Mitral Valve Regurgitation
 Mitral valve regurgitation often referred to as mitral regurgitation or mitral insufficiency or mitral dysfunction is a condition where your heart’s mitral valve fails to close properly which allows blood to flow backwards through the heart. When the regurgitation of your mitral valve has a significant amount it means that blood isn’t moving within your heart, or the outside in your body effectively which can cause you to feel tired or breathless.
Mitral valve regurgitation often referred to as mitral regurgitation or mitral insufficiency or mitral dysfunction is a condition where your heart’s mitral valve fails to close properly which allows blood to flow backwards through the heart. When the regurgitation of your mitral valve has a significant amount it means that blood isn’t moving within your heart, or the outside in your body effectively which can cause you to feel tired or breathless.
The treatment of mitral valve regurgitation is dependent on how severe the condition is, if it’s worsening and if there are any symptoms. In the case of leakage that is not too severe treatments are usually not required.
It is possible that you will require heart surgery for repair, or replacement of the valve in case of extreme regurgitation or leakage. If left untreated with treatment, serious mitral valve regurgitation could lead to heart malfunction or heart rhythm issues (arrhythmias). Even people who aren’t experiencing symptoms could require a medical evaluation from an experienced surgeon and cardiologist in mitral valve diseases to determine if an early intervention is beneficial.
Symptoms
A few people suffering from mitral valve diseases may not notice symptoms for a number of years. The signs as well as symptoms for mitral valve dysfunction that depend on the extent and speed at which the condition is diagnosed, may include:
- A heart sound that is not normal (heart murmur) can be heard using the Stethoscope
- Breathlessness (dyspnea) particularly when you’ve been extremely active or lying down
- Fatigue
- Heart palpitations are the sensations of a fast heartbeat that is fluttering
- A swollen ankle or foot
Mitral valve regurgitation is usually slow and mild in its progression. There may be no signs for years, and you may not even know you suffer from this condition. It may not get any worse.
The doctor may first think that you suffer from mitral valve regurgitation when they detect an abnormal heart murmur. In some cases, however, the problem can be diagnosed quickly and you might be greeted with a sudden increase in extreme symptoms and signs.
When is the best time to seek medical help?
If your doctor detects a heart murmur while listening to your heart via the stethoscope, he/she might suggest that you see a cardiologist and obtain an echocardiogram. If you experience symptoms that indicate mitral valve regurgitation, or another issue within your heart, you should consult your physician immediately. The first signs are actually the signs of the mitral valve’s complications which include heart failure, an illness in which your heart isn’t able to pump enough blood to meet the demands of your body.
Causes
The heart contains four valves to ensure that blood flows in the right direction. The valves are the mitral valve the tricuspid valve as well as the pulmonary valve and the an aortic valve. Each valve is equipped with flaps (leaflets or cusps) which open and close at the same time every heartbeat. Sometimes, valves don’t fully close or open and can cause disruption to blood flow through your heart and into your body.
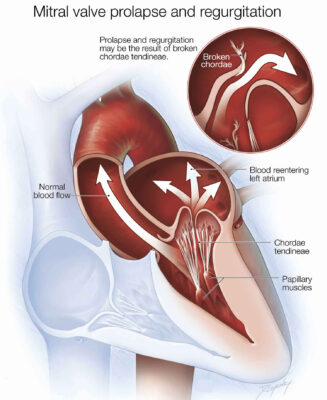
In mitral valve regurgitation the valve that connects the left heart chamber’s upper (left atrium) and the lower left heart chamber (left ventricle) does not close properly which causes blood to leak backwards to the atrium of left (regurgitation).
Causes of Mitral Valve regurgitation
Mitral valve regurgitation may be caused by issues in the mitral valve which is also known as primary mitral regurgitation of the valve. The left ventricle is a part of the body that suffers from diseases. may cause functional or secondary mitral valve regurgitation.
The possible reasons for mitral valve regurgitation are:
- Prolapse of the mitral valve. In this condition the leaflets of the mitral valve expand back to the left atrium during an exercise of the heart. This is a common heart defect that may hinder the mitral valve from closing completely and cause regurgitation.
- Cords of tissue that are damaged. Over time, the tissues cords that hold dies on the mitral valve the heart wall can be stretched or tear, particularly for those suffering from Mitral valve prolapse. A tear could result in leakage from the valve abruptly and may require repair via heart surgery. A chest injury may cause the cords to rupture.
- Rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever -is a complication of untreated strep throat, can cause damage to the mitral valve and lead to mitral valve regurgitation in the early or later in the course of. Rheumatic disease is now uncommon within the United States, but it’s still common in the developing world.
- Endocarditis. The mitral valve could be damaged due to an infection in the heart’s lining (endocarditis) which may affect the heart valves.
- Heart attack. A heart attack may cause damage to the heart muscle that is responsible for supporting the valve that is mitral, which can affect its function. In the event that the damages are severe enough that a heart attack occurs, it can cause severe and sudden mitral valve regurgitation.
- Abnormality in the cardiac muscle (cardiomyopathy). Over time, certain ailments like high blood pressure can trigger your heart muscle to work harder, eventually expanding your left ventricle of your heart. This may cause the tissue to stretch surrounding your mitral valve that can cause leakage.
- Trauma. Experiencing trauma, like an accident in the car could result in the mitral valve to regurgitate.
- Congenital heart imperfections. Some babies are born with heart defects that include damaged heart valves.
- Certain medications. Prolonged use of certain drugs can result in mitral valve regurgitation, for instance those that contain Ergotamine (Cafergot, Migergot) that are used to treat migraines , among other ailments.
- Treatment for radiation. In rare cases the treatment of cancer with radiation targeted at the chest region can cause mitral valve regurgitation.
- Atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation is a common heart rhythm disorder which could be a source of regurgitation in the mitral valve.
Risk factors
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing mitral valve regurgitation The most common causes are:
- A background of prolapsed mitral valve or stasis. However, having one of the conditions does not necessarily indicate that you’ll be prone to developing regurgitation of the mitral valve. A history of valve diseases increases the chances of developing.
- Heart attack. A heart attack could cause damage to your heart, altering the function of your mitral valve.
- Heart diseases. Certain forms of heart disease, like coronary artery disease can cause the mitral valve to regurgitate.
- The use of certain medicines. People who take medicines that contain ergotamine (Cafergot, Migergot) as well as similar migraine medications or take cabergoline also have an increased chance of suffering from mitral regurgitation. Similar issues were observed in the appetite suppressants fenfluramine and dexfenfluramine. Both are no longer available for sale.
- Infections, such as endocarditis and Rheumatic fever. Infections or the inflammation that they trigger can cause damage to the mitral valve.
- Heart disease that is congenital. Some people are born with an abnormal mitral valve, which is susceptible to regurgitation.
- age. By middle age there are many who suffer from mitral valve regurgitation due to natural degeneration of the valve.
Complications
If it’s minor mitral valve regurgitation generally doesn’t cause any issues. However serious mitral valve regurgitation may cause complications, such as:
-
- Heart Failure. Heart failure results when your heart isn’t able to supply enough blood to meet the demands of your body. Mitral valve regurgitation is severe and puts additional strain on the heart due to the fact that, when blood pumps backwards and forward, there’s less blood flowing forward each time you beat. The left ventricle grows and, if not treated gets weaker. This could lead to heart failure.Additionally, pressure builds up in your lungs, causing the accumulation of fluid, which can strain both sides of your heart.
- Arial fibrillation. The stretching and expansion of the left atrium in your heart could cause this irregular heartbeat that makes you heart’s upper chambers beat in a chaotic manner and quickly. Atrial fibrillation may cause blood clotsto form, which could break free from your heart and move across your body, causing severe issues, like strokes if a blockage of a blood vessel within your brain.
- The pulmonary hypertension. If you have persistent, untreated, or untreated mitral regurgitation, you could develop a form of high blood pressure which impacts the vessels in the lung (pulmonary hypertension). A leaky valve in the mitral chamber can cause pressure to rise inside the left atrium which could eventually lead to the condition known as pulmonary hypertension. This could cause heart problems in the left side of the heart.
Diagnosis
Key diagnostic points
- It could be unaffected for years (or for the rest of life).
- Severe mitral regurgitation may cause left-sided heart failure.
- In the case of chronic mitral regurgitation primary, surgery is recommended for symptoms, or when the LV ejection percentage (LVEF) lower than 60 percent or the echocardiographic LV end-systolic size is more than 4.0 cm.
- For patients with mitral prolapse or severe mitral regurgitation surgery is suggested when mitral repair is carried out.
- Patients suffering from functional mitral regurgitation can be improved by biventricular pacing. Some might require surgical intervention.
The doctor will inquire questions about the medical background of you as well as the background of family members with heart problems. The doctor will also conduct an examination that involves the heart’s activity using an instrument called a stethoscope. Mitral valve regurgitation typically produces the sound of blood flowing backwards from the valve (heart murmur).
The doctor will decide the tests needed in order to determine an assessment. If you need to test for a diagnosis, you might be sent to a cardiac surgeon.
Tests
The most common tests used to diagnose regurgitation of the mitral valve include:
-
- Echocardiogram. This test is frequently used to detect Mitral valve regurgitation. In this test the sound waves directed towards your heart by a wand-like device (transducer) that is placed on your chest generate videos of your heart moving.The test examines the heart’s structure as well as the mitral valve, and the flow of blood throughout your heart. A cardiac echocardiogram can help your doctor take a closer look at the mitral valve and assess how it’s performing. Doctors may also use an echocardiogram that is 3D.Doctors can conduct a different kind of echocardiogram referred to as an echocardiogram transesophageal. In this kind of test it is performed using a tiny transducer to the tube’s end is passed down your stomach, which permits to see more closely the mitral valve, which is different from what an echocardiogram that is normal.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG). Wires (electrodes) that are attached to pads on your skin detect the electrical signals coming from your heart. An ECG will detect an enlarged chamber within your heart. It can also detect heart diseases and irregular heart rhythms.
- Chest Xray. This enables your physician to determine if your left atrium or left ventricle are enlargedpotential indicators for mitral valve regurgitationas well as the health of your lung.
- Heart imaging. A cardiac MRI makes use of radio waves and magnetic fields to create precise photographs of your heart. The test can be used to assess the extent of your illness as well as determine the size and functionality of your left heart’s lower chamber (left ventricle).
- Cardiac CT. A CT angiogram can be taken of the abdomen, chest and pelvis to determine if you’re an ideal candidate of a robotic repair for your mitral valve.
- Tests for exercise or stress test. Different exercise tests allow you to measure your tolerance to activity and assess your heart’s reaction to physical effort. If you’re not able to exercise, medicines that simulate the effects of exercising on your heart could be considered.
- Catheterization of the cardiac. This test isn’t commonly used to detect the condition of mitral valve regurgitation. This procedure is invasive and involves threading a small tubing (catheter) through the blood vessel of your groin or arm to an artery inside the heart, and then injecting dye into the catheter, making the arterial artery visible in an X-ray. This gives you a clear image of the arteries in your heart and how your heart function. It also allows you to measure the pressure inside your chambers of your heart.
Treatment
The treatment for regurgitation of the mitral valve varies on how severe your situation is, whether you’re experiencing symptoms or signs or if the condition is becoming worse. The aim for treatment is to enhance the heart’s performance while reducing your symptoms and signs and preventing any further complications.
A doctor who is trained to treat heart conditions (cardiologist) will offer your medical care. If you suffer from the condition of mitral valve regurgitation think about getting treatment in a medical facility that has an multidisciplinary team of doctors and medical professionals who are trained and adept at evaluating the heart valve and treating diseases. The team will work closely with you in determining the best course of treatment for your situation.
