Precose
Generical name: acarbose
Name of the brand: Precose
Dosage formats: oral tablet (100 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg)
Drug class: Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
What is Acarbose
Precose(acarbose tablets) is an oral alpha-glucosidase inhibitor that is intended for usage in the treatment of diabetes type 2.
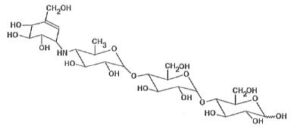
Precose is an oligosaccharide which is obtained from fermentation processes of a microorganism, Actinoplanes utahensis, and is chemically known as O-4,6-dideoxy- 4-[[(1S,4R,5S,6S)-4,5,6-trihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-2-cyclohexen-1-yl]amino]-a-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 – 4)-O-a-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 – 4)-D-glucose.
This is an off-white or off-white powder that has molecular weights of 645.6. Acarbose is water-soluble with a pKa value of 5.1. Its formula empirically can be described as C25H43NO18 with its chemical composition as it follows:
Precose comes in 25 mg 50 mg, 100 mg and 25 mg tablets to be taken orally. The active ingredients are microcrystalline cellulose, starch magnesium stearate, magnesium stearate and colloidal silicon dioxide.
 Acarbose reduces the digestion of carbohydrates by the body. This helps maintain the blood sugar level.
Acarbose reduces the digestion of carbohydrates by the body. This helps maintain the blood sugar level.
Acarbose is used in conjunction with exercise and diet to combat the condition of type 2 diabetes. Acarbose can be utilized in conjunction alongside insulin and other drugs you take in pill form.
Acarbose is also employed for other purposes that are not covered in this guideline.¶
Warnings and precautions
Acarbose should not be used when you suffer from an inflammatory bowel condition such as an ulcer or blockage of your intestines or liver, or liver cirrhosis. Don’t use acarbose if you are suffering from a condition of ketoacidosis due to diabetes (call your doctor to seek treatments with insulin).
General
Macrovascular Outcomes
There haven’t been any studies that have established conclusive proof of reduction in macrovascular risk by Precose or other anti-diabetic drugs.
Hypoglycemia
Due to the mechanism by which it works Precose alone when administered is unlikely to cause hypoglycemia when in the postprandial and fasting state. The sulfonylurea agent or insulin could cause hypoglycemia. Because Precose when used in conjunction with insulin or a sulfonylurea can cause further reductions in blood glucose levels, it can increase the chance for hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia is not a problem when patients are taking metformin in its own right under normal conditions of use. However, no higher incidence of hypoglycemia has been seen in patients who received Precose when it is added in conjunction with metformin treatment. The oral glucose (dextrose) which is absorbed is not impeded by Precose, must be utilized instead of sucrose (cane sugar) for the treatment of moderate to mild hypoglycemia.
Sucrose is a sugar whose hydrolysis to fructose and glucose is blocked by Precose is not suitable for rapid treatment of hypoglycemia. In severe hypoglycemia, it is possible to necessitate the use of an intravenous glucose infusion or the injection of glucagon.
Elevated Serum Transaminase Levels
In long-term research studies (up at 12 to 18 months and including doses of Precose up 30 mg t.i.d.) carried out throughout the United States, treatment-emergent elevations of serum transaminases (AST or ALT) over that of the normal upper limit (ULN) that were greater than 1.8 times the level and more than three times the ULN, occurred in 14%, 6%, and 33%, respectively of patients treated with Precose as opposed to 7% 22%, and 1 %, respectively, of placebo-treated patients.
While these distinctions in treatment between the two treatments were statistically significant, the elevations were asymptomatic and that was reversible, more frequent among females, and generally speaking, weren’t connected to any other indication of liver impairment.
Furthermore, these elevated levels of serum transaminase were believed to be related to dose. In US studies that included doses of Precose up to the maximum dosage approved that is 100 mg t.i.d. Treatment-related elevations of AST or ALT at any degree of intensity were similar between PRECOSE treated patients as well as placebo-treated patients (p greater than 0.496).
In the approximately 3 million patient-years of postmarketing experiences across the globe using Precose, 62 instances of transaminase serum elevations greater than 500IU/L (29 of which were linked with jaundice) have been documented.
One of the patients received treatment using 100 mg t.i.d. or more, and 33 of the 45 patients whose weight was recorded as less than 60 kg. In the 59 instances where the follow-up was documented, liver problems improved or disappeared after stopping Precose in 55, and remained the same in two. A few cases of fulminant hepatitis that have fatal outcomes have been reported and the connection to acarbose isn’t clear.
