Loxapine
- Loxitane
- Oxilapine
What is Loxapine
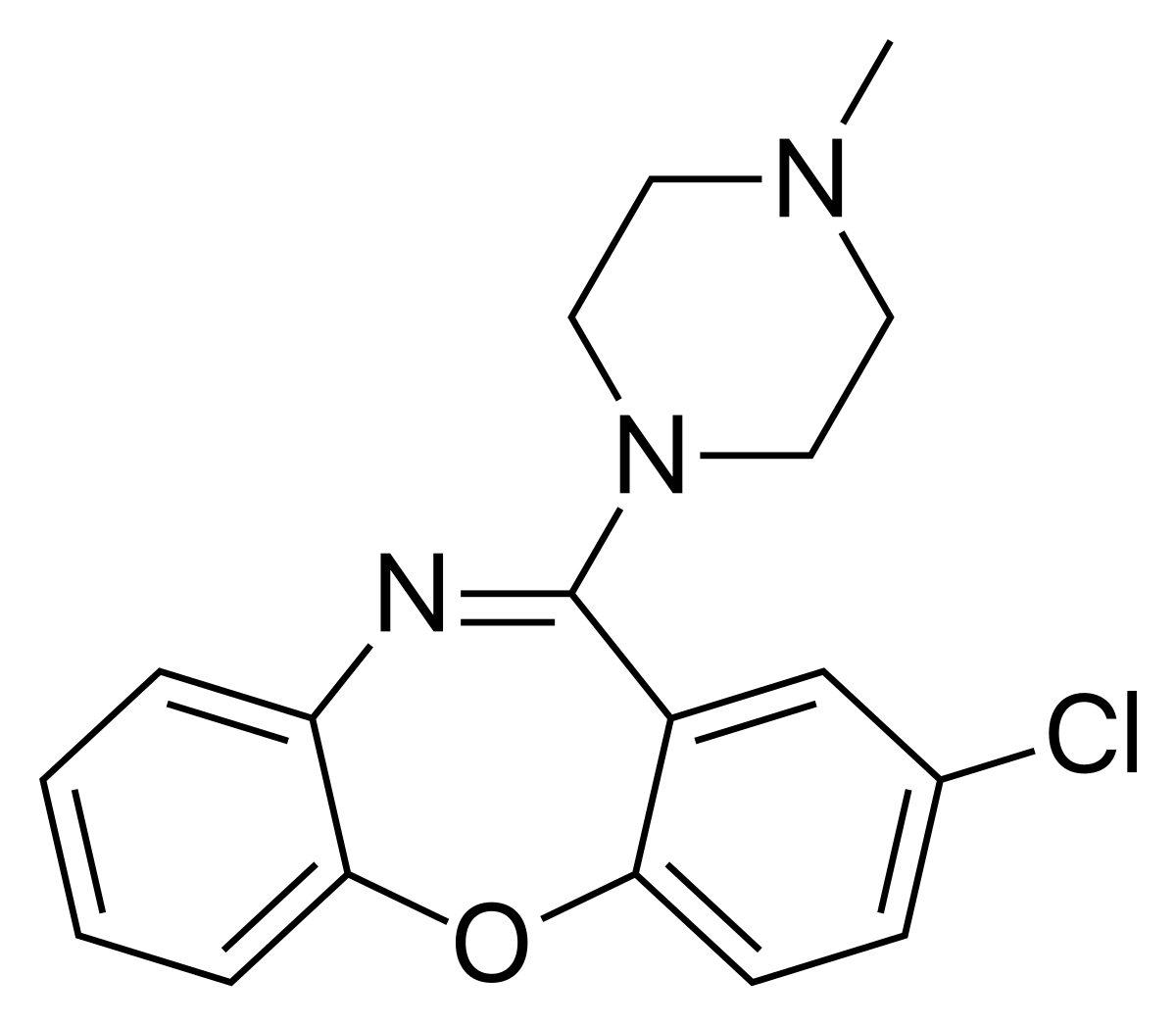
Loxapine is an antipsychotic drug that changes the activity of brain neurotransmitters.
The is used to treat agitation caused by schizophrenia or bipolar illness.¶
IMPORTANT WARNING:
Research has shown that people with dementia (a brain disorder that impacts the capacity to remember clearly, think clearly, communicate, and carry out everyday activities, and can alter moods and personality) who are taking antipsychotics (medications to treat mental disease) like loxapine are at an increased risk of dying when they are treated.