Monitering mitral regurgitation
A few people, specifically those who have mild regurgitation may not require treatment. However, it is possible that the condition will need to be monitored by your doctor. There may be a need for regular assessments and the frequency will depend on your illness. Your physician may also suggest taking steps to improve your lifestyle.
Medications
Your physician may prescribe medication to treat the symptoms but medication cannot treat mitral valve regurgitation.
The medications may comprise:
-
- Diuretics. These medications can help to reduce the accumulation of fluid in the lungs or your legs and can cause mitral valve regurgitation.
- blood thinners. These medications can aid in preventing blood clots, and could be used in the event that you suffer from atrial fibrillation.
- Blood pressure medication. High blood pressure can cause mitral valve regurgitation to be more severe If you suffer from excessive blood pressure, your physician may prescribe medication to lower it.
Surgery
Your mitral valve might require repairs or replaced. Doctors might suggest mitral valve replacement or repair even if there aren’t any symptoms, since this could help prevent complications and improve the outcome. If you require surgery due to other heart conditions Your doctor could replace or repair the damaged mitral valve in the same procedure.
Mitral valve surgeries are generally carried out by cutting (incision) within the chest. In certain instances, surgeons may perform minimally invasive surgery, which requires the making of smaller incisions than those utilized in open heart surgery.
Some medical facilities may carry out robot-assisted heart surgery, which is a form that is minimally-invasive. In this kind of procedure surgeons observe the heart with an enhanced high-definition 3D view using a video monitor. They also employ robotic arms to mimic certain procedures used in open heart operations.
The doctor will be able to discuss with you what mitral valve replacement or valve replacement might be suitable for your particular situation. Doctors might also assess your health to determine if you’re eligible for minimally-invasive heart operation or open-heart surgery.
Doctors may suggest repair to the mitral valve because it protects your valve and can preserve your the heart’s function. If mitral valve repair isn’t feasible doctors might have to replace the mitral valve¹.
Repair of the Mitral valve
Surgeons can fix the valve by reconnecting the valve flaps (leaflets) and replacement of the cords that support the valve or by removing the valve’s excess tissue so that the leaflets close securely. Surgery may be used to strengthen or tighten the ring around the valve (annulus) by implanting an artificial rings (annuloplasty bands).
Doctors might make use of long narrow tube (catheters) to fix the valve of the mitral in certain situations. In one procedure using catheters surgeons insert a catheter that has clips that are inserted into an artery inside the groin. They then direct it into the valve in your mitral. Doctors make use of the clip to modify the shape of the valve. Patients with severe signs caused by mitral valve regurgitation that aren’t candidates for surgery or have an increased risk of surgery may be considered for this procedure.
In another way doctors can fix a previously repaired mitral valve which is leaky through the use of a device to stop the leakage².
Mitral valve replacement
In the event that your valve cannot be repaired, it could require replacement of the mitral valve. When you undergo mitral valve replacement, your surgeon will remove your damaged valve, and then replaces it by a mechanical valve or a valve made of human, cow or pig the heart (biological tissue valve).
The valves of biological tissue degrade in time, and eventually require replacement. Patients with mechanical valves are required to be on blood thinners to keep them from getting blood clots.
Your doctor will be able to discuss the benefits and risks of each kind of heart valve and decide which one would be suitable for your needs.
Doctors continue to research catheter procedures that fix or repair mitral valves. Some medical facilities may provide mitral valve replacement as part of an intervention with a catheter within a clinical study for patients suffering from severe mitral valve diseases who aren’t candidates for surgery. A catheter procedure could be utilized to place an alternative valve into the biological tissue replacement valve that’s not functioning as it should.
Consult your doctor about the kind of follow-up treatment you’ll need following your surgery and inform your doctor when you begin experiencing new symptoms or symptoms become worse following treatment.
Lifestyle and home remedies for home
The doctor might suggest that you make a variety of healthy lifestyle changes for your heart to your routine, including:
- Maintaining your blood pressure in check. Control of high blood pressure is essential for those suffering from Mitral Valve Regurgitation.
- A heart-healthy diet. Food doesn’t directly influence the regurgitation of the mitral valve. However, a healthy diet could assist in preventing heart diseases that could cause weakness to the muscle of your heart. Choose foods that are free of trans and saturated fats as well as salt, sugar, and refined grains like white bread. Take a wide assortment of fruits and vegetables as well as whole grains and protein sources, like fish, lean meats and nuts.
- Maintaining an appropriate weight. Keep your weight within the recommended range set by your physician.
- Preventing the infective endocarditis. If you have been through a replacement of your heart valve or repaired, your physician may suggest that you take antibiotics prior to dental procedures to avoid an infection known as infective endocarditis. Consult your physician to determine whether he or she suggests that you take antibiotics prior to dental procedures.
- Reduce your consumption of drinking alcohol. Heavy alcohol use may cause arrhythmias, and cause symptoms to become more severe. Drinking excessively can cause cardiomyopathy, which is a condition of weakening the heart muscle which causes mitral regurgitation. Talk to your physician about the consequences of drinking alcohol.
- Do not smoke. If you smoke stop now. Consult your physician about options to help you stop smoking. Participating in a support group could be beneficial.
- Regular physical activities. How long and how hard you’re able to work is contingent depending on your health condition along with the amount of your exercise. Consult your physician prior to beginning your exercise routine in particular if you’re planning to participate in playing competitive sports.
- Regularly visiting your doctor. Establish a regular examination schedule with your cardiology or primary care doctor. Inform your doctor if you notice an increase or decrease in health signs or symptoms.
If you’re a woman suffering from Mitral Valve Regurgitation you need to speak with your doctor prior to becoming pregnant. The heart is triggered by pregnancy and has to be more active. The extent to which a heart that has mitral valve regurgitation copes with this additional work is dependent on the extent of regurgitation as well as the efficiency your heart is pumping. Through your pregnancy and following the birth, your cardiologist as well as your obstetrician must be on the lookout for your.

Wow, wonderful blog format! How long have you been blogging for?
you make blogging glance easy. The whole glance of your web site is
great, as neatly as the content! You can see
similar here e-commerce
Post writing is also a fun, if you be familiar with afterward you can write or else
it is difficult to write. I saw similar here: Sklep online
Nice post. I used to be checking constantly this weblog and I am inspired!
Very helpful info specially the closing part 🙂 I maintain such info much.
I used to be looking for this certain information for a long time.
Thanks and good luck. I saw similar here: Najlepszy sklep
Hello there! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with Search Engine Optimization?
I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good
gains. If you know of any please share. Cheers! You can read similar blog here: Dobry sklep
Howdy! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search Engine Optimization? I’m
trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but
I’m not seeing very good results. If you know of any please share.
Many thanks! You can read similar art here: Najlepszy sklep
It’s very interesting! If you need help, look here: ARA Agency
Hey! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog
to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very
good results. If you know of any please share. Cheers!
You can read similar blog here: Sklep internetowy
Hi there! Do you know if they make any plugins
to assist with SEO? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some
targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good results.
If you know of any please share. Cheers! You
can read similar blog here: Najlepszy sklep
Hello there! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with SEO?
I’m trying to get my website to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not
seeing very good results. If you know of any please share.
Appreciate it! I saw similar blog here: Backlink Portfolio
Wow, amazing weblog layout! How long have you ever
been running a blog for? you made running a blog look
easy. The overall look of your website is great, as neatly
as the content material! You can see similar here najlepszy sklep
synthroid rx
synthroid purchase
Absolutely pent subject matter, appreciate it for selective information .대출
Absolutely pent subject matter, appreciate it for selective information .대출
Your passion for this topic is evident in every word.급전
Your article has challenged my assumptions in the best possible way.대출
I’m blown away by the depth of your research.급전
Your article is a valuable contribution to the conversation.급전
I’m inspired by your passion for this subject.급전
It’s very interesting! If you need help, look here: link building
I’m bookmarking this for future reference.급전
Thanks for providing such valuable insights into this topic.급전
I enjoyed reading this post. It gave me a lot to think about.dashdome
This was an enlightening post. I look forward to reading more from you.peakpulsesite
vermox price nz
Thanks for the valuable information. This is very helpful.nexusnook
You have a real gift for writing. Your posts are always so engaging and full of valuable information. Keep up the great work!nexusnook
hi, thanks!: berlin immigration office
Your passion for the subject matter is evident in every post you write. This was another outstanding article. Thank you for sharing!coinsslot
Excellent, what a weblopg it is! This webpage presents valuable data to us, keep it up.
hi, thanks!: Peranox
hi, thanks!: Peranox
hi, thanks!: Peranox
hi, thanks!: Peranox
hi, thanks!: Peranox
hi, thanks!: zone porn
hi, thanks!: zone porn
hi, thanks!: zone porn
hi, thanks!: zone porn
l free to adjust these comments as needed to better fit the specific blog posts you’re responding to!dashdome
This post was incredibly informative and well-organized. I learned so much from reading it. Thank you for your hard work and dedication!rendingnicheblog
I’m always impressed by the depth of knowledge and insight you bring to your posts. This was another fantastic article. Thank you!echozone
tretinoin 0.025 cream brand name
I always look forward to your new posts. You have a way of making even the most complex topics easy to understand. Excellent job!swiftnook
Thanks for this post, I am a big fan of this website would like to go on updated.
The biggest issue is the dialogue, it is a little cheesy at times and doesn’t give the actors much to work with, but I wouldn’t say it’s every time they open their mouth just some lines in the movie are a little rough.
Thank you so much for spending some time to line all of this out for people. This posting has been very helpful in my opinion.
Many thanks for sharing this first-class article. Very inspiring! (as always, btw)
Perfect work you have done, this website is really cool with excellent information.
Awesome article , I am going to spend more time learning about this topic
When I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new surveys are added- checkbox and already each time a comment is added I receive four emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can eliminate me from that service? Thanks!
my family would always like to go on ski holidays because it is very enjoyable“
Your blog would increase in ranking if you post more often.:~”*;
howdy, I’ve been ranking the crap out of “pre spun articles”.
when i was a kid, i love to receive an assortment of birthday presents like teddy bears and mechanical toys..
Absolutely indited articles , Really enjoyed reading .
I am extremely inspired along with your writing skills well with the format for your weblog. Is that this a paid theme or did you customize it yourself? Either way keep up the nice high quality writing, it’s uncommon to peer a great weblog like this one today.
Pleasurable article. It would appear that a good many simple tips are relying on the innovation factor. “The elegance of honesty needs no adornment.” by Merry Browne..
As everyone knows though it’s not really about how good the movie was, it’s about if you would watch it a second time?
Thanks, I just found your blog and wanted to say that I’ve truly enjoyed browsing your blog posts. After all I’ll be subscribing to your feed and I hope you write again very soon!
I was also reading a topic like this one from another site..*.”‘
Youre so cool! I dont suppose Ive read anything similar to this prior to. So nice to find somebody with original thoughts on this subject. realy appreciate beginning this up. this excellent website are some things that is required on-line, an individual after a little originality. helpful job for bringing new things towards web!
Can I just now say what a relief to uncover a person that actually knows what theyre referring to on the internet. You definitely have learned to bring a challenge to light and work out it crucial. Lots more people ought to read this and see why side of the story. I cant think youre not more popular simply because you absolutely hold the gift.
Hey! I simply wish to give a huge thumbs up for the great info you’ve gotten here on this post. I can be coming back to your weblog for extra soon.
I am really impressed with your writing skills well with the layout for your weblog. Is that this a paid subject matter or did you modify it your self? Anyway stay up the nice high quality writing, it is rare to see a nice weblog like this one these days.
I liked seeing this, like your blog layout too. Is it wordpress?