Loss of Control of Blood Glucose
If diabetic patients are subjected to stress, such as trauma, fever, infection or surgical procedures there is a temporary decrease in control of blood glucose can be experienced. At times an insulin-based treatment for a short period could be required.
Information for Patients
Patients are advised to consume Precose 3 times per day at the beginning (with eating the very first bite) of every main meal. It is essential that patients adhere to the diet guidelines and a consistent exercise routine and regular tests of blood glucose and urine levels.
Precose by itself doesn’t cause hypoglycemia, even when it is administered to patients who are in a fasting state. Sulfonylurea medications and insulin, however, can reduce blood sugar levels to cause symptoms or life-threatening hypoglycemia.
Since Precose when used in conjunction with insulin or a sulfonylurea could result in a further decrease of blood sugar levels, it could enhance the hypoglycemic effects of these drugs. The presence of hypoglycemia is not evident when patients are taking metformin on its own in normal circumstances of use. However, no increase in the incidence of hypoglycemia was noticed in patients who received Precose when it is added in conjunction with metformin treatment.
The dangers of hypoglycemia, its symptoms and treatment and conditions that can lead to its development must be recognized by both patients and family members. Since Precose blocks break down of table sugar, they must have access to a reliable sugar source (dextrose and D-glucose) to treat the symptoms that indicate low blood sugar taking Precose with insulin or sulfonylurea.
If there are any side effects that occur during Precose, they typically develop within the first few weeks of treatment. They’re typically mild to moderate digestive effects, like flatulence or diarrhea, as well as abdominal pain, and tend to decrease in frequency and severity over time.
Laboratory Tests:
The therapeutic response to Precose must be evaluated by the frequent test of blood sugar levels. Monitoring the glycosylated hemoglobin level is recommended for the monitoring of long-term glucose control.
Precose, especially when doses are greater than 50 mg t.i.d. can cause elevations in transaminases in the serum and, in rare cases hyperbilirubinemia. It is suggested that the levels of serum transaminase be examined every 3 months for the initial year following treatment using Precose, and regularly following that. If transaminases levels are elevated A reduction in dosage or discontinuation of treatment may be recommended especially if the elevated levels persist.
Renal Impairment
Precose plasma concentrations in patients with renal impairment were greater in proportion to the degree of renal impairment. Clinical trials over the long term in diabetic patients who have a severe renal impairment (serum creatinine greater than 2.0 mg/dL) are not being conducted. Thus, treating those patients with Precose is not advised.
Drug Interactions
Certain medications are known to cause hyperglycemia, which can lead to an increase in blood glucose levels. These include diuretics and thiazides corticosteroids, phenothiazines and estrogens, thyroid products, oral contraceptives like phenytoin sympathomimetics, nicotinic acid calcium channel blocking drugs and isoniazid.
If these drugs are given to a patient who is receiving Precose, the patient must be monitored closely for any loss in blood sugar control. If these drugs are removed from patients who are receiving Precose when they are in combination with insulin or sulfonylureas patients must be closely observed to look for signs of hypoglycemia.
Patients Receiving Sulfonylureas or Insulin: Sulfonylurea agents or insulin could cause hypoglycemia. When used in conjunction with sulfonylurea, insulin or both could result in a further decrease of blood glucose levels and could increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
If hypoglycemia does occur, the appropriate adjustments to how much of these drugs must be taken. Infrequently, instances of hypoglycemic shock were discovered in patients on Precose in combination with insulin or sulfonylureas.
Intestinal adsorbents (for example, charcoal) and digestive enzyme preparations containing carbohydrate-splitting enzymes (for example, amylase, pancreatin) may reduce the effect of Precose and should not be taken concomitantly.
Precose has been demonstrated to alter the bioavailability of digoxin when combined, and this could require adjustments to the dose of digoxin.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Eight studies on carcinogenicity were conducted using Acarbose for eight studies. Six studies were carried out on rodents (two strains, Sprague-Dawley as well as Wistar) as well as two research studies were conducted on Hamsters.
In the very first study of rats, the Sprague Dawley rats were given acarbose in food in high doses (up to about 500 mg per kg body mass) for the duration of 104 weeks. The treatment caused significant increases in the prevalence of kidney tumours (adenomas and Adenocarcinomas) in addition to benign Leydig-cell tumours. The same study was replicated with the same results.
