is actually a handful of whining about something you could fix in the event you werent too busy searching for attention.
geinoutime.com
Xiao Jing은 옆에서 미소를 지으며 말했습니다. “전하…”
Wholesale Gucci Shoes Saved! Found yourself on google and i’m glad Used to do. Great site you will need to get a pile of traffic here’ desire to own a blog like this.
Thank you for the sensible critique. Me and my neighbor were just preparing to do some research about this. We got a grab a book from our local library but I think I learned more from this post. I’m very glad to see such wonderful info being shared freely out there.
Having read this I believed it was rather enlightening. I appreciate you finding the time and energy to put this content together. I once again find myself personally spending a significant amount of time both reading and leaving comments. But so what, it was still worth it!
The subsequent time I learn a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as much as this one. I mean, I do know it was my option to read, but I really thought youd have something attention-grabbing to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you could possibly repair should you werent too busy on the lookout for attention.
I discovered your website web site on the search engines and check a couple of your early posts. Continue to keep up the great operate. I additional encourage Feed to my MSN News Reader. Seeking forward to reading much more within you at a later date!…
This amazing put up usually get a wide selection of guests. Find out how to market it? The situation offers a excellent one-of-a-kind turn relating to matters. Just maybe developing point honest and / or a lot of giving information about is the main event.
I want looking at and I think this website got some really useful stuff on it! .
I really love the way you discuss this kind of topic.”‘*,-
I always visit your blog everyday to read new topics.’**.;
tamoxifen pill
every woman needs fine jewelries because it becomes a fashion statement of your personality’
Absolutely composed subject matter, thankyou for information .
It’s difficult to find knowledgeable people on this topic, nevertheless, you appear to be you know what you’re referring to! Thanks
This site is usually a walk-through its the knowledge you wished concerning this and didn’t know who need to. Glimpse here, and you’ll certainly discover it.
It’s rare knowledgeable people during this topic, however, you seem like do you know what you’re discussing! Thanks
genuine cialis canada
When I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and already whenever a comment is added I buy four emails with similar comment. Could there be in whatever way it is possible to remove me from that service? Thanks!
Oh my goodness! an incredible article dude. Thank you Nonetheless I am experiencing problem with ur rss . Don’t know why Unable to subscribe to it. Is there anyone getting an identical rss downside? Anyone who is aware of kindly respond. Thnkx
Very great post. I simply stumbled upon your weblog and wanted to mention that I have really enjoyed surfing around your weblog posts. In any case I’ll be subscribing to your feed and I hope you write again soon!
I feel much better informed about asbestos removal after reading this blog.
Wohh just what I was looking for, appreciate it for putting up.
Thanks for the clear and concise information on asbestos removal.
Thanks for shedding light on the importance of professional asbestos removal.
Excellent post. I was checking constantly this blog and I am impressed! Very helpful info particularly the last part I care for such information a lot. I was seeking this certain information for a long time. Thank you and good luck.
Thanks for shedding light on the importance of professional asbestos removal.
Thanks for that magnificent write-up, great site to! It makes be want to get a weblog. What software do you have to get started? I hear a good deal about this WordPress?!!
Great tips on asbestos safety! This is a must-read for homeowners.
Thanks for one’s wonderful post! We definitely liked reading it, you could be an great contributor. I shall always take a note of this blog page and will often come back later on, I wish to motivate that you continue this great job, enjoy your evening? BTW have you read Gaddafi remarkable headlines Regards Independent Financial Advisor
Thanks for the tips on safely handling asbestos removal. Very useful!
Very informative blog on asbestos removal! Thanks for sharing.
I loved as much as you’ll receive carried out right here. The sketch is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an edginess over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come more formerly again since exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this increase.
I discovered your website website online and check many of your early posts. Keep in the top notch operate. I simply additional increase RSS feed to my MSN News Reader. Looking for forward to reading far more by you at a later date!…
This post was an eye-opener about the risks of asbestos removal. Thanks!
woh I enjoy your articles , saved to bookmarks ! .
Great information. Lucky me I recently found your website by chance (stumbleupon). I have saved it for later!
Get upset! Simply letting the quota happen isn’t acceptable. This will help you stay above the curve.