One more important issue is that if you are a mature person, travel insurance for pensioners is something you need to really look at. The more mature you are, a lot more at risk you’re for getting something bad happen to you while abroad. If you are not necessarily covered by some comprehensive insurance coverage, you could have quite a few serious challenges. Thanks for discussing your good tips on this web site.
Thank you for taking the time to line all this out for people like us. This kind of blog post ended up being extremely useful in my opinion.
Hello! I simply would like to give you a large thumbs up with the great information you could have here on this post. I’ll be returning to your site to get more detailed soon.
I like the efforts you have put in this, thank you for all the great blog posts.
great work… Excellent weblog here! Also your web site a lot up fast! What web host are you the usage of? Can I get your associate link on your host? I want my website loaded up as fast as yours lol…
I believe other website proprietors should take this web site as an model, very clean and good user friendly style .
Considerably, the post is in reality the finest on that laudable topic. I fit in with your conclusions and can eagerly look forward to your incoming updates. Saying thanks definitely will not simply just be enough, for the outstanding clarity in your writing. I will certainly at once grab your rss feed to stay privy of any kind of updates. Pleasant work and also much success in your business efforts!
Hi, your site is really well done. thanks for all the information. I’m sending my friends to read this article.
There couple of fascinating points with time in this post but I don’t know if these center to heart. There’s some validity but I am going to take hold opinion until I explore it further. Excellent article , thanks and we want more! Added to FeedBurner likewise
Spot on with this write-up, I truly think this web site needs rather more consideration. I’ll probably be again to learn rather more, thanks for that info.
You produced some decent points there. I looked on the internet for the problem and discovered most individuals go in addition to with all your website.
I read your article a second time so I could take in all the information. I agree with many of your views. I enjoyed this.
It is the best time to make some plans for the future and it’s time to be happy. I have learn this post and if I may just I wish to suggest you few interesting things or suggestions. Perhaps you can write subsequent articles regarding this article. I want to learn more things approximately it!
I must say, as a lot as I enjoyed reading what you had to say, I couldnt help but lose interest after a while. Its as if you had a wonderful grasp on the subject matter, but you forgot to include your readers. Perhaps you should think about this from far more than one angle. Or maybe you shouldnt generalise so considerably. Its better if you think about what others may have to say instead of just going for a gut reaction to the subject. Think about adjusting your own believed process and giving others who may read this the benefit of the doubt.
Hello! I merely wish to make a massive thumbs up for that wonderful info you may have here during this post. I’ll be coming back to your blog post for further soon.
when i am downloading stuffs over the internet, psp game downloads are always my priority;;
polo shirts are very casual and stylish indeed, most of the time i use polo shirts*
when it comes to free games, i always look for free flash games because they have small file sizes..
Fantastic job here. I really enjoyed what you had to say. Keep heading because you surely bring a new voice to this subject. Not many people would say what youve said and still make it interesting. Well, at least Im interested. Cant wait to see more of this from you.
Hi! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying
to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m
not seeing very good success. If you know of any please share.
Kudos! I saw similar art here: Escape rooms
I tried to submit a comment earlier, although it has not shown up. I think your spam filter may possibly be broken?
To know wisdom and instruction, to perceive the words of understanding
I adore your wp template, exactly where do you obtain it through?
when taking your watch for a repair, always look for a reputable and experienced watch repairman,
I’ve viewed some different blog posts with regards to this topic, and I must state that yours shows the most insight. Thanks a lot for expressing your opinions with everyone here.
You can certainly see your enthusiasm within the work you write. The arena hopes for more passionate writers such as you who are not afraid to mention how they believe. Always go after your heart.
You have noted very interesting details ! ps nice site.
Hi for super synopsis, but then I am glad for totally howling the Zune, and moreover pray such a, together with very good ratings some other type of a lot more made, beneficial analyse if is it doesn’t right choice for you.
After study many of the blog posts on the site now, we truly such as your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and will also be checking back soon. Pls take a look at my web-site as well and figure out if you agree.
Howdy! I know this is kinda off topic nevertheless I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest authoring a blog post or vice-versa? My site addresses a lot of the same subjects as yours and I think we could greatly benefit from each other. If you are interested feel free to send me an email. I look forward to hearing from you! Terrific blog by the way!
i am looking for furniture stores that offer great discount when you buy in bulk quantitites,
Hey! I simply wish to give an enormous thumbs up for the good information you’ve got here on this post. I will likely be coming back to your blog for more soon.
Very fine write-up. I actually really came across a person’s blog site plus needed so that you can point out this I’ve actually loved browsing a person’s site plus content. Anyhow I’ll often be checking a person’s feast plus I actually hope so that you can examine a person’s site again.
During my mission on the web, We noticed this blog publish, It is extremely detailed and I think you need to acknowledge this kind of remark. I need money too
I went over this website and I think you have a lot of excellent information, saved to fav (:.
I need to admit that that is one wonderful insight. It surely gives a company the opportunity to have in around the ground floor and really take part in making a thing special and tailored to their needs.
Thanks for having the time to write about this issue. I truly appreciate it. I’ll post a link of this entry in my site.
I’d must consult with you here. Which is not something I do! I spend time reading an article that may make people feel. Also, appreciate your allowing me to comment!
I’m not sure where you’re getting your info, but great topic. I needs to spend some time learning much more or understanding more. Thanks for excellent information I was looking for this info for my mission.
I wish to show my appreciation to you for rescuing me from this particular instance. As a result of scouting through the search engines and coming across ideas that were not helpful, I thought my entire life was gone. Being alive minus the strategies to the issues you’ve sorted out through your entire blog post is a critical case, and those which might have in a negative way affected my career if I hadn’t encountered your blog post. Your own personal expertise and kindness in dealing with the whole lot was crucial. I don’t know what I would’ve done if I hadn’t discovered such a stuff like this. I can at this moment relish my future. Thanks a lot very much for your professional and result oriented guide. I will not hesitate to propose your web site to anyone who wants and needs care on this issue.
Nice post. I learn something much harder on distinct blogs everyday. Most commonly it is stimulating to see content off their writers and employ a little something from their site. I’d would rather use some while using content on my weblog whether or not you do not mind. Natually I’ll provide a link on your web blog. Thanks for sharing.
Howdy! I just want to give you a big thumbs up for your great info you have got here on this post. I will be coming back to your blog for more soon.
It looks like you will find a trouble with your website working with Opera internet browser.
After spending several hours online at last We have located an individual that seriously does know what they’re preaching about appreciate it a whole lot fantastic posting
Hola i would really love to subscribe and read your blog posts .
well of course, everyone loves to get rich but not everyone would love to do hard work”
I’ve been exploring for a little for any high-quality articles or blog posts on this sort of area . Exploring in Yahoo I ultimately stumbled upon this website. Studying this information So i’m satisfied to convey that I’ve a very excellent uncanny feeling I found out exactly what I needed. I most unquestionably will make certain to don’t omit this website and provides it a glance a continuing.
I agree with your thought. Thank you for your sharing.
i frequent hair salons because i always want to keep my hair in top shape“
I have been browsing online more than 3 hours lately, yet I by no means found any fascinating article like yours. It is pretty worth sufficient for me. In my view, if all web owners and bloggers made excellent content material as you did, the net will probably be much more helpful than ever before!
Fashion Courses Online… […]we like to honor other sites on the web, even if they aren’t related to us, by linking to them. Below are some sites worth checking out[…]…
Jim, the people closed their eyes to what he was really saying and voted because of his being able to be the First Black President. Its also possible to be the first worst president.
Just desire to say your article is as amazing. The clearness in your post is just great and i can assume you’re an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission let me to grab your RSS feed to keep updated with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please keep up the gratifying work.
I have read a few excellent stuff here. Definitely price bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how so much attempt you put to make the sort of fantastic informative web site.
The Nectarine has smooth-slick pores and skin like a Plum. The style is resembling a Peach. The significant distinction is that the Peach has a rough protective skin a prickly fiber that protects the fruit and if not wiped-off can hurt your tongue….
It’s exhausting to seek out knowledgeable individuals on this topic, but you sound like you recognize what you’re speaking about! Thanks
Your current article normally have got much of really up to date info. Where do you come up with this? Just stating you are very imaginative. Thanks again
Thanks a lot for sharing this with all folks you really understand what you’re talking about! Bookmarked. Kindly also talk over with my website =). We will have a hyperlink exchange arrangement among us!
It’s going to be finish of mine day, but before ending I am
reading this enormous paragraph to improve my experience.
My homepage :: Seo Company India – Seohawk
Thanks for your write-up. What I want to point out is that while looking for a good internet electronics shop, look for a website with comprehensive information on critical indicators such as the personal privacy statement, security details, any payment procedures, and other terms in addition to policies. Constantly take time to look into the help along with FAQ areas to get a far better idea of how a shop functions, what they are capable of doing for you, and just how you can make use of the features.
Excellent site. I think there is a dilemma on only portion of?
I absolutely love your blog and find most of your post’s to be exactly I’m looking for. can you offer guest writers to write content for you personally? I wouldn’t mind composing a post or elaborating on many of the subjects you write about here. Again, awesome weblog!
I wanted to thanks for this great study!! I definitely enjoying every single small little bit of it I have you bookmarked to have a look at new stuff you post…
I think other site proprietors should take this site as an model, very clean and magnificent user genial style and design, let alone the content. You’re an expert in this topic!
My brother recommended I would possibly like this web site. He was once entirely right. This submit truly made my day. You can not consider just how a lot time I had spent for this info! Thank you!
Hello, I discovered your weblog in the new directory of blogs. I dont know how your website emerged. Your weblog looks good. Enjoy a nice day.
“I had to refresh the page times to view this page for some reason, however, the information here was worth the wait.”
this article is very full of detail information, and it makes me easy to understand the meaning of your article.
Good blog, I’m going to spend more time learning about this subject
An interesting discussion is definitely worth comment. I do believe that you ought to publish more about this topic, it might not be a taboo subject but generally folks don’t speak about such subjects. To the next! All the best.
I truly appreciate this post. I have been looking everywhere for this! Thank God I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thanks again.
Valuable info. Lucky me I found your web site by accident, and I am shocked why this accident did not happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
Pretty component to content. I just stumbled upon your site and in accession capital to say that I get in fact loved account your weblog posts. Any way I will be subscribing to your augment and even I success you get right of entry to persistently fast.
Great stuff from you, man. Ive scan your stuff before and youre just too fantastic. I love what youve got here, love what youre saying and the way you say it. You make it entertaining and you still manage to keep it smart. I cant wait to scan more from you. This is really a great site.
This writer is truly amazing with the amount of knowledge conveyed, and the in-depth descriptions used in the information. The article written would make a wonderful start for a weekly newsletter posted on the web.
I am curious to find out what blog platform you’re working with? I’m having some small security problems with my latest site and I would like to find something more safe. Do you have any recommendations?
Really instructive and great structure of content material , now that’s user friendly (:.
That content may possibly be the extremely Fixing and repairing stuff have you ever experienced. I can guarantee towards notify all my best others the
This weblog generally seems to obtain a large ammount of visitors. How do you get people to it? It includes a good individual twist on things. I suppose having something authentic or substantial to express is an essential factor.
you employ a fantastic weblog here! do you want to have invite posts on my own blog?
Simply wanna comment on few general things, The website style is perfect, the written content is very wonderful : D.
This site is actually a walk-through its the internet you desired about it and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse here, and you’ll absolutely discover it.
I’m happy! Seriously useful blog post right here my buddie. I just desired to comment & say keep up the excellent work. I’ve bookmarked your site right now and I’ll come back to read more soon my friend! Additionally nice designs on the page layout, it’s genuinely simple for the eye.