Further research was conducted to distinguish the direct carcinogenic effects of acarbose and indirect effects that result from the malnutrition caused by carbohydrates by the high doses of acarbose used in the study. In one study with Sprague Dawley rats, Acarbose was added to food but the deprivation of carbohydrates was prevented through the introduction of glucose into the diet. In a 26-month study on rats from Sprague Dawley, acarbose had been administered via a daily postprandial gavage to prevent adverse effects that the drug can have on the body.
In both studies, the higher frequency of renal tumours seen in the initial research did not happen. Acarbose was also administered as food and via gavage after postprandial administration in two distinct studies on Wistar rats. A lower rate of tumours in the kidney was detected in either of these Wistar rats studies. In two feeding studies with Hamsters, both with and with glucose supplements, there was no evidence of carcinogenicity.
Acarbose does not cause harm to the DNA using the CHO test for chromosomal aberration or the bacterial Mutagenesis (Ames) test as well as a DNA-binding test. In vivo, no DNA damage was found in the predominant lethal test of male mice, or in the micronucleus test in mice.
Studies on fertility in rats following oral administration resulted in no negative effect on fertility, or on the general capacity to reproduce.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category B
Its safety for pregnant women is not confirmed. Studies on reproduction have been conducted in rodents at doses of up to 408 mg/kg (corresponding to approximately 9 times the dose in humans in relation to blood drug concentrations) and have found no evidence of decreased fertility or harm to the fetus caused by exposure to the acarbose.
In rabbits, decreased weight gain of the mother is likely the result of the pharmacodynamic effects of large doses of acarbose within the intestines, which could have contributed to an increase in the amount of embryonic loss. But, rabbits who received 160 mg/kg of acarbose (corresponding to approximately 10x the dosage of man according to the body’s surface area) did not show any evidence of embryotoxicity. Likewise, there is no proof of teratogenicity even at 32 times that of man (based on the body’s size).
However, there are studies that are well-controlled and adequate of Precose in women who are pregnant.
Since studies on reproduction in animals do not always provide a reliable indicator of the human response to the drug, it is recommended to be administered during pregnancy only when required. Since current research strongly suggests that elevated level of glucose in the blood during pregnancy is linked with an increased risk of congenital anomalies, as well as a higher rate of neonatal morbidity and death, many experts suggest the use of insulin during pregnancy to keep blood sugar levels at a level that is as normal as feasible.
Nursing Mothers:
A tiny amount of radioactivity was discovered in the milk of lactating animals following the administration of radiolabeled acarbose. It isn’t known if the drug is excreted into human milk. Since many substances are excreted from human milk, the drug Precose shouldn’t be administered to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use:
The safety and efficacy of Precose in children are not yet established.
Geriatric Use:
From the number of participants who participated in clinical studies conducted by Precose conducted in the United States, 27% were aged 65 or over 4 % were over 75. There were no significant differences in efficacy or safety were observed between younger and older subjects. The average steady-state area under the curve (AUC) and the highest levels of acarbose were about 1.5 times higher for the older group.
How to take Precose?
Follow the directions on the prescription label. Do not take this medication in smaller or larger doses or for longer than prescribed.
You should take acarbose at the first bite after a principal meal except if your physician informs you otherwise.
Your blood sugar level will have to be monitored regularly as well as you may require additional blood tests in the doctor’s office.
If you are taking acarbose along with insulin or any other diabetes medication it is possible that your blood sugar level drops to dangerous levels.
Blood sugar levels are low (hypoglycemia) can be experienced by anyone with diabetes. The symptoms include hunger, headache sweating, anxiety, confusion, dizziness or feeling unsteady. Always carry a supply of dextrose (D-glucose) to hand in the event of low blood sugar levels. I
f you are taking acarbose medication, dextrose will be more effective than table sugar when treating hypoglycemia. Dextrose sources include dates, honey or raisins, dried prunes, plums grapes as well as glucose tablets. Make sure your family members and close family members know how to assist you in case of an emergency.
If you are suffering from severe hypoglycemia that makes it difficult to consume food or drink, consider the glucagon injection. Your physician can recommend an emergency glucagon injection kit and instruct you on how to utilize it.