Naturally, when you make your own beats online, there are limitations as to what you can do. Depending on the age and power of your computer system you will have varying results.
Dzięki za praktyczne porady dotyczące radzenia sobie z SEO.
you use a excellent weblog here! do you wish to develop invite posts in this little weblog?
Świetne wskazówki dotyczące znalezienia wiarygodnych usług SEO. Dzięki!
Bardzo przydatny artykuł o SEO. Planuję zastosować te wskazówki na mojej stronie.
An interesting discussion might be priced at comment. I think that you simply write regarding this topic, it will not be described as a taboo subject but typically everyone is not enough to dicuss on such topics. Yet another. Cheers
Can I just say what a relief to discover a person that actually understands what they are talking about online. You certainly know how to bring a problem to light and make it important. More people should read this and understand this side of the story. It’s surprising you’re not more popular given that you most certainly possess the gift.
Ten post był bardzo pomocny w zrozumieniu ryzyk związanych z SEO.
cipro canada
Ten post to świetne źródło informacji dla każdego, kto potrzebuje SEO.
Czuję się dużo lepiej poinformowany o SEO. Dzięki!
Ten blog to cenne źródło informacji dla każdego, kto martwi się o SEO.
advair 230
Doceniam nacisk na zdrowie i bezpieczeństwo w kontekście SEO.
doxycycline 100mg online
To było bardzo pomocne w zrozumieniu ryzyk i procedur SEO.
Doceniam szczegółowe wyjaśnienia na temat SEO i bezpieczeństwa.
Cieszę się, że znalazłem blog, który tak dokładnie omawia SEO. Dzięki!
Dzięki za praktyczne porady dotyczące radzenia sobie z SEO.
Dzięki za kompleksowy przewodnik po SEO. Bardzo pouczający!
Ten post był bardzo pomocny w zrozumieniu procesu SEO. Dzięki!
90 furosemide
Czuję się dużo lepiej poinformowany o SEO. Dzięki!
Nie miałem pojęcia, że SEO dotyczy tak wielu aspektów strony. Świetne informacje!
To było bardzo pomocne w zrozumieniu właściwych procedur SEO.
Ten blog to cenne źródło informacji dla właścicieli stron internetowych.
Cieszę się, że znalazłem blog, który tak dokładnie omawia SEO. Dzięki!
lyrica drug
Doceniam nacisk na zdrowie i bezpieczeństwo w kontekście SEO.
Czuję się dużo lepiej poinformowany o SEO. Dzięki!
Dzięki za cenne informacje na temat SEO i bezpieczeństwa.
Dzięki za praktyczne wskazówki dotyczące bezpiecznego SEO. Bardzo przydatne!
online pharmacy without prescription
Good artcile, but it would be better if in future you can share more about this subject. Keep posting.
I am glad to be a visitant of this thoroughgoing site ! , thanks for this rare information! .
This would be the correct blog for anybody who would like to be made aware of this topic. You realize so much its nearly tricky to argue along with you (not too I just would want…HaHa). You certainly put a new spin using a topic thats been written about for several years. Fantastic stuff, just excellent!
buy nolvadex online india
Its like you read my thoughts! You appear to understand a lot about this, such as you wrote the ebook in it or something. I feel that you simply could do with a few percent to drive the message home a little bit, but instead of that, that is great blog. A fantastic read. I’ll definitely be back.
i can see that most mobile phones today are equipped with cameras and stuffs**
appreciate the effort you put into getting us this information. Was searching on google and found your post randomly.
Nice execution!
Do you have a spam issue on this site; I also am a blogger, and I was wondering your situation; many of us have created some nice practices and we are looking to trade techniques with others, why not shoot me an email if interested.
I just want to tell you that I’m very new to weblog and honestly liked this web site. More than likely I’m planning to bookmark your blog post . You certainly come with exceptional articles and reviews. Bless you for sharing your web site.
Fee controller will be able to promise this batteries’ situations.
hello good site i will definaely come back and see again.
Wow, fantastic blog layout! How lengthy have you ever been blogging for? you made running a blog look easy. The whole look of your website is wonderful, well the content material!
I like the helpful information you provide in your articles. I’ll bookmark your weblog and check again here regularly. I am quite sure I will learn many new stuff right here! Good luck for the next! xrumer
I’m sure you will find a issue with your internet site utilizing Flock browser.