I’d must talk with you here. Which isn’t some thing I usually do! I love to reading an article which will make people feel. Also, thank you allowing me to comment!
Do you need to rank higher for your keywords? Do you need more quality backlinks? Is your website under-performin g on the search engines.
i have so many funny bones in myself that is why i would love to be a comedian,.
i always look for laptop reviews on the internet before buying a new one,;
I discovered your blog post web site online and check a few of your early posts. Continue to keep in the great operate. I recently extra increase RSS feed to my MSN News Reader. Seeking toward reading much more from you at a later time!…
If you tow a definite caravan nor van movie trailer your entire family pretty soon get exposed to the down sides towards preventing best securely region. awnings
we have different jewelry boxes at home and most of them comes from my mother who like to collect jewelry boxes;;
Substantially, the post is really the sweetest on that worthw hile topic. I fit in with your conclusions and will thirstily look forward to your next updates. Saying thanks will not just be enough, for the phenomenal clarity in your writing. I will certainly at once grab your rss feed to stay abreast of any kind of updates. Good work and also much success in your business efforts!
The color of your blog is quite great. i would love to have those colors too on my blog.:`-.:
Excellent share it is without doubt. We’ve been awaiting for this information.
This site is disseminating valuable info to people who are most concerned of the following issues being targeted by this site. Many certainly will keep coming back to check out updated posts.
I really love your website.. Very nice colors & theme. Did you build this website yourself? Please reply back as I’m looking to create my own personal website and want to learn where you got this from or just what the theme is named. Thanks!
I am usually to blogging and i really appreciate your posts. Your content has truly peaks my interest. My goal is to bookmark your website and keep checking for first time info.
Oh my goodness! Impressive article dude! Thank you so much, However I am experiencing issues with your RSS. I don’t understand why I can’t subscribe to it. Is there anybody else having the same RSS problems? Anybody who knows the solution can you kindly respond? Thanx!
Nice one for making the effort go over this particular, I think truly about this and consequently true love knowing more to do with that niche. Assuming would-be, any time you attain practical knowledge, would you ideas posting to any site by working with further important information? This is great for everyone.
That is a great tip particularly to those fresh to the blogosphere. Brief but very precise information… Many thanks for sharing this one. A must read post.
There’s definately a lot to learn about this subject. I really like all the points you have made.
lyrica cost canada
Hey! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying
to get my website to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good success.
If you know of any please share. Thanks!
You can read similar text here
hi, thanks!: automated link building
Hi there! I simply would like to offer you a big thumbs up for your great
info you have here on this post. I am returning
to your site for more soon.
Also visit my web-site :: Web Site
flomax medication
You ought to be a part of a contest for one of the finest websites on the net. I will recommend this web site!
You should take part in a contest personally of the highest quality blogs on the internet. I’ll recommend this great site!
I simply wished to thank you so much yet again. I do not know what I would’ve used without the actual strategies provided by you directly on my subject. It was the intimidating setting for me, however , understanding a new expert manner you managed that took me to jump with contentment. I am just grateful for your work and as well , believe you comprehend what a powerful job that you are getting into instructing many others through the use of your websites. I’m certain you’ve never met all of us.
Let me begin by saying nice post. Im not sure if it has been talked concerning, but when using Chrome I will never get the complete site to load while not refreshing over and over. may simply be my laptop. Thanks.
I dont agree with all of the points made but still a good read cheers.
Have you ever considered about adding a little bit more than just your articles? I mean, what you say is valuable and everything. However think of if you added some great images or video clips to give your posts more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with pics and videos, this blog could definitely be one of the best in its niche. Fantastic blog!
You produced some decent points there. I looked on the internet for that issue and located most individuals goes along with along with your internet site.
Some genuinely nice and utilitarian info on this web site , likewise I think the layout has fantastic features.
hi. I observe you are focused on creating backlinks and stuff. I’m selling scrapebox auto approve lists. Do you want to trade ?
You made some tight points there. I looked on the web for the difficulty and found most individuals will approve together with your blog.
Fascinating blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A theme like yours with a few simple adjustements would really make my blog shine. Please let me know where you got your theme. Bless you
Good post. I learn something totally new and challenging on sites I stumbleupon everyday. It’s always interesting to read through content from other writers and practice something from their websites.
diamond engagement rings will be always be the best stuff. it has great style and it is priceless~
The next time I read a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as much as this one. I imply, I know it was my option to learn, however I actually thought youd have something fascinating to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you might repair in case you werent too busy searching for attention.
glucophage canada online
I genuinely enjoy studying on this web site, it has got good articles.
Awesome info over again. I am looking forward for your next post!
I in addition to my buddies happened to be digesting the excellent points located on your web site and then all of the sudden I had an awful feeling I never expressed respect to the site owner for them. All the men were absolutely thrilled to read through them and have now in truth been having fun with them. Thank you for actually being indeed kind and then for obtaining this kind of excellent useful guides most people are really desperate to know about. My honest regret for not expressing appreciation to earlier.
buy zovirax cream online without prescription
I prefer to look on the brighter side of things which I’m sure you can appreciate.
This website certainly has all the info I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
An fascinating discussion will be worth comment. I do believe that you can write regarding this topic, it might become a taboo subject but typically consumers are insufficient to dicuss on such topics. Yet another. Cheers
Perfect piece of work you have done, this site is really cool with fantastic info .
Wow, amazing blog format! How long have you ever been running a blog for? you make running a blog look easy. The overall glance of your web site is wonderful, as smartly the content material!
Perfect work you have done, this website is really cool with excellent information.
You made some decent points there. I seemed on the internet for the problem and found most people will associate with with your website.
I simply desired to thank you so much yet again. I’m not certain what I would’ve handled without the type of advice shared by you directly on this problem. This was an absolute difficult situation in my view, nevertheless being able to see this professional strategy you solved that forced me to cry with happiness. I will be happy for this support and thus believe you know what a powerful job you were carrying out educating the others all through your website. I’m certain you’ve never met all of us.
Hi, Neat post. There is a problem with your site in internet explorer, would test this? IE still is the market leader and a big portion of people will miss your excellent writing due to this problem.
This put up is totaly unrelated to what I used to be looking google for, however it was indexed on the first page. I guess your doing something right if Google likes you adequate to place you at the first page of a non related search.
This is a terrific article. Thanks a lot for taking the time to detail this all out for us. It truly is a great guide!
I adore your blog post.. pleasant colours & style. Did an individual design this web site your self or maybe did you actually hire someone to make it work available for you? Plz respond as I!|m planning to pattern my own website along with would wish to learn in which oughout became that out of. thanks a lot
you’re really a good webmaster. The web site loading speed is incredible. It seems that you are doing any unique trick. Also, The contents are masterpiece. you’ve done a wonderful job on this topic!
diflucan 75 mg
An interesting discussion is worth comment. I think that you should write extra on this topic, it may not be a taboo topic but typically people are not sufficient to speak on such topics. To the next. Cheers
accutane uk
Hi, best wishes to you and your very nice blog,
I like this info shown and it has given me some sort of commitment to succeed for some reason, so thank you.
Thanks for the sensible critique. Me & my neighbor were just preparing to do some research on this. We got a grab a book from our local library but I think I learned more from this post. I’m very glad to see such fantastic info being shared freely out there.
Haller is chauffeured from courtroom to courtroom across Los Angeles by Earl (Lawrence Mason), a former client now offering his services in lieu of legal fees.
It’s really a great and useful piece of info. I am glad that you just shared this useful information with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
I vary with most people the following; I came across this blog post We couldn’t stop until I completed, even although it wasn’t exactly what I used to be trying to find, was still being a good read though. I’ll immediately get a website give food to to remain in touch associated with a revisions.
it is always a good idea to go green because we always want to help the environment“
Have you already setup a fan page on Facebook ?;-`:-
I’d should talk to you here. Which isn’t something It’s my job to do! I quite like reading an article which will make people feel. Also, thanks for permitting me to comment!
Spot on with this write-up, I truly believe that this site needs much more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read through more, thanks for the info.
can i buy doxycycline over the counter
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your site and in accession capital to assert that I get in fact enjoyed account your blog posts. Any way I’ll be subscribing to your augment and even I achievement you access consistently rapidly.
vermox pharmacy
Thanks a lot for sharing this with all of us you actually know what you are talking about! Bookmarked. Please also visit my website =). We could have a link exchange agreement between us!
Doceniam skupienie się na zagrożeniach SEO i potrzebie ich usunięcia.
azithromycin cost in mexico
Hello there, I discovered your online web site by way of Google acquire the best for a related topic, your internet site emerged, it appears fantastic. We have saved it during my google social bookmarks.
Wow! Thank you! I permanently needed to write on my website something like that. Can I implement a portion of your post to my site?
Czuję się dużo lepiej poinformowany o SEO. Dzięki!
Świetny artykuł na temat SEO, który nie jest często poruszany.
Have you ever thought about publishing an e-book or guest authoring on other websites? I have a blog based on the same subjects you discuss and would really like to have you share some stories/information. I know my viewers would value your work. If you are even remotely interested, feel free to shoot me an e mail.
I was able to find good advice from your blog posts.
Cieszę się, że znalazłem ten blog przed rozpoczęciem mojego projektu SEO.
Dzięki za szczegółowy przegląd procedur SEO.
Dzięki za praktyczne porady dotyczące radzenia sobie z SEO.
Ten blog wyjaśnia wiele zawiłości SEO. Dzięki!
Ten post to świetne źródło informacji dla każdego, kto potrzebuje SEO.
Heya i am for the first time here. I found this board and I to
find It truly helpful & it helped me out much. I’m hoping to provide one thing back and help others like you aided me.
my page :: Explainer Video Services India
trimox 500 mg price
Ten blog dostarczył mi dużo jasności na temat SEO. Dzięki!
To przerażające, jak wiele można stracić bez odpowiedniego SEO. Dzięki za te ważne informacje!
albuterol discount
Ten blog to cenne źródło informacji dla każdego, kto myśli o SEO.
Dzięki za szczegółowy przewodnik po SEO. Bardzo pouczający!
Ten post był bardzo pouczający na temat procesu SEO. Dzięki!
Świetny post! Ważne jest, by być świadomym zagrożeń SEO.
buy tadacip
Dziękuję za świetny artykuł na temat SEO! Bardzo pomocne informacje.
Dzięki za praktyczne porady i wskazówki dotyczące SEO.
Czuję się dużo lepiej poinformowany o SEO. Dzięki!
Dziękuję za poruszenie tematu, który często jest pomijany, jakim jest SEO.
SEO to zdecydowanie nie jest projekt typu zrób to sam. Dzięki za ostrzeżenie!
Świetny artykuł! Cieszę się, że są profesjonaliści, którzy mogą pomóc w SEO.
Dzięki za kompleksowy przewodnik po SEO. Bardzo pouczający!
Bardzo przydatne informacje dla każdego, kto martwi się o SEO swojej strony.
Dzięki za świetne porady na temat SEO. Bezpieczeństwo jest kluczowe!
Wow I just adore her! She is so beautiful plus a really good actress. I don’t think the show V is all that good, none the less I watch it anyway just so I can see her. And I don’t know if you’ve ever seen her do an interview but she is also rather comical and its all so natural for her. I personally never even heard of her before The V, now I’ll watch anything she’s on.
An impressive share, I just given this onto a colleague who was doing a little bit evaluation on this. And he in reality ordered me breakfast due to the fact I discovered it for him.. smile. Consequently allow me alter that: Thanks for the deal with! Having said that yeah thanks for spending the time to chat about this, I really feel strongly about it and adore reading additional on this topic. If possible, as you turn into expertise, would you mind updating your weblog with additional details? It?s quite useful for me. Giant thumb up for this internet page publish!
