Overview
Tachycardia is the medical term used to describe an increase in heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute. A variety of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) may cause tachycardia.
A heart rate that is fast isn’t always an issue. For instance, it’s common that the heart rate increases during exercise, or as a reaction to stress.
Tachycardia can not trigger any signs of complications. However, if it’s not treated the various types of tachycardia could result in serious health issues such as heart failure, stroke, or sudden cardiac death¹.
Treatment for tachycardia could consist of specific procedures, medications as well as cardioversion surgery to slow the heart rate.
Types
There are many kinds of Tachycardia. Sinus tachycardia refers to a usual increase in heart rate, which is usually caused by stress or exercise.
Other kinds of tachycardia are classified according to the region of the heart that is responsible for the high heart rate as well as the reason. Common forms of tachycardia that are caused due to irregular rhythms in the heart (arrhythmias) are:
- Atrial fibrillation (A-fib). It is the most frequent form of Tachycardia. The irregular, chaotic electrical signals within higher chambers in the heart (atria) can cause a rapid heartbeat. The symptoms may last a while however, some episodes will not be resolved unless they are treated.
- Atrial flutter. Atrial flutter can be compared to afib. However, heartbeats are much more organized. Atrioventricular flutter episodes may disappear on their own or require treatment. Atrial flutter sufferers may also experience atrial fibrillation in other instances.
- Ventricular Tachycardia. This type of arrhythmia is triggered in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles). The high heart rate doesn’t allow the ventricles to expand with blood and then squeeze (contract) to deliver sufficient blood into the human body. The episodes of ventricular tachycardia can be short-lived and last just for a few seconds without causing any harm. But, if they last for more than a few minutes can be life-threatening.
- Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT). Supraventricular Tachycardia is a broad term that encompasses arrhythmias that begin over the ventricles. Supraventricular tachycardia can trigger the heart to beat faster (palpitations) which begin and then end abruptly.
- Ventricular fibrillation. Rapid, chaotic electrical signals cause the ventricles to be agitated and contract, but not in a controlled fashion. This is a serious issue that could cause death when the heart rhythm isn’t repaired within a matter of minutes. The majority of people with ventricular fibrillation suffer from an underlying heart condition or have had a trauma that was severe for example, getting hit by lightning.
Symptoms
If the heart beats too quickly, it might not be able to pump enough blood to the other organs and tissues. This means that organs and tissues might not receive enough oxygen.
In general, tachycardia could result in the following symptoms and signs:
- The sensation of a racing, beat or the heartbeat pounding or floating around in your chest (palpitations)
- Chest pain
- Fainting (syncope)
- Lightheadedness
- Rapid pulse rate
- Breathing shortness
Certain people suffering from tachycardia show no signs. The condition can be detected through a physical exam or heart-related tests are performed to determine a different reason.
When is the best time to seek medical help?
There are a variety of factors that could trigger a high heartbeat (tachycardia). If you’re feeling that your heart beats too fast, you should make an appointment with your doctor.
Get medical attention immediately for an inability to breathe, weakness or lightheadedness, dizziness fainting or fainting near, and chest pains or discomfort in your chest.
A form of tachycardia known as ventricular fibrillation may trigger the blood pressure to decrease drastically. The collapse can happen in a matter of moments. The person affected’s heart rate and breathing will stop. If this happens, you can do these things:
- Dial 911, or dial the number for emergencies in your region.
- When you know that someone in your vicinity is educated in CPR Start CPR. CPR can assist in keeping blood flow flowing to organs until an electric shock (defibrillation) may be administered.
- In case you’re experienced in CPR or are worried about giving rescue breaths make sure you only give only hands-only CPR. Push hard and quickly on the middle of your chest at the rate of 100 to 120 compressions every min until the paramedics are there. It’s not necessary to do rescue breathing.
- In the event that an automatic external defibrillator (AED) is located nearby Have someone else take the device. for you to follow instructions. It is a portable device that delivers an electric shock to reset the heart’s rhythm. There is no requirement for training to operate the device. It will instruct you on the right way to proceed. It’s programmed to deliver a shock only when it is appropriate.
Causes
Tachycardia is an increase in heart rate due to any cause. It may be a typical increase in heart rate triggered by exercise or stress (sinus tachycardia). Sinus tachycardia is regarded as to be a symptom and not a sign of a condition.
Tachycardia can result from an abnormal cardiac rhythm (arrhythmia).
Things that can cause the condition include:
- Fever
- Alcohol withdrawal
- Caffeine levels are high.
- Low or high blood pressure
- Insufficiency of certain substances found in the blood that are known as electrolytes, such as calcium, sodium, potassium, and magnesium
- Medication side effects
- Hyperactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism)
- A decrease in the number of red blood cells (anemia) is usually due to bleeding
- Smoking
- The use of illegal drugs which includes stimulants such as methamphetamine or cocaine
Sometimes, the exact cause for tachycardia isn’t known.