Good – I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your website. I had no trouble navigating through all tabs and related info ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Quite unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, web site theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Excellent task.
generic diflucan 150 mg
there are many different book genres online but i would really love to read about self help books“
When do you think this Real Estate market will go back in a positive direction? Or is it still too early to tell? We are seeing a lot of housing foreclosures in Longwood Florida. What about you? I would love to get your feedback on this.
You got a really useful blog I have been here reading for about an hour. I am a newbie and your success is very much an inspiration for me.
Liebesman’s choice of shooting this faux-documentary style makes the movie seem like a first-person shooter game at times, but works brilliantly in placing you right in the heart of the action.
I like this post, enjoyed this one regards for putting up.
Hello! I just would wish to make a enormous thumbs up for your great info you have here for this post. I’ll be coming back to your site for further soon.
After study several of the web sites on your own internet site now, and I really appreciate your technique of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark internet site list and will be checking back soon. Pls consider my website likewise and told me if you agree.
i wish to have some diamond necklace but they are quite expensive-
You’re making a lot of great points during this blog post however it is very hard in my opinion to concentrate on this article on the complicated page design.
You should take part in a contest for probably the greatest blogs on the web. I’ll recommend this web site!
I would like to thanks for that attempts you have made in producing this guide. I’m going to the exact same best do the job in the future too. In fact your fanciful writing skills has motivated me to begin my personal blog now. Really the blog is distribution its wings rapidly. Your create up is really a fine sample of it.
An intriguing discussion might be priced at comment. There’s no doubt that that you need to write much more about this topic, it might be considered a taboo subject but typically consumers are too little to communicate in on such topics. Yet another. Cheers
Just right points?I’d word that as anyone who truly doesn’t write on blogs a lot (if truth be told, this can be my first put up), I don’t assume the term ‘lurker’ may be very changing into to a non-posting reader. It’s not your fault the least bit , however most likely the blogosphere may get a hold of a better, non-creepy name for the ninety people that experience reading the content .
I am frequently to blogging i truly appreciate your content. Your content has truly peaks my interest. My goal is to bookmark your web site and maintain checking for brand spanking new details.
Throughout the great scheme of things you get a B+ with regard to effort. Where you actually lost us was on all the details. As it is said, details make or break the argument.. And that could not be much more true in this article. Having said that, let me inform you what exactly did do the job. Your text can be very engaging and this is probably why I am making an effort to opine. I do not make it a regular habit of doing that. Second, even though I can notice the jumps in logic you come up with, I am not certain of exactly how you appear to unite your details which in turn help to make the final result. For the moment I shall subscribe to your issue however hope in the future you actually connect your facts much better.
I think this is among the most vital info for me. And i am glad reading your article. But should remark on few general things, The website style is great, the articles is really nice : D. Good job, cheers
This web site is usually a walk-through like the info you desired about this and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse here, and you’ll definitely discover it.
I really appreciate this post. I¡¦ve been looking everywhere for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You’ve made my day! Thanks again
I really like your article. It’s evident that you have a lot knowledge on this topic. Your points are well made and relatable. Thanks for writing engaging and interesting material.
Hello there, have you by chance considered to publish regarding Nintendo or PS handheld?
After a brief firefight that results in the hood of Highsmith’s car getting blown into the windshield, the two inadvertently crash into the side of a double decker bus.
Very informative and fantastic bodily structure of content material , now that’s user friendly (:.
Wow, awesome weblog structure! How lengthy have you ever been running a blog for? you made running a blog glance easy. The whole look of your website is magnificent, let alone the content material!
You actually dealt with several engaging things in this article. I came across it by using Bing and I’ve got to admit that I am now subscribed to your website, it is very decent (:
1g amoxicillin
Good aftie, i am a blogger too. and i can see that you are a nice blogger too.
I’m no longer positive the place you are getting your info, however great topic. I must spend some time learning more or working out more. Thank you for great info I was in search of this information for my mission.
You made some first rate factors there. I seemed on the internet for the difficulty and located most people will go along with together with your website.
Perfectly indited subject material , Really enjoyed studying.
Have you tried twitterfeed on your blog, i think it would be cool.