Be aware of indications that indicate excessive glucose levels (hyperglycemia) including an increase in thirst, more frequent urine output, hunger dry mouth, fruity breath smell poor vision, dry and flaky skin as well as weight gain.
Be sure to check your blood sugar levels when you are under tension or illness, travel, medical emergency or surgery intense exercise or when you drink alcohol or avoid meals. These can affect the levels of your glucose and your dosage requirements could alter. Don’t alter your dose of medication or your schedule with your doctor’s permission.
Acarbose is just one part of a comprehensive treatment plan which may include exercise, diet and weight management, as well as regular blood sugar tests, and medical treatment that is specific to you. Follow the instructions of your physician precisely.
Keep the bottle at room temperature, free of heat and moisture. Close the bottle when not being used.
If I don’t take the dose?
Do not miss the dose when you remember (be sure to do it before the meal). If it’s been more than 15 mins since the time you began your meal, you could still be taking acarbose, but it could be less effective than taking it after the first bite of your meal. Do not take acarbose during meals, and don’t use a second medicine to make up for a missed dose.
How do I react if take too much?
For medical emergencies, seek emergency medical attention or contact toll-free the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222.
In the event of an overdose, you should not eat or drink anything that contains carbohydrates for up to six hours.
What to avoid while taking Precose?
Do not drink alcohol. It could lower blood sugar levels.
Do not take digestive enzymes such as amylase, pancreatin or lipase when you take Acarbose. These enzymes may cause problems for you to absorb the acarbose. The products that contain digestion enzymes are Arco-Lase, Cotazym, Donnazyme, Pancrease, Creon, and Ku-Zyme.
Precose side effects
Seek medical attention immediately If you are experiencing symptoms that indicate an allergic reaction such as asthma; hives and swelling of your lips, face or tongue.
Consult your physician immediately If you suffer from:
- severe constipation severe;
- extreme stomach pain, diarrhea that’s liquid or bloody
- simple bleeding, unusual bruising (nose vagina, mouth or the rectum) either red or purple small spots on your skin and
- liver issues–nausea, stomach discomfort, itching, fatigue feeling and loss of appetite. black stools, dark urine and jaundice (yellowing of the eyes or skin), chest pain.
Common side effects could be:
- stomach discomfort, gas, bloating;
- mild diarrhea moderate diarrhea
- A mild rash on the skin or itching.
This isn’t a complete list of possible side effects, and other side effects could occur. Consult your physician for advice regarding medical adverse effects. You can report any side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Precose dosing information
Usual Adult Dose for Diabetes Type 2:
Dose-independently based on effectiveness and tolerance:
Initial dosage: 25 mg orally three times a day.
Adjust dosage between 4 and 8-week intervals, based on the efficacy and tolerance
Dosage for maintenance 50-100 mg orally, 3 times per day.
The maximum dose is: of 60 kilograms or less: 50 mg taken orally three times per day. If you weigh more than 60 kg 100 mg orally three times per day.
Comments:
Take it at the beginning (with the first bite) of every main meal. Patients must adhere to a diet for diabetics to limit GI adverse negative effects.
Some patients can are benefited by beginning at 25 mg daily, with a subsequent gradual increase to 3 times a day to reduce GI adverse effects.
If no further reduction in postprandial HbA1c or glucose is noticed with titration at 100 mg 3 times per day, think about reducing the dosage.
Use as an adjunct to exercise and diet to increase glycemic control for those suffering from type 2 diabetes mellitus.
What other drugs can impact Precose?
It is possible to suffer from the condition of hyperglycemia (high levels of blood sugar) in the event that you are taking Acarbose in conjunction with other drugs which can increase blood sugar levels, including:
- Isoniazid (for the treatment of tuberculosis);
- Niacin (Advisor, Niaspan, Niacor, Simcor, Slo Niacin and more) nicotine patches, or gum
- birth hormones and other birth control pills;
- diuretic or “water pills”;
- Heart or blood pressure medication;
- oral diabetes medication or insulin;
- Diet pills, stimulants, or other medicines for treating allergies, colds, asthma or other respiratory conditions;
- Phenothiazines (Compazine and other);
- seizure medicines (Dilantin and other);
- steroids (prednisone and other) or
- thyroid medication (Synthroid and other).
This list isn’t complete. Other drugs can be incompatible with acarbose, such as prescription and over-the-counter medicines as well as vitamins and herbal supplements.
More details
Always consult your doctor to make sure the information presented on this site is appropriate to your particular situation