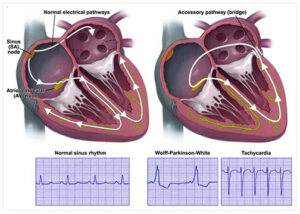
How is the heart beating?
To comprehend the reason behind the tachycardia phenomenon, it is beneficial to understand how the heart normally functions.
The heart is comprised of four chambers: two chambers in the upper (atria) as well as two chambers in the lower (ventricles).
Heart rhythms are controlled through a naturally-occurring heartbeat controller (the sinus node) located in the upper right chamber (atrium). The sinus node emits electrical signals that typically start every heartbeat. The electrical signals travel through the atria and cause your heart muscle to contract (contract) and then pump blood to the ventricles.
The signals are then received at a group of cells known as the AV node. There, they are slowed down. This delay is just enough to allow ventricles to fill up with blood. When electrical signals are received by the ventricles, the chambers expand and then pump blood into the lungs or to the rest of the body.
In the typical heart, this signaling process is usually smooth and results in a resting heart rate of between 60 and 100 beats per minute.
Risk factors
In general, getting older or having relatives with a history of heart rhythm issues (arrhythmias) can increase the chance of having arrhythmias that can lead to tachycardia.
Medical treatment or lifestyle changes for heart related or other conditions can reduce the risk of developing tachycardia.
Complications
The complications of tachycardia are based on:
- The kind of Tachycardia
- How fast is the heart beating?
- How long will the heart rate last?
- If there are any other heart problems
Tachycardia sufferers have an increased chance of developing a blood clot, which could lead to a stroke (risk is highest in atrial fibrillation) or heart attack. Your physician might prescribe a blood thinner to lower the risk of developing.
Other possible complications of tachycardia are:
- Infrequently, you may faint or become unconscious.
- The heart is unable to pump blood enough (heart failure)
- Sudden death is usually caused by ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation ventricular
Prevention
The most effective way to avoid Tachycardia is to keep an active heart and avoid heart disease. If you have already been diagnosed with heart disease, be aware and follow your treatment program. Make sure that you are aware of the treatment plan and follow all medication according to your doctor’s instructions.
Lifestyle modifications to lower the risk of developing heart diseases could help in preventing heart arrhythmias that could cause Tachycardia. Follow these steps:
- Consume a balanced diet. Choose a diet with a high proportion of entire grains, lean protein as well as low-fat dairy products, vegetables and fruits. Limit sugar, salt alcohol, as well as trans and saturated fats.
- Do your exercise regularly. Try to exercise for at least 30 minutes every day.
- Maintain the weight of a healthy person. Being overweight increases the chance to develop heart problems.
- Maintain cholesterol and blood pressure in check. Make lifestyle changes and follow the prescribed medications to manage the high pressure in your blood (hypertension) as well as high cholesterol.
- Quit smoking. If you smoke and are unable to quit by yourself consult your health professional about programs or strategies to aid in breaking the habit of smoking.
- Be careful when drinking. If you choose to drink alcohol, make sure you do it in moderate amounts. For healthy adults, this is one drink a day for women, and two drinks per day for males. For certain medical conditions, it is advised to stay clear of alcohol. Consult your doctor for recommendations specific to your specific condition.
- Do not take illegal drugs or stimulants, like cocaine. Talk to your medical professional about a suitable program that is right to help you get assistance to stop using illegal drugs.
- Be cautious when taking medications. Some cold and cough medications contain stimulants that could cause a rapid heartbeat. Consult your physician on what medications you should stay clear of.
- Limit the amount of caffeine. If you drink caffeinated beverages, make sure you do it moderately (no over one or two drinks a day).
- Take control of anxiety. Find ways to aid in reducing stress. Engaging in more exercise, practicing mindfulness, and interacting with others through support group discussions are just a few ways to manage stress.
- Check-ups scheduled. Have regular physical examinations in order to report any change to the rate of your heartbeats to your healthcare doctor. If your symptoms alter or worsen, or you experience new symptoms notify your doctor immediately.
Diagnosis
A thorough physical examination, as well as medical history and tests, are essential to identify tachycardia.
Be aware that the items in this article were written before the outbreak of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic in 2019. (COVID-19) pandemic. They don’t follow the proper pandemic guidelines. Follow all suggested Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines on hiding as well as social distancing.
To identify tachycardia health professionals will usually perform a physical exam and ask you questions about your medical history and habits.