I usually dont commonly post on many another Blogs, nevertheless Thank you continue the astonishing work. Ok unfortunately its time to get to school.
I do agree with all of the ideas you’ve presented in your post. They’re very convincing and will definitely work. Still, the posts are too short for newbies. Could you please extend them a bit from next time? Thanks for the post.
It’s difficult to acquire knowledgeable people about this topic, but the truth is be understood as there’s more you’re referring to! Thanks
Just where maybe you’ve discovered the supply for the purpose of this kind of post? Wonderful studying I have subscribed to your site feed.
It is very interesting topic you’ve written here..The truth I’m not related to this, but I think is a good opportunity to learn more about, And as well talk about a different topic to which I used to talk with others
I do not even know the way I stopped up here, however I assumed this post used to be great. I do not know who you are however certainly you are going to a well-known blogger when you aren’t already Cheers!
Where do you come up with this? Just saying you are very imaginative. I wish I had your blogging style.
I discovered your website website on yahoo and check several of your early posts. Keep the top notch operate. I recently additional encourage RSS feed to my MSN News Reader. Seeking toward reading far more from you finding out at a later date!…
Howdy sir. you have a really nice blog layout “
Sorry for the large evaluation, but I’m really loving the new Zune, as well as hope this particular, as well as the superb reviews some other individuals have written, will help you determine if it’s the right choice for you.
Good article , I am going to spend more time researching this topic
I love your blog.. excellent shades & design. Does a person layout this amazing site your self and also do anyone hire someone to accomplish it in your case? Plz react when I!|m trying to style my own, personal blog site in addition to would want to recognize where u became this particular via. thanks a lot
This sort of considering develop change in an individual’s llife, building our Chicago Pounds reduction going on a diet model are a wide actions toward making the fact goal in mind. lose weight
I like it. I will be waiting for any future updates to this article.
I’d have got to consult you here. Which is not something I usually do! I spend time reading an article that will make people believe. Also, many thanks for
I got what you intend, appreciate it for posting .Woh I am lucky to find this website through google.
Your blog is amazing dude. i love to visit it everyday. very nice layout and content .
Hi, Neat post. There is an issue with your web site in web explorer, would test this¡K IE nonetheless is the market leader and a large element of folks will omit your excellent writing because of this problem.
prescription retin a cream uk
prescription propecia cost
so much great information on here, : D.
I admire your piece of work, thankyou for all the informative content .
Perhaps you should also a put a forum site on your blog to increase reader interaction.~”~~~
Some genuinely nice stuff on this internet site , I it.
How-do-you-do, just needed you to know I have added your site to my Google bookmarks because of your extraordinary blog layout. But seriously, I think your site has one of the freshest theme I’ve came across. It really helps make reading your blog a lot easier.
I would like to thank you for the efforts you’ve put in writing this blog. I’m hoping the same high-grade web site post from you in the upcoming as well. Actually your creative writing skills has inspired me to get my own blog now. Actually the blogging is spreading its wings quickly. Your write up is a good example of it.
Can I recently say such a relief to get someone that really knows what theyre referring to on the net. You certainly have learned to bring a problem to light and earn it critical. More and more people should check out this and see why side from the story. I cant think youre no more well-known as you certainly develop the gift.
fantastic post, very informative. I wonder why the other specialists of this sector do not notice this. You must continue your writing. I am confident, you have a great readers’ base already!
very nice post, i certainly enjoy this amazing site, continue it
I’d end up being mendacity basically stated i do not like this article, in truth, I like this a great deal I needed to put upward a discuss right here. I would like to say sustain the good work, and that i will likely be arriving once again for good since I already saved the page.
Woh I like your content , bookmarked ! .
you have got an amazing blog here! would you wish to make some invite posts on my weblog?
buy accutane without prescription
compare prescription prices
This is the sort of information I’ve long been in search of. Thanks for posting this information.
Fascinating article. Certain I’ll keep coming back the following. Great work.
Hi! I ran across your site accidentally today, but am really pleased that people did! Its not only entertaining, but additionally straightforward to make use of compared with lots that Ive viewed!
Merely wanna input that you have a very decent site, I like the style and design it really stands out.