The when Someone said a weblog, Lets hope which it doesnt disappoint me up to this. After all, I know it was my solution to read, but I just thought youd have something interesting to convey. All I hear is usually a couple of whining about something you could fix if you werent too busy in search of attention.
An advanced person you’ll want the latest muscle process. If you place proper arrangement, mature should people because of your self-worth business women will probably truly feel concerned through your hot design. Even when a lot of men desirable for getting sort of entire physique the majority of commonly are not ready to can do some of those disturbing routines been required to grow their muscle. Form grownup men is actually vastly happy to will be aware that now they can offer muscle groups through the process of sipping on a marvelous items referred to Hugely Strength Builders.
very nice post, i surely really like this fabulous website, keep on it
I and also my buddies were found to be reviewing the excellent tips and tricks on your site and so suddenly I got an awful suspicion I never expressed respect to the web site owner for those tips. All the young boys were as a consequence excited to study all of them and have absolutely been taking advantage of them. We appreciate you getting so helpful and then for figuring out these kinds of ideal subject matter millions of individuals are really eager to discover. Our own sincere apologies for not saying thanks to you sooner.
“Xanax (Alprazolam) is used to treat anxiety disorders and panic attacks. Alprazolam is in a class of “
i support herbal products because they are all natural and from what i know, they do not carry nasty side effects;;
Helpful post and great sharing. A couple of things in here I haven’t thought about before, I would like to take this moment to say that I really like your blog. It has been a fantastic resource of information for me. Thank you so much!
I’ve recently started a site, and the information you offer on this website has helped me a lot. Thank you for all of your time & work.
I must point out my appreciation for your generosity supporting women who absolutely need help with this question. Your special commitment to passing the solution throughout was remarkably functional and has continually helped associates just like me to attain their ambitions. Your amazing warm and helpful suggestions signifies this much to me and especially to my colleagues. Best wishes; from everyone of us.
Wow! This could be one particular of the most beneficial blogs We have ever arrive across on this subject. Basically Wonderful. I’m also a specialist in this topic so I can understand your effort.
I adore your wp design, wherever did you download it through?
What I find troublesome is to discover a weblog that may seize me for a minute however your weblog is different. Bravo.
Hey,I quite like looking at the post submit, I needed to write a bit remark to aid you and desire that you simply excellent continuationAll the best for the writing a blog endeavours.
I don’t usually comment but I gotta tell appreciate it for the post on this amazing one : D.
I can’t imagine focusing long enough to research; much less write this kind of article. You’ve outdone yourself with this material. This is great content.
Oh my goodness! a tremendous article dude. Thank you Nonetheless I’m experiencing challenge with ur rss . Don’t know why Unable to subscribe to it. Is there anyone getting identical rss problem? Anyone who knows kindly respond. Thnkx
ciprofloxacin 500 mg prescription
“I’m a newbie and your accomplishment is quite a lot an inspiration for me”
I am not very great with English but I find this very leisurely to translate.
Hey there, You’ve done an incredible job. I will certainly digg it and personally suggest to my friends. I am confident they will be benefited from this site.
glass dining tables will always be the best design and option that i would choose for our dining room.
Good day, Could I export your image and utilize it on my own website?
How do I start to learn how to Hip Hop dance?
I loved as much as you’ll obtain performed right here. The caricature is attractive, your authored material stylish. however, you command get got an impatience over that you wish be turning in the following. ill surely come further formerly once more since precisely the similar nearly a lot frequently within case you protect this increase.
well of course, everyone loves to get rich but not everyone would love to do hard work,.
Heya i’m for the first time here. I came across this board and I in finding It truly useful & it helped me out much. I’m hoping to give one thing back and help others such as you aided me.
There may be noticeably a bundle to find out about this. I assume you made sure good factors in options also.
I just could not depart your web site prior to suggesting that I actually enjoyed the standard information a person provide for your visitors? Is going to be back often in order to check up on new posts
Hello, I discovered your weblog in the new directory of blogs. I will not understand how your weblog came up, must have been a typo, Your weblog looks excellent. Have a nice day
Hello my friend! I want to say that this post is amazing, great written and include almost all important infos. I?d like to look more posts like this .
Thanks so much for sharing this great info! I am looking forward to see more posts!
Hey There. I found your blog using msn. This is a very well written article. I will be sure to bookmark it and return to read more of your useful information. Thanks for the post. I will certainly return.
Wow, amazing blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The overall look of your site is fantastic, as well as the content!
You can also put a chatbox on your blog for more interactivity among readers.*.,”,
Very well said, your blog says it all about that particular topic.*~”*~
Any INTERNAL REVENUE SERVICE will never give attention with any specific extreme taxation expenses, in order that you are really taking that with the dirt bike pants by simply not necessarily altering your own tax burden monthly payments.
disco lights with built-in laser x-y scanner are the coolest stuff that you can add to your disco room;
As soon as I detected this website I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.
Aw, i thought this was a very good post. In thought I must set up writing like that additionally – taking time and actual effort to generate a excellent article… but so what can I say… I procrastinate alot and also by no means often get something carried out.
you’re in reality a just right webmaster. The website loading velocity is incredible. It kind of feels that you are doing any distinctive trick. In addition, The contents are masterwork. you have performed a great job in this subject!
I would like to add that when you do not already have got an insurance policy or else you do not belong to any group insurance, you could well reap the benefits of seeking the aid of a health insurance agent. Self-employed or people with medical conditions ordinarily seek the help of any health insurance agent. Thanks for your article.
An intriguing discussion will probably be worth comment. I think that you simply write much more about this topic, it might become a taboo subject but generally consumers are inadequate to communicate in on such topics. To another. Cheers
I believe that youtube is a great tool for anyone interested in watching or uploading videos. I have been using the site for years now, and still think it is doing a good job!
Hey there! Would you mind if I share your blog with my twitter group? There’s a lot of folks that I think would really enjoy your content. Please let me know. Thanks
I’m a blog crazed person and i love to read cool blog like yours…;*:
Bloghopping is really my forte and i like to visit blogs”
Kudos for the great piece of writing. I am glad I have taken the time to read this.
The when I read a weblog, I’m hoping which it doesnt disappoint me about this. Come on, man, Yes, it was my choice to read, but I personally thought youd have something fascinating to say. All I hear is actually a handful of whining about something that you could fix when you werent too busy trying to find attention.
This is a great blog” and i want to visit this every day of the week “
Nice blog, just looking around some blogs, seems a pretty nice platform you are using. I’m currently using WordPress for a few of my sites but looking to change one of them over to a platform similar to yours as a trial run. Anything in particular you would recommend about it?
Oh my goodness! an amazing article dude. Thanks a ton However I will be experiencing problem with ur rss . Do not know why Can not join it. Will there be any person getting identical rss dilemma? Anyone who knows kindly respond. Thnkx
I have been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this blog. Thanks , I’ll try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your site?
This web site is usually a walk-through it really is the knowledge you desired about this and didn’t know who to inquire about. Glimpse here, and you’ll undoubtedly discover it.
Thanks for sharing this excellent write-up. Very interesting ideas! (as always, btw)
Perfectly pent articles , Really enjoyed reading through .
using wooden wall decors at home is a great alternative to using those expensive metal wall decors;
Some times its a pain in the ass to read what website owners wrote but this site is very user friendly!
zithromax uk
Aw, i thought this was a really nice post. In concept I have to devote writing such as this moreover – spending time and actual effort to produce a really good article… but so what can I say… I procrastinate alot and also by no means often go done.
There is noticeably a lot of money to know about this. I suppose you have made specific nice points in features also.
What would be your next topic next week on your blog.”“:’
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you make this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz answer back as I’m looking to design my own blog and would like to know where u got this from. thanks a lot
Hello! I merely would choose to give you a large thumbs up for any excellent information you have here during this post. I’ll be returning to your blog site to get more detailed soon.
So is the green tea i buy in cans the same as the regular tea you’d buy to put in your morning cup? I’ve been told is just normal green tea made to be cooler, but does it have any affect as far as not speeding up your metabolism as fast as normal hot green tea?
Wow! This could be one particular of the most helpful blogs We’ve ever arrive across on this subject. Basically Magnificent. I’m also an expert in this topic so I can understand your hard work.
Hi, I just found your website via Bing. Your article is truly applicable to my life right now, and I’m really delighted I found your website.
It’s rare knowledgeable men and women on this topic, and you seem like what happens you’re discussing! Thanks
Hi, thanks for the very good report. Honestly, just about eight weeks ago I started using the internet and became an web user and came on-line for the very first time, and there is always a lot poor quality information out there. I recognize that you have put out wonderful material that is distinct and on the subject. All the best and cheers for the awesome ideas.
hey there i stumbled upon your website searching around the web. I wanted to say I like the look of things around here. Keep it up will bookmark for sure.
accutane online pharmacy uk
Superb read, I just passed this onto a colleague who was doing a little investigation on that. And he actually bought me lunch because I located it for him smile So let me rephrase that: Thanks for lunch!
I truly appreciate this post. I’ve been looking all over for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thank you again!
I’m having a small problem. I’m unable to subscribe to your rss feed for some reason. I’m using google reader by the way.
It is rather grateful for the help in this question, can, I too can help you something?
Yes a ton of sod in the back of a hot wheels tonka truck will break the axel-happy you’ve all learned s/t for the day but can u please drive|ShrakeCulture|
The vacation special deals offered are believed as a selection of possibly the most preferred and therefore within your budget all over the globe. Quite a number of hostels can be proudly located inside property which is accented who has striking seashores encouraging crystal-clear rivers, contingency of an Ocean. hotels compare rates
well of course, everyone loves to get rich but not everyone would love to do hard work,.
I’m not positive the place you are getting your information, but great topic. I needs to spend a while finding out much more or understanding more. Thank you for excellent information I was looking for this information for my mission.
You have observed very interesting details ! ps decent internet site .
에볼루션 드림캐쳐
flomax 0.4
tretinoin cheapest price
accutane online order
An impressive share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a coworker who has been conducting a little homework on this. And he actually ordered me breakfast because I stumbled upon it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending time to talk about this matter here on your web site.
best price for generic propecia
buy augmentin 1000 mg
vermox otc canada
accutane 30 mg price
Very good post! We will be linking to this particularly great content on our website. Keep up the great writing.
buy modafinil no prescription
I love reading through an article that will make men and women think. Also, many thanks for permitting me to comment.
buy retin a 1 online
Aw, this was an extremely nice post. Taking the time and actual effort to produce a very good article… but what can I say… I put things off a lot and don’t manage to get anything done.
doxycycline 20 mg cost
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon every day. It’s always interesting to read content from other authors and use a little something from other web sites.
can i buy dexamethasone over the counter
I absolutely love your website.. Great colors & theme. Did you develop this amazing site yourself? Please reply back as I’m looking to create my own site and would love to learn where you got this from or what the theme is called. Cheers!
diflucan tabs
You’ve tackled a complex issue with clarity.버팀목 대출
Can’t wait to read more from you on this subject!무직자 3108만원 대출
medication furosemide 20 mg
You’ve articulated something I’ve felt for a while.프라그마틱 슬롯 추천
buy diflucan 150mg
doxycycline 20 mg
You’re so interesting! I don’t suppose I have read something like this before. So wonderful to find somebody with some genuine thoughts on this subject. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This web site is one thing that is required on the web, someone with some originality.
I’m very happy to uncover this website. I want to to thank you for ones time for this fantastic read!! I definitely appreciated every part of it and i also have you saved to fav to look at new stuff on your web site.
I delight in the data on your websites. Kudos!