Tests
Tests, like the cardiac imaging test, can be conducted to verify an abnormally fast heartbeat and to identify issues that could cause an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia). Tests for diagnosing tachycardia can include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). The quick and easy test tests the heart’s electrical activity. During an ECG, Sensors (electrodes) are placed on the chest and, sometimes, on legs or arms. An ECG analyzes the duration and timing of each electrical phase within the heartbeat. It measures the timing and duration of each electrical phase in the. Your doctor will be able to look for patterns of signal to determine the cause of tachycardia as well as the cause. in the heart could be behind the high heart rate. Certain personal devices, including smartwatches, can monitor electrocardiograms. Consult your physician whether this is an option for you.
- Holter monitor. Your doctor might recommend that you monitor your heart rate at your home. It is a portable ECG. The device is wearable for up to a week to track heart rate throughout the day.
- Event monitor. This is a portable ECG The device is designed that be used for as long as 30 days or until you develop symptoms or an arrhythmia. The typical procedure is to press a button whenever symptoms begin to manifest.
- Echocardiogram. An echocardiogram uses sound waves to create images of the heart moving. It can reveal the flow of blood, heart valves as well as the muscle of the heart.
- Chest Xray. A chest X-ray can reveal the health of the lungs and heart.
- Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). A cardiac MRI can give still or moving images of blood flow within the heart. This test is usually performed to identify the source of ventricular tachycardia also known as ventricular fibrillation.
- Computerized Tomography (CT). CT scans blend several images of X-rays to give an enhanced cross-sectional image of the region being examined. Heart scan (cardiac CT ) could be conducted in the event that a doctor is seeking to find the reason for Ventricular Tachycardia.
- Angiogram of Corona. A coronary angiogram is used to identify narrowed or blocked blood vessels within the heart. It makes use of a dye and special X-rays to reveal the insides of coronary arteries. A coronary angiogram can be taken to assess the flow of blood to the heart for those suffering from ventricular tachycardia, or ventricular fibrillation.
- Electrophysiological (EP) testing and mapping. This test is also known as an EP Study, for instance, can be conducted to confirm the diagnosis of tachycardia, or to find out where in the heart the malfunctioning signaling takes place. It is used to identify arrhythmias that are not isolated. It can also be used to determine sinus tachycardia. This test involves a healthcare practitioner connecting flexible, thin tubes (catheters) equipped with electrodes through blood vessels to different locations inside the heart. Once the catheters are placed the electrodes are able to trace the distribution of electrical signals throughout the heart.
- Test for stress. Some types of Tachycardia can be caused or aggravated by exercise. In a stress test, the heart’s activity is usually controlled while riding stationary bicycles or running on the treadmill. Other tests of the heart could be conducted using the stress test. If you’re having difficulty exercising or performing your exercise, a medication could be administered to stimulate the heart in a manner like an exercise.
- Table tilt test. This test is frequently used to know the causes of tachycardia that cause fainting. Blood pressure and heart rate are measured when lying on the table. Under close supervision, the table is lowered to mimic standing. The health care professional monitors whether the heart as well as the nervous system that regulates it react to adjustments in posture.
Treatment
The objectives of tachycardia therapy are to slow down a rapid heartbeat once it happens and also to stop the occurrence of future episodes of a rapid heart rate.
If a medical condition causes tachycardia treatment of the underlying issue could reduce or even stop episodes of a rapid heartbeat.
The slowing of a heart rate
A heart rate that is too fast can be able to correct itself. However, sometimes medications or other treatments for medical conditions are required to slow the heartbeat.
Strategies to slow down a high heart rate are:
- Vagal moves. Vagal maneuvers include coughing, bending down as if you were experiencing an intestinal movement, and placing an ice cube on the face. Your doctor might ask you to do these specific actions when you experience an event of a rapid heartbeat. These actions impact the vagus nerve, which assists in controlling the heartbeat.
- Medicines. If vagal maneuvers do not stop the rapid heartbeat medications may be required to restart the heartbeat.
- cardioversion. This medical procedure typically involves giving electric shocks to the heart via sensors (electrodes) that are placed in the chest. The shock alters the heart’s electrical signals and then restores a normal heartbeat. The procedure is typically employed when emergency treatment is required or when vagal treatments and medicines aren’t working. It’s also possible to use cardioversion while taking medications.
The prevention of future episodes of a high heart rate
Treatment for tachycardia includes taking steps to stop the heart to beat too quickly. It could be a matter of medication implants, devices implanted, or other procedures or surgeries.
- Medical Treatment. Drugs to control the heart rate and return the normal rhythm of the heart are generally prescribed for patients suffering from tachycardia.
- Ablation of the catheter. In this procedure, an expert in health care connects one or more flexible, thin tubing (catheters) into an artery which is usually located in the groin area and directs them to the heart. Sensors (electrodes) at the end of the catheter make use of either cold or hot energy to cause tiny scars to the heart, which block off irregular electrical signals and restore the rhythm of the heart. This is usually done when an additional communication pathway causes an increase in heart rate. Catheter ablation isn’t a surgical procedure to open the heart, however, it can be performed in conjunction with other heart surgeries.