Hi there, thanks for the awesome blog post. I’m having troubles subscribing to your blogs feed. Thought I’d let you know
Excellent read, I just passed this onto a colleague who was doing a little research on that. And he really bought me lunch because I located it for him smile So let me rephrase that: Thanks for lunch!
It’s difficult to find knowledgeable folks with this topic, however you sound like do you know what you’re dealing with! Thanks
에볼루션 라이트닝 가입 머니
The project is no doubt a high-quality website. Do you write fresh teeth care content every day?
flomax 04 mg
buy cheap doxycycline
Saved as a favorite, I love your blog!
synthroid 0.088 mg
크립토 골드
그러나 한 내시가 급히 다가왔다. “폐하, 폐하…”
1200 mg modafinil
After looking at a few of the articles on your blog, I seriously like your way of writing a blog. I added it to my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back in the near future. Please visit my website as well and tell me how you feel.
Good article and straight to the point. I am not sure if this is in fact the best place to ask but
do you folks have any ideea where to hire some professional writers?
Thanks 🙂 Escape room
metformin 500 mg tablets
This is a topic which is near to my heart… Take care! Where can I find the contact details for questions?
diflucan 125mg
vermox pills for sale
This excellent website truly has all the information and facts I wanted about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Very interesting information!Perfect just what I was searching for!?
acyclovir cream from canada
doxycycline 200 mg cost
I’m looking forward to your next article.프리랜서 대출
Your article has broadened my understanding.월세 보증금 대출
zovirax over the counter australia
dexamethasone 75 mg
My developer is trying to persuade me to move to .net from PHP.
I have always disliked the idea because of the expenses.
But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using Movable-type on a number of
websites for about a year and am anxious about switching to another platform.
I have heard good things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can import all my wordpress posts into it?
Any kind of help would be really appreciated!
I couldn’t agree more with your conclusions.프라그마틱 슬롯 조작
price of amoxicillin 875 mg
generic clomid online
Your writing is insightful and thought-provoking.검색엔진최적화 방법
accutane 30 mg price
hot pot canggu bali chinese food most popular authentic restaurant culinary traditional recommendation: https://kulinerdibali.com/chinese-food-hot-pot-canggu-bali
buy generic lyrica online
You’re so cool! I do not think I’ve read through something like this before. So great to discover another person with some original thoughts on this issue. Seriously.. thanks for starting this up. This web site is something that is needed on the web, someone with a little originality.
You made some decent points there. I checked on the internet for more information about the issue and found most individuals will go along with your views on this web site.
buy clomid paypal
how to get lasix without a prescription
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful post. Thanks for supplying these details.
There is noticeably a bundle to understand about this. I assume you made specific nice points in functions also.
You seem to be very professional in the way you write,
Great goods from you, man. I’ve understand your stuff previous to and you’re just extremely wonderful. I actually like what you have acquired here, really like what you’re saying and the way in which you say it. You make it entertaining and you still take care of to keep it sensible. I can not wait to read far more from you. This is really a great site.
celine dion will always be one of the best singer, she has the unique sounding voice;
Some genuinely terrific work on behalf of the owner of this website , perfectly great articles .
I only wish that I had the ability to convey what I wanted to say in the manner that you have presented this information. Thanks.
Hello there, just became alert to your blog through Google, and found that it’s truly informative. I’m gonna watch out for brussels. I will appreciate if you continue this in future. A lot of people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers! xrumer
When I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new surveys are added- checkbox now when a comment is added I receive four emails with similar comment. Will there be however you possibly can get rid of me from that service? Thanks!
Nice post. I discover something harder on diverse blogs everyday. Most commonly it is stimulating to read content off their writers and rehearse a specific thing at their store. I’d would rather apply certain with the content on my small weblog whether or not you don’t mind. Natually I’ll provide a link in your internet blog. Many thanks sharing.
I am not real fantastic with English but I come up this real leisurely to interpret .
Excellent and really nice blog. I really enjoy blogs that have to do with weight loss and fitness, so this is of particular interest to me to see what you have here. Keep it going! force factor
This important put up appears to be redeem a majority of customers. How would you market it? That it provides a fantastic one of a kind style directly on factors. My partner and i getting a specific product realistic or just sizeable furnish information on is a vital process.
lioresal 20 mg
doxycycline 500 mg capsules
https://artdaily.com/news/171650/Mp3Juice-Review–The-Pros-and-Cons-You-Need-to-Know
A fascinating discussion is definitely worth comment. I do think that you need to write more on this issue, it might not be a taboo matter but typically people do not discuss such topics. To the next! All the best!