Loxapine isn’t recognized as a medication by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat behavioral issues in people with dementia. Consult your doctor who prescribed the medication for you, your family member, or someone you care about who suffers from dementia and taking the medication loxapine. For more information visit the FDA website: http://www.fda.gov/Drugs
What is Loxapine is prescribed?
Loxapine can be used for treating symptoms that are associated with schizophrenia (a mental illness that can cause abnormal or disturbed thinking, lack of interest in the world, and a heightened or inappropriate expression of emotions). Loxapine is part of a class of medicines known as antipsychotics conventional. It reduces abnormal stimulation in the brain.
What is the best to use it?
Loxapine is available as capsules to be taken by mouth. It is typically taken between two and every four hours. It is recommended to take loxapine at approximately the same time every day. Follow the directions on the prescription label and ask your doctor or pharmacist for clarification on any portion you don’t understand. Follow the directions exactly. Don’t use more or less of it, or take it more frequently than what is prescribed by your physician.
Your doctor may begin you on a lower dose of loxapine, and then raise your dose in the first 7-10 days of treatment until symptoms have been controlled. When your symptoms are reduced for a period of time the doctor might reduce the dose. Make sure to inform your doctor how you’re experiencing during treatment with the medication loxapine.
Loxapine can help manage your symptoms, but it will not treat your illness. It could take several weeks or more to fully experience the benefits of the loxapine. Continue taking loxapine it you feel better. Don’t stop taking the loxapine, without speaking to your doctor.
Other uses
The medication is sometimes used in other ways. Talk to your pharmacist or doctor for more details.
What precautions must I take?
Before you take loxapine,
- Tell your pharmacist and doctor in the event that you have an allergy to loxapine or other medication.
- Inform your pharmacist and doctor of the prescription and nonprescription medicines and nutritional supplements, vitamins, and herbal supplements you’re currently taking or plan to use. Be sure to include one of them: antidepressants, antihistamines and atropine (in Motofen, in Lomotil and in Lonox) and barbiturates, such as pentobarbital (Nembutal) Phenobarbital, pentobarbital (Luminal) as well as secobarbital (Seconal) and epinephrine (Epipen) Ipratropium (Atrovent) as well as Lorazepam (Ativan) medication for anxiety, irritable and bowel diseases motion sickness, mental illness and seizures, Parkinson’s disease, urinary tract problems, or ulcers as well as narcotic medicines for pain and sedatives, tranquilizers; and sleeping pills. Your doctor might need to adjust the doses of your medications or observe closely for adverse effects.
- inform your doctor if you have had or experienced seizures, trouble urinating or the condition known as glaucoma (a condition that causes increased pressure on the eyes could cause the gradual loss of vision) or difficulty keeping your equilibrium, breast cancer, and heart diseases. Inform your doctor if been forced to stop using any medication for mental illness because of severe adverse side consequences.
- inform your physician if you are expecting, especially when you are in the final few months of your pregnancy or if you intend to become pregnant or nursing. If you fall pregnant while you are taking loxapine consult your physician. Loxapine could cause problems for newborn babies following birth in the final weeks of pregnancy.
- If you’re having surgical procedures, including dental be sure to inform the dentist or doctor that takes loxapine.
- It is important to know that this medication can cause you to become drowsy, and could alter your thoughts and movements. Don’t drive a vehicle or use machinery until you are aware of the effects of this medication on you.
- consult your doctor regarding the appropriate use of alcohol in your treatment with loxapine. Alcohol can cause the side effects of loxapine even more serious.
- You should be aware that loxapine could cause fainting, dizziness, and lightheadedness. This is especially true after a rise from a sitting position. To prevent this from happening you should get up slowly and rest upon the ground for a couple of minutes prior to standing.
Dosage and administration
Oral Administration
A starting dose at 10 mg, twice per day is recommended. However, for patients with severe disorders, an initial dose of 50 mg daily could be beneficial. The dosage should be then gradually increased in the initial seven to ten days until you have good control over the symptoms associated with schizophrenia. The typical therapeutic and maintenance dosage is 60 to 100 mg per day. As with other medications used to treat schizophrenia, certain patients react to lower doses while others require a higher dose for maximum benefits. A daily dose of more than 250 mg is not recommended.
Maintenance Therapy
In the case of maintenance therapy, dosages should be reduced to an amount that is in line with the control of symptoms Many patients have been successfully treated with doses that fall within the range between 20 mg and 60 mg per day.
