Orkambi
Generic name: ivacaftor and lumacaftor
Drug class: CFTR combinations
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Orkambi?
Orkambi is a prescription medicine used for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF) in patients age 2 years and older who have two copies of the F508del mutation (F508del/F508del) in their CFTR gene.
Orkambi should not be used in patients other than those who have two copies of the F508del mutation in their CFTR gene.
It is not known if Orkambi is safe and effective in children under 2 years of age.
Description
The active ingredients in ORKAMBI tablets are lumacaftor, which has the following chemical name: 3-[6-({[1-(2,2-difluoro-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)cyclopropyl]carbonyl}amino)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl]benzoic acid, and ivacaftor, a CFTR potentiator, which has the following chemical name: N-(2,4-di-tert-butyl-5-hydroxyphenyl)-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxamide. The molecular formula for lumacaftor is C24H18F2N2O5 and for ivacaftor is C24H28N2O3. The molecular weights for lumacaftor and ivacaftor are 452.41 and 392.49, respectively. The structural formulas are:
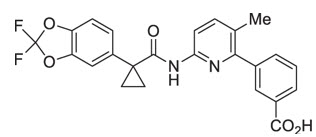
lumacaftor
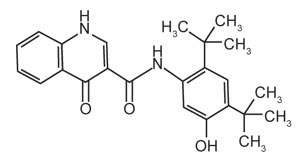
ivacaftor
Lumacaftor is a white to off-white powder that is practically insoluble in water (0.02 mg/mL). Ivacaftor is a white to off-white powder that is practically insoluble in water (<0.05 microgram/mL).
Mechanism of Action
The CFTR protein is a chloride channel present at the surface of epithelial cells in multiple organs. The F508del mutation results in protein misfolding, causing a defect in cellular processing and trafficking that targets the protein for degradation and therefore reduces the quantity of CFTR at the cell surface. The small amount of F508del-CFTR that reaches the cell surface is less stable and has low channel-open probability (defective gating activity) compared to wild-type CFTR protein.
Lumacaftor improves the conformational stability of F508del-CFTR, resulting in increased processing and trafficking of mature protein to the cell surface. Ivacaftor is a CFTR potentiator that facilitates increased chloride transport by potentiating the channel-open probability (or gating) of the CFTR protein at the cell surface. In vitro studies have demonstrated that both lumacaftor and ivacaftor act directly on the CFTR protein in primary human bronchial epithelial cultures and other cell lines harboring the F508del-CFTR mutation to increase the quantity, stability, and function of F508del-CFTR at the cell surface, resulting in increased chloride ion transport. In vitro responses do not necessarily correspond to in vivo pharmacodynamic response or clinical benefit.
Who should not take Orkambi?
Do not take Orkambi if you take certain medicines or herbal supplements such as:
- antibiotics: rifampin (Rifamate, Rifater) or rifabutin (Mycobutin)
- seizure medications: phenobarbital, carbamazepine (Tegretol, Carbatrol, and Equetro), or phenytoin (Dilantin, Phenytek)
- sedatives and anti-anxiety medicines: triazolam (Halcion) or midazolam (Dormicum, Hypnovel, and Versed)
- immunosuppressant medicines: cyclosporine, everolimus (Zortress), sirolimus (Rapamune), or tacrolimus (Astagraf XL, Envarsus XR, Prograf, Protopic)
- St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum)
Talk to your doctor before taking Orkambi if you take any of the medicines or supplements listed above.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Orkambi?
Before taking Orkambi, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have or have had liver problems
- have had an organ transplant
- have kidney problems
- are using birth control (hormonal contraceptives, including oral, injectable, transdermal, or implantable forms). Hormonal contraceptives should not be used as a method of birth control when taking Orkambi. Talk to your doctor about the best birth control method you should use while taking Orkambi.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Orkambi will harm your unborn baby. You and your doctor should decide if you will take Orkambi while you are pregnant.
- are breastfeeding or planning to breastfeed. It is not known if Orkambi passes into your breast milk. You and your doctor should decide if you will take Orkambi while you are breastfeeding.
Orkambi may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how Orkambi works.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements, because the dose of Orkambi may need to be adjusted when taken with certain medications.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of these medicines if you are not sure.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- antifungal medications including ketoconazole (such as Nizoral), itraconazole (such as Sporanox), posaconazole (such as Noxafil), or voriconazole (such as Vfend)
- antibiotics including telithromycin (such as Ketek), clarithromycin (such as Biaxin), or erythromycin (such as Ery-Tab)
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take Orkambi?
- Take Orkambi exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
- Always take Orkambi tablets or granules with foods that contain fat. Examples of fat containing foods include eggs, avocados, nuts, butter, peanut butter, cheese pizza, whole-milk dairy products (such as whole milk, cheese, and yogurt).