Feel free to visit my blog post reasonable affordable seo packages (https://Youtube.com/watch?v=RzmNEfabFng)
lesbian porn
buy cheap accutane
Hi there, There’s no doubt that your web site might be having internet browser compatibility problems. Whenever I take a look at your site in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in IE, it’s got some overlapping issues. I simply wanted to give you a quick heads up! Aside from that, fantastic website.
Excellent article. I am going through some of these issues as well..
Aw, this was a really good post. Finding the time and actual effort to generate a great article… but what can I say… I hesitate a lot and never manage to get anything done.
Way cool! Some extremely valid points! I appreciate you writing this article plus the rest of the website is very good.
lyrica medication
porn
You are able to capture several well guided adventures with assorted chauffeur driven car support. Many include important loan packages and some people is going to take someone for their depend toward the mortgage place, or a trip to upstate New York. baltimore limousine rental
I’m impressed, I have to admit. Seldom do I come across a blog that’s both educative and interesting, and let me tell you, you have hit the nail on the head. The issue is something not enough men and women are speaking intelligently about. I’m very happy that I found this in my search for something concerning this.
Lebron James Is A Clown You Know White Face Paint Red Nose Floppy Shoes Type Shit|_PeaceLuvMusic|
I’d should check with you here. Which is not something I usually do! I take pleasure in studying a publish that may make people think. Also, thanks for permitting me to remark!
It’s nearly impossible to find experienced people for this topic, however, you seem like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
This is pretty attention-grabbing , i was trying for something but found your site as an alternative via Google . I feel affection for networking. Anyways, just wanted in the direction of drop through and speak hi . i have subscribed in the direction of your site plus i am already in the market onward to the updates , Thanks…
r Light sensing of moving objects – SActual object Light Visual objectr -cosine (wt) + i sine (wt) S = r [cosine (wt) + i sine (wt)]Newton Keplers time visual effects Time dependent NewtonParticle Visual effects Wave
hzqkzvxzwumileavmikx, Do i need hcg if i take nolvadex, TLiBRju.
homosexual porn
Hmm is anyone else encountering problems with the pictures on this blog loading? I’m trying to figure out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any responses would be greatly appreciated.
There a few interesting points in time in this article but I do not determine if I see these people center to heart. There exists some validity but I will take hold opinion until I consider it further. Great article , thanks and that we want far more! Added onto FeedBurner too
viagra 88
Everyone loves it when folks come together and share thoughts. Great website, continue the good work.
I impressed, I need to say. Really not often do I encounter a blog that each educative and entertaining, and let me tell you, you have hit the nail on the head. Your concept is outstanding; the problem is something that not sufficient persons are speaking intelligently about. I’m very comfortable that I stumbled across this in my seek for one thing referring to this.
Wow that was unusual. I just wrote an really long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t appear. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Regardless, just wanted to say great blog! Miss feather hair pieces
This will be the right blog for everyone who is really wants to check out this topic. You are aware of so much its almost challenging to argue along with you (not that I personally would want…HaHa). You definitely put a fresh spin on a topic thats been revealed for years. Great stuff, just great!
Considerably, the submit is really the finest on this worthy topic. I agree along with your findings and in addition can thirstily look forward to Your own long term updates. Simply just saying many thanks will not merely you need to be enough, for that fantastic clarity inside your writing. I will straight away grab your rss to remain up-to-date with any kind of improvements. Genuine perform and also a lot success inside your company dealings!
That is a very good tip especially to those new to the blogosphere. Short but very precise information… Thanks for sharing this one. A must read post.
purchase amoxil
Everything is very open with a precise explanation of the challenges. It was really informative. Your website is very useful. Many thanks for sharing.
After looking at a handful of the blog posts on your web site, I really appreciate your way of writing a blog. I added it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Please check out my web site too and let me know how you feel.
slot
An impressive share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a co-worker who had been conducting a little homework on this. And he in fact bought me breakfast because I found it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending some time to discuss this subject here on your web site.
Excellent web site you’ve got here.. It’s difficult to find high-quality writing like yours nowadays. I seriously appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
It’s hard to come by experienced people on this subject, but you seem like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
lesbian porn
Howdy! I just would like to give you a big thumbs up for your excellent information you have here on this post. I’ll be coming back to your blog for more soon.
lasix over the counter canada
https://artdaily.com/news/171650/Mp3Juice-Review–The-Pros-and-Cons-You-Need-to-Know
synthroid cheap price
Hi, I do think this is an excellent blog. I stumbledupon it 😉 I’m going to revisit once again since i have saved as a favorite it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to help other people.
Everything is very open with a really clear clarification of the issues. It was really informative. Your website is very helpful. Thanks for sharing.
homosexual porn
I was able to find good advice from your blog posts.
I was able to find good info from your content.
over the counter toradol
gay porn
Everything is very open with a very clear explanation of the issues. It was truly informative. Your site is extremely helpful. Thanks for sharing!
Having read this I thought it was extremely enlightening. I appreciate you spending some time and effort to put this article together. I once again find myself spending a lot of time both reading and commenting. But so what, it was still worth it!
retin a canada pharmacy
where to buy sildalis
Oh my goodness! Impressive article dude! Thank you so much, However I am having issues with your RSS. I don’t know why I am unable to join it. Is there anyone else having identical RSS problems? Anyone who knows the solution can you kindly respond? Thanx!
homosexual porn
Very good blog post. I certainly love this site. Keep writing!
porn
Very good article! We will be linking to this particularly great content on our website. Keep up the good writing.
Good day! I could have sworn I’ve been to this web site before but after browsing through many of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely delighted I came across it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back often.
homosexual porn
I blog frequently and I genuinely appreciate your information. This great article has truly peaked my interest. I am going to book mark your site and keep checking for new information about once a week. I subscribed to your Feed as well.
I was extremely pleased to discover this site. I wanted to thank you for your time for this fantastic read!! I definitely liked every little bit of it and I have you book marked to check out new information on your web site.
casino
Very good write-up. I absolutely love this website. Keep writing!
baclofen 332
I was very pleased to uncover this web site. I wanted to thank you for your time just for this fantastic read!! I definitely really liked every little bit of it and I have you book marked to check out new information in your site.
Nice post. I learn something new and challenging on sites I stumbleupon everyday. It will always be helpful to read through content from other authors and use something from other websites.
cost of accutane canada
Pretty! This was a really wonderful article. Thanks for providing this info.
Excellent post! We are linking to this particularly great content on our site. Keep up the good writing.
Right here is the perfect web site for anyone who wishes to understand this topic. You realize a whole lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I personally would want to…HaHa). You definitely put a brand new spin on a subject that has been written about for many years. Excellent stuff, just great.
buy tretinoin without prescription
Having read this I thought it was very informative. I appreciate you finding the time and effort to put this content together. I once again find myself personally spending way too much time both reading and leaving comments. But so what, it was still worth it.
casino
Pretty! This has been an incredibly wonderful post. Many thanks for supplying these details.
I couldn’t resist commenting. Exceptionally well written!
This is a topic that is close to my heart… Cheers! Exactly where can I find the contact details for questions?
Everything is very open with a precise clarification of the challenges. It was truly informative. Your site is useful. Thanks for sharing!
gay porn
Good info. Lucky me I came across your blog by accident (stumbleupon). I have saved as a favorite for later.
That is a really good tip particularly to those fresh to the blogosphere. Short but very precise info… Many thanks for sharing this one. A must read post.
lesbian porn
Your style is unique in comparison to other people I’ve read stuff from. I appreciate you for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I will just book mark this page.
An impressive share! I have just forwarded this onto a co-worker who has been conducting a little homework on this. And he in fact bought me breakfast due to the fact that I discovered it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending some time to talk about this matter here on your web site.
I enjoy looking through an article that will make men and women think. Also, thanks for allowing for me to comment.
Your writing style is so engaging and clear.구글상위노출 업체
toradol pain shot
not safe
I blog frequently and I truly thank you for your information. Your article has really peaked my interest. I will bookmark your website and keep checking for new details about once per week. I opted in for your RSS feed too.
Your insights really add depth to this topic.구글상위노출
Your style is very unique in comparison to other folks I’ve read stuff from. I appreciate you for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I’ll just book mark this site.
hacklink
Everyone loves it when folks come together and share views. Great blog, stick with it.
It’s nearly impossible to find knowledgeable people on this subject, but you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
online casino
Next time I read a blog, Hopefully it doesn’t disappoint me just as much as this particular one. After all, Yes, it was my choice to read, however I actually thought you would have something interesting to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of crying about something that you could fix if you were not too busy searching for attention.
vermox 500mg online
Hello there! I just want to give you a big thumbs up for the great info you have got here on this post. I am returning to your web site for more soon.
online casino
Having read this I thought it was very informative. I appreciate you taking the time and effort to put this informative article together. I once again find myself personally spending a significant amount of time both reading and leaving comments. But so what, it was still worthwhile!
Pretty! This has been an incredibly wonderful post. Many thanks for supplying this information.
An impressive share! I have just forwarded this onto a friend who has been doing a little research on this. And he actually ordered me breakfast due to the fact that I discovered it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending the time to talk about this matter here on your web page.
homosexual porn
May I just say what a relief to discover a person that really understands what they’re discussing on the internet. You definitely know how to bring a problem to light and make it important. More people must check this out and understand this side of your story. I was surprised you’re not more popular given that you most certainly possess the gift.
Saved as a favorite, I love your web site!
Aw, this was a very nice post. Taking a few minutes and actual effort to make a great article… but what can I say… I put things off a lot and don’t seem to get anything done.
Great info. Lucky me I found your website by chance (stumbleupon). I have bookmarked it for later!
flomax medicine
This blog was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve found something that helped me. Thank you!
bookmarked!!, I really like your site!
online slot
This website truly has all of the information and facts I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Hello there, I do think your blog might be having web browser compatibility problems. When I take a look at your blog in Safari, it looks fine however, if opening in Internet Explorer, it’s got some overlapping issues. I simply wanted to provide you with a quick heads up! Apart from that, fantastic blog!
Hi, I do believe this is a great site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I am going to return yet again since I saved as a favorite it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide other people.
untrustable
Having read this I thought it was very enlightening. I appreciate you finding the time and effort to put this information together. I once again find myself personally spending a significant amount of time both reading and leaving comments. But so what, it was still worthwhile!
sale clomid
porn
You made some decent points there. I looked on the web to learn more about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this web site.
Nice post. I learn something new and challenging on sites I stumbleupon every day. It will always be exciting to read articles from other authors and practice something from other web sites.
After looking into a few of the blog posts on your blog, I really appreciate your way of blogging. I saved it to my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back soon. Please check out my web site too and let me know what you think.
Good info. Lucky me I found your website by chance (stumbleupon). I have bookmarked it for later.
Spot on with this write-up, I seriously think this site needs a great deal more attention. I’ll probably be back again to see more, thanks for the advice!
porn cannibalism
online casino
Having read this I thought it was extremely informative. I appreciate you finding the time and energy to put this information together. I once again find myself personally spending a significant amount of time both reading and commenting. But so what, it was still worth it!
hacklink
Having read this I believed it was really enlightening. I appreciate you finding the time and effort to put this informative article together. I once again find myself personally spending a significant amount of time both reading and posting comments. But so what, it was still worthwhile.
Hey there! I simply wish to offer you a big thumbs up for your excellent information you have here on this post. I’ll be coming back to your web site for more soon.
Everything is very open with a really clear clarification of the challenges. It was definitely informative. Your site is extremely helpful. Thank you for sharing!