What specific dietary guidelines do I need to follow?
Unless your physician advises that you shouldn’t, follow your normal diet.
What do I do if have forgotten an amount?
You should take the dose missed when you can remember. If it’s nearing the time to take your next dose, avoid the dose you missed and follow your usual dosing routine. Don’t take a second dose to compensate for the missed dose.
Loxapine side effetcs
Loxapine may cause side effects
Consult your physician when any of the following manifestations are extreme or don’t disappear:
- Feeling unsteady, dizzy, or having trouble maintaining your balance
- faintness
- weak spots
- trouble getting to sleep or not being able to fall in bed
- blurred vision
- dry mouth
- Increased saliva
- nausea
- vomiting
- constipation
- trouble with urination
- excessive thirst
- loss or gain in weight
- The agitation
- Speech slurred
- headache
- Rash
- Itching
- hair loss
- flushing
- Eyelids that are drooping
- puffing up of the face
- blank expression of the face
- walking in a shuffle
- unnatural, slow or uncontrollable movements of any body part
- anxiety
- burning, numbness or tingling in the feet or hands
- Production of breast milk
- Breast expansion
- menstrual period that is not occurring
- lower sexual ability of men
Some side effects could be severe
If you notice any of the symptoms listed below, contact your physician immediately:
- The fever
- Muscle stiffness
- falling
- confusion
- Heartbeats that are irregular or fast
- sweating
- neck pains
- Tightness in the throat, chest pain
- difficulties breathing or difficulties swallowing
- tongue sticking out from the mouth
- fine, worm-like tongue movements
- uncontrollable, erratic mouth, face or jaw movements that are uncontrollable, rhythmic, and unpredictable.
- seizures
- reduced vision, particularly in dim light
Loxapine can cause additional negative side reactions. Inform your doctor if experience any unusual symptoms during your treatment with this medication.
If you experience a serious side effect, you or your doctor may send a report to the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program online (http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch) or by phone (1-800-332-1088).
Storage and disposal of this medicine
Store the medicine in the bottle that it was placed from, tightly sealed and out of the reach of children. Keep it in a cool, dry place and away from excessive humidity and heat (not inside bathrooms).
In the event of an emergency, medications that are not required must be eliminated with special methods to make sure that children, pets, and others are not able to consume the drugs. However, you shouldn’t flush the medication into the drain. The most efficient way to get rid of the medication is to use a take-back program. Consult your pharmacist or call your local garbage or recycling department to find out about the programs that offer take-backs in your local area. See the FDA’s Safe Disposal of Medicines website (http://goo.gl/c4Rm4p) for more information if you do not have access to a take-back program.
It is crucial to keep all medications away from the reach of children since numerous containers (such as daily pill minders, as well as ones for eye drops patches, creams, as well as Inhalers) are not safe for children and children are able to open them with ease. To guard children against poisoning, ensure that you lock caps that protect you from poisoning and place the medicine in a safe place which is high and away, and out of their reach and view. http://www.upandaway.org
In the event of an emergency or overdose
In the event of an overdose If you suspect that you have taken an overdose, dial toll-free at 1-800-222-1222. Information is also available online at https://www.poisonhelp.org/help. If the patient has fallen down or had a seizure, has difficulty breathing, or cannot be resuscitated immediately dial emergency assistance at 911.
Signs of an overdose can include:
- Sleepiness
- loss of consciousness
- Breathing is slowed
- slowed heartbeat
- abnormal, slow or uncontrollable movements of any body part
- seizures
How supplied
5 mg capsule
- Loxapine
Capsules USP
5 mg
100 Capsules
Rx Only

10 mg Capsule
- Loxapine
Capsules USP
10 mg
100 Capsules
Rx Only

25 mg Capsule
- Loxapine
Capsules USP
25 mg
100 Capsules
Rx Only

50 mg capsule
-
Loxapine
Capsules USP
50 mg
100 Capsules
Rx Only
What else do I need to know?
Always keep all appointments with your physician.
Don’t allow anyone else to take your medication. Talk to your doctor about any concerns regarding refilling your prescription.
It is crucial to keep a detailed record of all medications, both prescription as well as nonprescription (over-the-counter) medications you are using, as well as all products, such as minerals, vitamins, and other nutritional supplements. This list should be brought every when you see a physician or are admitted to the hospital. It’s also important to keep in case of emergency.