Hi, I do think this is an excellent site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I will come back once again since I bookmarked it. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide other people.
I seriously love your blog.. Pleasant colors & theme. Did you develop this amazing site yourself? Please reply back as I’m hoping to create my own blog and would like to find out where you got this from or just what the theme is called. Kudos.
A fascinating discussion is definitely worth comment. There’s no doubt that that you ought to publish more about this subject matter, it might not be a taboo subject but typically people don’t discuss these topics. To the next! All the best.
That is a good tip especially to those new to the blogosphere. Short but very accurate info… Many thanks for sharing this one. A must read article.
May I just say what a comfort to find someone who truly understands what they are discussing on the web. You certainly understand how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More people need to read this and understand this side of your story. I was surprised you’re not more popular because you surely possess the gift.
Very good post. I will be experiencing many of these issues as well..
baclofen tabs
Nice post. I learn something new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon every day. It will always be interesting to read content from other authors and practice a little something from their sites.
lyrica 150 mg
buy propecia us
Awesome! Its genuinely remarkable post, I have got much clear idea regarding from this post
baclofen prescription cost
diflucan brand name in india
Way cool! Some very valid points! I appreciate you writing this post plus the rest of the site is extremely good.
Hey there! I simply wish to offer you a big thumbs up for the excellent info you have got here on this post. I will be coming back to your web site for more soon.
vermox prescription
Your article has broadened my understanding.Google Genius
ciprofloxacin tablet price
Saved as a favorite, I really like your site.
I appreciate the effort you’ve put into this.백링크 구매
After looking over a number of the blog posts on your site, I truly like your technique of blogging. I added it to my bookmark site list and will be checking back soon. Take a look at my web site too and tell me your opinion.
dexamethasone 10 mg
Good web site you’ve got here.. It’s difficult to find excellent writing like yours nowadays. I really appreciate people like you! Take care!!
This site definitely has all of the information and facts I needed about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
diflucan medicine buy
I could not resist commenting. Very well written!
advair asthma
Aw, this was an extremely nice post. Taking the time and actual effort to create a very good article… but what can I say… I procrastinate a lot and don’t manage to get anything done.
I blog often and I truly thank you for your information. This great article has truly peaked my interest. I am going to bookmark your blog and keep checking for new details about once per week. I opted in for your Feed too.
You’ve made some really good points there. I looked on the internet for more info about the issue and found most individuals will go along with your views on this site.
Right here is the right web site for everyone who wants to find out about this topic. You understand a whole lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I personally would want to…HaHa). You definitely put a fresh spin on a subject that has been written about for ages. Wonderful stuff, just great.
zithromax 500mg cost
Way cool! Some very valid points! I appreciate you writing this write-up and also the rest of the website is really good.
naturally like your web site however you need to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very bothersome to tell the truth on the other hand I will surely come again again.
Howdy, I do think your web site could be having browser compatibility issues. Whenever I take a look at your site in Safari, it looks fine however, if opening in Internet Explorer, it’s got some overlapping issues. I simply wanted to provide you with a quick heads up! Aside from that, excellent blog.
Excellent web site you have here.. It’s hard to find high-quality writing like yours these days. I honestly appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
diflucan 150 mg price
After I initially left a comment I appear to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get four emails with the exact same comment. There has to be an easy method you are able to remove me from that service? Kudos.
A motivating discussion is worth comment. I do think that you should write more about this subject, it may not be a taboo matter but typically people do not discuss these subjects. To the next! Many thanks.
You should be a part of a contest for one of the most useful sites online. I will recommend this blog!
can you order accutane online
Good write-up. I definitely appreciate this site. Continue the good work!
I’m impressed, I have to admit. Rarely do I encounter a blog that’s both equally educative and interesting, and without a doubt, you have hit the nail on the head. The issue is something not enough folks are speaking intelligently about. Now i’m very happy that I came across this in my hunt for something regarding this.