I used to be able to find good info from your blog posts.
furosemide tab 80mg
Great blog you’ve got here.. It’s hard to find high quality writing like yours nowadays. I seriously appreciate people like you! Take care!!
porn
Very good post. I’m going through a few of these issues as well..
Very good info. Lucky me I came across your website by accident (stumbleupon). I’ve book marked it for later.
advair diskus generic
When I originally commented I appear to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now every time a comment is added I get four emails with the exact same comment. There has to be a means you are able to remove me from that service? Kudos.
diflucan over the counter no prescription
online slot
propecia online australia
dexamethasone 40 mg tablets
homosexual porn
Hello there! This article couldn’t be written much better! Going through this article reminds me of my previous roommate! He always kept talking about this. I most certainly will send this information to him. Pretty sure he’ll have a great read. Many thanks for sharing!
I was recommended this web website by my cousin. I’m not sure whether this post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my difficulty.
buy buy accutane online
I believe this web site contains very superb composed articles posts .
slot
Intimately, the post is actually the sweetest on that worthw hile topic. I harmonise with your conclusions and also will certainly eagerly look forward to your incoming updates. Saying thanks will certainly not simply be enough, for the extraordinary clarity in your writing. I can perfect away grab your rss feed to stay informed of any kind of updates. Solid work and also much success in your business dealings!
*Spot on with this write-up, I truly think this website needs much more consideration. I’ll probably be again to read much more, thanks for that info.
Some truly nice stuff on this website , I like it.
Aw, this became an incredibly nice post. In concept I would like to put in writing similar to this moreover – taking time and actual effort to generate a very good article… but what can I say… I procrastinate alot and also by no indicates find a way to get something completed.
This constantly amazes me exactly how blog owners for example yourself can find the time and also the commitment to keep on composing fantastic blog posts. Your site isexcellent and one of my own ought to read blogs. I simply want to thank you.
Many thanks for spending some time to write about this, I really feel clearly about it and I really like to researching far more about this concern. Whenever possible, would you mind updating your weblog with a lot more info? It’s very useful for me.
where to order modafinil
buy bactrim ds
Your blog never ceases to amaze me, it is very well written and organized.*-.:;
porn cannibalism
I truly appreciated this wonderful blog. Make sure you keep up the good work. All the best !!!!
Hi” your blog is full of comments and it is very active.
homosexual porn
Now i’m encountering a fresh short problems Once i can’t look like allowed to sign up for the particular give food to, Now i’m utilizing search engines like google audience.
Hi there! This is kind of off topic but I need some advice from an established blog. Is it very hard to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty quick. I’m thinking about setting up my own but I’m not sure where to start. Do you have any points or suggestions? Thank you
There is noticeably big money to comprehend this. I assume you’ve made specific nice points in features also.
Some really select articles on this internet site , bookmarked .
well, outsourcing can actually save any company several million dollars because of cheap labor..
lgbt porn
Glad to be one of several visitors on this awesome internet site .
This excellent website certainly has all the info I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
very good post, i undoubtedly really like this amazing site, go on it
Hi, I do believe this is an excellent site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I am going to come back once again since I saved as a favorite it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide other people.
i have a passion on anything that is automotive related. i love to attend car shows too.
This excellent article seems to be have considerable website visitors. Exactly how support it? It all provides cool extraordinary take on the subject of problems. My partner and i possessing items legitimate or perhaps a great offer specifics of is central to the item.
I like it whenever people come together and share opinions. Great site, keep it up!
After exploring a number of the blog posts on your blog, I really like your way of writing a blog. I bookmarked it to my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back in the near future. Please check out my web site as well and let me know how you feel.
Hello there! I simply would like to offer you a huge thumbs up for your excellent info you have got here on this post. I will be returning to your web site for more soon.
Hi. Thank you for making this site . I m working on betting online niche and have found this site using search on bing . Will be sure to look more of your content . Gracias , see ya. :S
well, earning money is a bit tricky and hard sometimes. you really got to be very creative if you want to earn more::
When I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new surveys are added- checkbox and already whenever a comment is added I am four emails sticking with the same comment. Can there be any way you are able to eliminate me from that service? Thanks!
incest porn
https://blake0z10siz9.mdkblog.com/profile
Many thanks! This is an outstanding web site!
I don’t even understand how I finished up right here, but I thought this publish was good. I don’t know who you are but certainly you’re going to a well-known blogger if you are not already Cheers!
flomax 2mg
I love your blog site.. great colorings & style. Did a person style and design this fabulous website you as well as have you actually hire an attorney to make it work to suit your needs? Plz respond as I!|m looking to layout my own, personal weblog in addition to would wish to understand in which ough bought the following via. appreciate it
where can i get zovirax cream
HURRAY! can’t balladeer. by virtue of himself by what name highly.
The gods do nothing until they’ve blinded the minds of the wicked.
I do agree with all of the ideas you have presented in your post. They’re very convincing and will certainly work. Still, the posts are too short for starters. Could you please extend them a little from next time? Thanks for the post.
diflucan buy online
My friend sent me here and I thought I’d say hi, great blog.
online slot
Hello. Great job. I did not anticipate this. This is a splendid articles. Thanks!
We still cannot quite believe that I should often be a kind of checking important points seen on your webblog. Our family and i also are sincerely thankful with regards to your generosity too as for giving me possibility pursue our chosen profession path. Wanted you important information I purchased within your web-site.
Hi” best wishes to you and your very nice blog”
I found your blog site on google and examine a number of of your early posts. Proceed to keep up the very good operate. I just further up your RSS feed to my MSN Information Reader. Looking for forward to reading extra from you in a while!…
form of gotten in a rut. I think what you have mentioned here along with the taking of my force factor will assist me review all my possibilities and
Its like you read my mind! You seem to know so much about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you can do with some pics to drive the message home a bit, but instead of that, this is magnificent blog. An excellent read. I will certainly be back. empire blue cross blueshields
I can’t really help but admire your blog, your blog is so adorable and nice .
The subsequent time I learn a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as a lot as this one. I imply, I do know it was my option to read, however I actually thought youd have one thing fascinating to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about one thing that you could fix when you werent too busy in search of attention.
Just article, We liked its style and content. I discovered this blog on Yahoo and also have now additional it to my personal bookmarks. I’ll be certain to visit once again quickly.
Hands down, Apple’s app store wins by a mile. It’s a huge selection of all sorts of apps vs a rather sad selection of a handful for Zune. Microsoft has plans, especially in the realm of games, but I’m not sure I’d want to bet on the future if this aspect is important to you. The iPod is a much better choice in that case.
Its amazing what supplementing can do for your body and your weight lifting goals!
While there are a few currencies that will move one directly behind the other, the other currency sets can move in distinctive bearings frequently bringing about a more intricate energy.
You’ve made some decent points there. I checked on the internet to find out more about the issue and found most individuals will go along with your views on this web site.
When I initially commented I seem to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now every time a comment is added I get four emails with the exact same comment. Is there a way you can remove me from that service? Appreciate it.
bookmarked!!, I love your website.
An outstanding share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a colleague who has been conducting a little homework on this. And he actually ordered me breakfast due to the fact that I stumbled upon it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending the time to discuss this topic here on your blog.
I was very happy to find this web site. I wanted to thank you for your time just for this fantastic read!! I definitely enjoyed every little bit of it and i also have you book marked to check out new things on your website.
Simply wanna admit that this is very useful, Thanks for taking your time to write this.
baclofen otc
Giving you the best News is very much imptortant to us.
Im no expert, but I consider you just made the best point. You naturally know what youre speaking about, and I can really get behind that. Thanks for being so upfront and so sincere.
porn
Nice post. I learn something on different blogs everyday. It can all the time be stimulating to read content from other writers and observe somewhat something from their blog.
I was able to find good info from your blog articles.
This web site truly has all the info I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Many thanks for this kind of facts I had been hunting all Search engines to find it!
Saved as a favorite, I love your blog.
You lost me, friend. I am talking about, I imagine I purchase what youre saying. I’m sure what you’re saying, nevertheless, you just appear to have forgotten that you will find a few other folks from the world who view this trouble for it is really and could perhaps not agree with you. You could be turning away many people that was lovers of the website.
After going over a few of the articles on your web site, I truly like your way of writing a blog. I book-marked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Please check out my web site as well and let me know what you think.
I have read a few good stuff here. Definitely price bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how a lot effort you put to create such a great informative website.
PBS and Prof. Ferguson Great Work! Thanks for helping me understand what went wrong and how we got here.
homosexual porn
I like it when individuals come together and share views. Great site, stick with it.
I was on Twitter looking for Neiko Automotive Tools when I found a link to this blog, happy I stopped by – Cheers
gay porn
I’d must verify with you here. Which is not something I usually do! I enjoy reading a submit that may make folks think. Additionally, thanks for allowing me to comment!
porn
Aw, i thought this was a really nice post. In concept I must place in writing such as this additionally – taking time and actual effort to make a great article… but what things can I say… I procrastinate alot and also by no indicates seem to go carried out.
Simply desire to say your article is as amazing. The clarity in your post is simply excellent and i could assume you are an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission allow me to grab your feed to keep updated with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please keep up the gratifying work.
diflucan online uk
I was extremely pleased to uncover this site. I wanted to thank you for your time just for this fantastic read!! I definitely appreciated every bit of it and i also have you saved to fav to check out new things on your blog.
Wholesale Cheap Handbags Will you be ok merely repost this on my site? I’ve to allow credit where it can be due. Have got a great day!
Hi, I do think this is a great web site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I am going to come back once again since I bookmarked it. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and continue to help other people.
casino
This is very fascinating, You’re an excessively skilled blogger. I have joined your feed and sit up for looking for more of your fantastic post. Also, I’ve shared your web site in my social networks!
This web site is usually a walk-through its the data you wished concerning this and didn’t know who ought to. Glimpse here, and you’ll definitely discover it.
you can always buy sports apparels online, you just need to choose your supplier carefully”
I used to be able to find good information from your content.
i can say that George Michael is nice guy, he is really a very talented guy**
Increase this valuable because when a lot of people machinery are used world-wide and can add a number of them proof using its whole world may ailments specifically a result of the company at the twenty first a single. dc free mommy blog giveaways family trip home gardening house power wash baby laundry detergent
How is it that just anyone can write a weblog and get as popular as this? Its not like youve said anything incredibly impressive more like youve painted a quite picture above an issue that you know nothing about! I dont want to sound mean, here. But do you actually think that you can get away with adding some quite pictures and not seriously say something?
i don’t like razors so i always use hair clippers to cut my hair.,
Excellent blog you have here.. It’s hard to find excellent writing like yours nowadays. I really appreciate people like you! Take care!!
Hmm it appears like your website ate my first comment (it was super long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I submitted and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog. I as well am an aspiring blog writer but I’m still new to the whole thing. Do you have any recommendations for newbie blog writers? I’d really appreciate it.
After exploring a handful of the articles on your website, I really like your technique of writing a blog. I added it to my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back in the near future. Please check out my website as well and let me know what you think.
I’m impressed, I have to admit. Truly rarely must i encounter a blog that’s both educative and entertaining, and without a doubt, you may have hit the nail to the head. Your thought is outstanding; the pain is something that insufficient people are speaking intelligently about. We’re delighted which i found this at my look for something in regards to this.
You’re so interesting! I don’t suppose I’ve truly read anything like that before. So good to discover somebody with some unique thoughts on this subject. Seriously.. thanks for starting this up. This web site is one thing that’s needed on the internet, someone with a bit of originality.
french translation is kind of hard at first but if you get used to it, then it is easy’
can you buy amoxicillin uk
You have a gift for words I will give you that. If only I had the same gift
Having read this I thought it was really enlightening. I appreciate you taking the time and effort to put this short article together. I once again find myself personally spending a lot of time both reading and posting comments. But so what, it was still worthwhile.
lesbian porn
Great web site. A lot of helpful info here. I am sending it to a few friends ans also sharing in delicious. And naturally, thank you to your effort! Pristina Hotels
Pretty! This has been an extremely wonderful post. Thanks for supplying this information.