- Take your doses of Orkambi 12 hours apart.
- If you miss a dose within 6 hours of when you usually take it, take your dose with fat-containing food as soon as possible.
- If you miss a dose and it is more than 6 hours after the time you usually take it, skip that dose only and take the next dose when you usually take it. Do not take 2 doses at the same time to make up for your missed dose.
- Tell your doctor if you stop Orkambi for more than 1 week. Your doctor may need to change your dose of Orkambi or other medicines you take.
Orkambi Tablets (ages 6 years and older):
- Each Orkambi box contains 4 weekly cartons.
- Each carton contains 7 daily blister strips.
- Each blister strip contains 4 tablets so you can take 2 tablets for the morning and 2 tablets for the evening.
- You may cut along the dotted line to separate your morning dose from your evening dose.
- To take your morning dose, unpeel the paper backing from a blister strip (do not push tablet through backing) to remove 2 Orkambi tablets and take them with fat-containing food.
- 12 hours after your previous dose, open another blister strip (do not push tablet through backing) to remove 2 Orkambi tablets and take them with fat-containing food.
Orkambi Oral Granules (ages 2 to under 6 years old):
- Hold the packet with the cut line on top.
- Shake the packet gently to settle the Orkambi granules.
- Tear or cut packet open along cut line.
- Carefully pour all of the Orkambi granules in the packet into 1 teaspoon (5 mL) of soft food or liquid in a small container (like an empty bowl).
- The food or liquid should be at or below room temperature.
- Examples of soft foods or liquids include puréed fruits, flavored yogurt or pudding, and milk or juice.
- Mix the Orkambi granules with food or liquid.
- After mixing, give Orkambi within 1 hour. Make sure all medicine is taken.
- Give a child fat-containing food just before or just after the Orkambi granules dose (see examples above).
What are the possible side effects of Orkambi?
Orkambi can cause serious side effects, including:
- Worsening of liver function in people with severe liver disease. The worsening of liver function can be serious or cause death. Talk to your doctor if you have been told you have liver disease as your doctor may need to adjust the dose of Orkambi.
- High liver enzymes in the blood, which can be a sign of liver injury in people receiving Orkambi. Your doctor will do blood tests to check your liver:
- before you start Orkambi
- every 3 months during your first year of taking Orkambi
- every year while you are taking Orkambi
Call your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms of liver problems:
- Breathing problems such as shortness of breath or chest tightness in patients when starting Orkambi, especially in patients who have poor lung function. If you have poor lung function, your doctor may monitor you more closely when you start Orkambi.
- An increase in blood pressure in some people receiving Orkambi. Your doctor should monitor your blood pressure during treatment with Orkambi.
- Abnormality of the eye lens (cataract) in some children and adolescents receiving Orkambi. If you are a child or adolescent, your doctor should perform eye examinations before and during treatment with Orkambi to look for cataracts.
The most common side effects of Orkambi include:
- breathing problems such as shortness of breath and chest tightness
- nausea
- diarrhea
- fatigue
- increase in a certain blood enzyme called creatine phosphokinase
- rash
- gas
- common cold, including sore throat, stuffy or runny nose
- flu or flu-like symptoms
- irregular, missed, or abnormal periods (menses) and increase in the amount of menstrual bleeding
Additional side effects in children
Side effects seen in children are similar to those seen in adults and adolescents. Additional common side effects seen in children include:
- cough with sputum
- stuffy nose
- headache
- stomach pain
- increase in sputum
These are not all the possible side effects of Orkambi.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Orkambi
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Orkambi for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Orkambi to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about Orkambi that is written for health professionals.
How should I store Orkambi?
- Store Orkambi at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Do not use Orkambi after the expiration date on the package.
Keep Orkambi and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Orkambi?
Active ingredients: lumacaftor and ivacaftor
Inactive ingredients:
Tablets: cellulose, microcrystalline; croscarmellose sodium; hypromellose acetate succinate; magnesium stearate; povidone; and sodium lauryl sulfate.
The tablet film coat contains: carmine, FD&C Blue #1, FD&C Blue #2, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide.
The printing ink contains: ammonium hydroxide, iron oxide black, propylene glycol, and shellac.
Oral Granules: cellulose, microcrystalline; croscarmellose sodium; hypromellose acetate succinate; povidone; and sodium lauryl sulfate.
Label
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 200 MG/125 MG TABLET BOX
- Rx only
NDC 51167-809-01 - ORKAMBI®
(Lumacaftor/Ivacaftor) tablets
200 mg/125 mg per tablet - 112 tablets


PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 100 MG/125 MG TABLET BOX
- Rx only
NDC 51167-700-02 - ORKAMBI®
(Lumacaftor/Ivacaftor) tablets
100 mg/125 mg per tablet - 112 tablets