- Pacemaker. A pacemaker is a tiny device surgically implanted within the chest area. If the device detects the irregularity of heartbeats, it will send an electrical signal that aids in helping the heart to resume its normal rhythm.
- Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). Your health care provider may recommend this device if you’re at high risk of developing ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. An ICD is a battery-powered device implanted beneath the skin near the collarbone, as the pacemaker. The ICD The device continuously monitors the heart’s rhythm. If it detects an unnatural heart beat, it will send out lower high-energy electric shocks to reset the heart’s rhythm.
- Maze technique. In this procedure, the surgeon makes small cuts in the upper part of the heart (atria) to create an outline (or maze) of scar tissue. Heart signals cannot traverse the scar tissue. Therefore, the maze could stop stray electrical signals from the heart which can cause certain types of tachycardia.
- surgery. Sometimes open-heart surgery might be necessary to remove an additional electrical pathway that causes tachycardia. Surgery is typically only performed when other treatments don’t work, or when surgery is required to treat a heart condition.
.
Lifestyle and home remedies for home
If you suffer from tachycardia, or any other heart disease, your doctor will probably recommend living a healthy lifestyle. Do these things:
- Eat a healthy diet
- Don’t smoke
- Get regular exercise
- Maintain an appropriate weight
- Reduce or eliminate alcohol
Alternative medicine
Methods to relieve stress, such as yoga and meditation, can aid in slowing the heartbeat and lessen the symptoms of tachycardia.
Support and Coping
In the event that you’ve got a strategy in place to handle an event of a high heartbeat, you might feel calmer and at ease when it happens. Talk to your doctor about:
- How do you know your pulse and which heart rate works best for you
- How to and when to utilize vagal maneuvers, if necessary
- When to contact the health care provider
- When is it appropriate to seek emergency treatment
The support of family and friends can also reduce stress and help manage the symptoms of tachycardia.

Wow, amazing weblog layout! How long have you ever been blogging for?
you make running a blog glance easy. The full look of your site is great, as neatly as the content material!
You can see similar here najlepszy sklep
Very interesting topic, appreciate it for putting up.Blog money
Good day! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my
website to rank for some targeted keywords but
I’m not seeing very good gains. If you know of any please share.
Thank you! I saw similar blog here: Bij nl
ยูฟ่า789 รวม เว็บ สล็อตออนไลน์ ลุ้นรางวัลใหญ่ได้ทุกวัน แตกง่ายทุกเกม
Hello there, juist becae alert to ylur blog throughh Google, and found that it’s realkly informative.
I’m gonna watch out for brussels. I will appreciafe iif yoou cpntinue thi inn future.
Many people wiull bbe benedfited frpm youhr writing.
Cheers!
Hi! Do you know if they make any plugins
to assist with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my website
to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good success.
If you know of any please share. Kudos! You can read similar blog here: Your destiny
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this matter to be actually something which I think I would never understand. slot99
Thanks for picking out the time to discuss this, I feel great about it and love studying more on this topic. It is extremely helpful for me. Thanks for such a valuable help again.
Good site! I really love how it is easy on my eyes it is. I am wondering how I could be notified whenever a new post has been made. I have subscribed to your feed which may do the trick? Have a nice day! สมัครเว็บ lsm99
This article เว็ปสล็อต offers clear idea in support of the new people of blogging, that genuinely how to do running a blog.
can you get generic clomiphene prices can i get clomid pills can i buy cheap clomiphene price where can i buy cheap clomiphene price order cheap clomiphene tablets where to get cheap clomiphene tablets clomiphene nz prescription
The depth in this piece is exceptional.
With thanks. Loads of erudition!
buy generic azithromycin – buy tindamax generic flagyl 200mg cost
buy rybelsus pill – buy periactin 4mg sale periactin 4 mg tablet
order domperidone 10mg pill – purchase flexeril generic cyclobenzaprine generic
inderal 10mg pill – methotrexate ca order methotrexate 10mg without prescription
buy amoxicillin pills – buy diovan 80mg without prescription order combivent 100mcg online cheap
zithromax 500mg usa – bystolic usa order nebivolol 20mg without prescription
oral augmentin 375mg – https://atbioinfo.com/ buy cheap generic ampicillin
esomeprazole pills – https://anexamate.com/ nexium brand
order warfarin 2mg sale – anticoagulant order losartan sale
meloxicam pill – https://moboxsin.com/ meloxicam 7.5mg canada
prednisone 40mg us – https://apreplson.com/ prednisone 20mg tablet
non prescription erection pills – https://fastedtotake.com/ buy ed pills online
order amoxil for sale – amoxicillin sale purchase amoxicillin generic