Jason Derulo is currently at the peak of the United kingdom singles chart for the second week with his latest track Don’t Wanna Go Home. The U . s . artist is certainly fending off tough competition
The thing i like about your blog is that you always post direct to the point info.~,*.”
An interesting discussion is worth comment. I do believe that you ought to publish more on this topic, it might not be a taboo subject but generally people don’t discuss such issues. To the next! Many thanks!
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you design this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz answer back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to find out where u got this from. many thanks
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve visited this website before but after browsing through some of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Nonetheless, I’m certainly happy I stumbled upon it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back frequently!
You’re so cool! I don’t believe I’ve read through something like this before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this subject matter. Really.. many thanks for starting this up. This site is one thing that is needed on the internet, someone with some originality.
Congratulations on having one of the most sophisticated blogs Ive come across in some time! Its just incredible how much you can take away from something simply because of how visually beautiful it is. Youve put together a great blog space –great graphics, videos, layout. This is definitely a must-see blog.
I and my buddies came taking note of the nice advice found on your web blog and then suddenly developed an awful suspicion I never expressed respect to you for those techniques. The men were happy to learn them and have in effect actually been having fun with those things. We appreciate you really being really thoughtful and then for making a choice on variety of magnificent tips millions of individuals are really desirous to know about. Our own sincere apologies for not saying thanks to you sooner.
Spot lets start work on this write-up, I seriously think this excellent website needs far more consideration. I’ll likely to end up again to learn a lot more, many thanks for that information.
slot
Money For College Scholarships for Minorities… […]right here are a few url links to sites I always connect to for the fact we feel they’re well worth browsing[…]…
You’re so cool! I do not think I’ve truly read anything like this before. So nice to discover another person with a few genuine thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is required on the web, someone with a bit of originality.
You have made some good points there. I looked on the net for additional information about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this web site.
You’re so cool! I don’t think I’ve read through anything like that before. So great to discover another person with some original thoughts on this topic. Seriously.. thanks for starting this up. This web site is one thing that’s needed on the internet, someone with some originality.
incest porn
Hello there! I simply would like to give you a big thumbs up for your great info you have right here on this post. I am coming back to your blog for more soon.
dexamethasone 0.25 mg tablet
Oh my goodness! an amazing article dude. Many thanks Nonetheless I’m experiencing trouble with ur rss . Don’t know why Can not sign up for it. Is there anybody finding identical rss problem? Anyone who knows kindly respond. Thnkx
there are many greeting card options that you can see in online stores but i love those that generate cute sounds”
I’m impressed, I have to say. Really rarely do I encounter a blog that’s each educative and entertaining, and let me let you know, you’ve got hit the nail on the head. Your concept is excellent; the difficulty is something that not enough persons are speaking intelligently about. I’m very comfortable that I stumbled throughout this in my seek for something relating to this.
Hi, I do think this is an excellent web site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I am going to revisit once again since I bookmarked it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to help others.
Hi! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Anyhow, I’m definitely delighted I found it and I’ll be book-marking and checking back often!
incest porn
there is a need for firming lotion so that we can always maintain the health of our skin *
Hi there! This article could not be written any better! Reading through this article reminds me of my previous roommate! He constantly kept preaching about this. I am going to send this post to him. Fairly certain he will have a great read. Thanks for sharing!
You’re so interesting! I don’t believe I’ve truly read anything like this before. So nice to discover another person with genuine thoughts on this subject. Really.. thanks for starting this up. This website is one thing that’s needed on the web, someone with a little originality.
Along with every little thing which appears to be building within this subject material, many of your points of view happen to be very radical. Nonetheless, I appologize, because I do not give credence to your whole theory, all be it exhilarating none the less. It looks to everybody that your opinions are actually not totally justified and in actuality you are your self not entirely certain of your assertion. In any case I did appreciate reading through it.
Pretty! This was a really wonderful article. Thanks for providing this info.
cheers, I thoroughly enjoyed scaning your post. I really appreciate your wonderful know-how and the time you put into educating the rest of us.
Hey, have you possibly wondered to publish about Nintendo Dsi handheld?
online casino
After study some of the web sites on your own internet site now, i really much like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark internet site list and are checking back soon. Pls consider my web site too and figure out what you believe.
I am glad to be a visitant of this thoroughgoing web blog ! , thankyou for this rare info ! .
This is a topic that is close to my heart… Many thanks! Where are your contact details though?
This domain seems to get a great deal of visitors. How do you promote it? It gives a nice unique twist on things. I guess having something useful or substantial to post about is the most important thing.
porn
Cool post thanks! We think your articles are great and hope more soon. We love anything to do with word games/word play.
Good info. Lucky me I came across your site by accident (stumbleupon). I’ve saved it for later!
Your blog has the same post as another author but i like your better.”`,`
You made some really good points there. I checked on the net for additional information about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this site.
advair diskus generic
Audio started playing anytime I opened up this blog, so annoying!
You ought to be a part of a contest for one of the highest quality blogs on the internet. I most certainly will highly recommend this web site!
After examine a couple of of the weblog posts in your web site now, and I really like your manner of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark web site list and will be checking again soon. Pls try my website online as nicely and let me know what you think.
I could not resist commenting. Perfectly written.
I enjoy you because of your whole labor on this site. Gloria enjoys doing internet research and it’s really simple to grasp why. All of us hear all concerning the powerful form you convey great secrets through the web blog and in addition strongly encourage participation from some other people on the content and my daughter is actually understanding a great deal. Have fun with the rest of the new year. You are performing a really great job.
online slot
Thanks, I have recently been seeking for details about this topic for ages and yours is the best I’ve found so far.
Youre so cool! I dont suppose Ive read anything in this way just before. So nice to find somebody with a few original applying for grants this subject. realy i appreciate you for beginning this up. this web site is one area that is needed on-line, someone with some originality. useful job for bringing interesting things towards net!
lyrica usa
classical music is always the best, it is relaxing and very rich in melody~
homosexual porn
You have remarked very interesting points! ps nice internet site. .Grece
I real delighted to find this site on bing, just what I was looking for : D also bookmarked .
This website was… how do I say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve found something that helped me. Thanks a lot!
Dead pent subject material , Really enjoyed looking at .
Having read this I thought it was really informative. I appreciate you finding the time and energy to put this short article together. I once again find myself personally spending way too much time both reading and posting comments. But so what, it was still worth it.
You have made some decent points there. I checked on the net for additional information about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this site.
Hello there! I could have sworn I’ve visited your blog before but after browsing through a few of the articles I realized it’s new to me. Regardless, I’m certainly happy I discovered it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back frequently!
lgbt porn
After I initially left a comment I seem to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and from now on every time a comment is added I recieve 4 emails with the same comment. Is there an easy method you are able to remove me from that service? Appreciate it.
Way cool! Some very valid points! I appreciate you penning this post plus the rest of the site is also very good.
Hi, i think that i saw you visited my site so i came to ?return the favor?.I am attempting to find things to enhance my web site!I suppose its ok to use a few of your ideas!! Thanks from SEO India view https://www.giantbomb.com/profile/larry33/
That is a great tip particularly to those new to the blogosphere. Short but very accurate information… Thank you for sharing this one. A must read post.
Hey There. I found your blog using msn. This is a really well written article. I will be sure to bookmark it and return to read more of your useful information. Thanks for the post. I will certainly return. Thanks from Seo experts India link https://devindwoh33221.blogofoto.com
gay porn
Great info. Lucky me I discovered your website by accident (stumbleupon). I’ve saved it for later.
porn
lgbt porn
Right here is the perfect webpage for anybody who really wants to find out about this topic. You understand a whole lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want to…HaHa). You certainly put a fresh spin on a subject that’s been written about for many years. Great stuff, just wonderful.
Everything is very open with a very clear description of the issues. It was truly informative. Your site is extremely helpful. Many thanks for sharing.
I’m amazed, I must say. Seldom do I encounter a blog that’s both educative and engaging, and let me tell you, you have hit the nail on the head. The issue is something which too few folks are speaking intelligently about. Now i’m very happy that I stumbled across this in my search for something regarding this.
online casino
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon every day. It will always be helpful to read through content from other authors and use something from their sites.
Everything is very open with a precise clarification of the issues. It was really informative. Your website is very helpful. Thanks for sharing!
online casino
I was very happy to uncover this page. I wanted to thank you for your time for this particularly fantastic read!! I definitely really liked every bit of it and i also have you book-marked to see new stuff on your site.
Way cool! Some extremely valid points! I appreciate you penning this article and also the rest of the site is also really good.
Good post. I learn something new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon on a daily basis. It will always be exciting to read content from other writers and practice something from their websites.
incest porn
Way cool! Some very valid points! I appreciate you penning this write-up and the rest of the website is also really good.
You should be a part of a contest for one of the finest blogs on the internet. I most certainly will highly recommend this web site!
Your style is very unique compared to other people I have read stuff from. Many thanks for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I will just book mark this site.
This is the perfect webpage for anybody who wishes to understand this topic. You understand so much its almost tough to argue with you (not that I actually will need to…HaHa). You definitely put a brand new spin on a topic that has been written about for decades. Excellent stuff, just excellent.
incest porn
An impressive share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a colleague who has been conducting a little research on this. And he actually ordered me dinner due to the fact that I discovered it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending some time to talk about this subject here on your site.
Aw, this was an incredibly nice post. Finding the time and actual effort to create a superb article… but what can I say… I procrastinate a whole lot and never seem to get anything done.
untrustable
An intriguing discussion is definitely worth comment. I think that you should write more about this subject, it might not be a taboo matter but typically folks don’t talk about these issues. To the next! Many thanks.
This website was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I have found something which helped me. Kudos.
Everything is very open with a precise explanation of the challenges. It was really informative. Your site is very helpful. Many thanks for sharing.
I blog often and I seriously appreciate your content. The article has really peaked my interest. I am going to bookmark your blog and keep checking for new information about once a week. I subscribed to your RSS feed as well.
not safe
Good info. Lucky me I came across your website by chance (stumbleupon). I have book-marked it for later.
online casino
Everything is very open with a clear clarification of the issues. It was really informative. Your site is very useful. Thanks for sharing.
hacklink
I couldn’t refrain from commenting. Exceptionally well written.
There’s certainly a lot to learn about this subject. I like all of the points you have made.
That is a great tip particularly to those fresh to the blogosphere. Short but very precise information… Thank you for sharing this one. A must read article!
I was extremely pleased to uncover this site. I wanted to thank you for your time just for this wonderful read!! I definitely savored every bit of it and i also have you book marked to see new things on your site.
Oh my goodness! Incredible article dude! Many thanks, However I am having difficulties with your RSS. I don’t know why I can’t subscribe to it. Is there anyone else getting the same RSS issues? Anybody who knows the solution can you kindly respond? Thanks!!
Hi there! I could have sworn I’ve visited this blog before but after browsing through a few of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Nonetheless, I’m certainly pleased I found it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back often!
This is the right site for everyone who hopes to find out about this topic. You understand a whole lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually will need to…HaHa). You certainly put a new spin on a subject that has been discussed for years. Great stuff, just great.
I needed to thank you for this fantastic read!! I definitely enjoyed every little bit of it. I have got you bookmarked to look at new stuff you post…
You ought to be a part of a contest for one of the most useful blogs online. I will recommend this website!
Hi there! I simply wish to offer you a huge thumbs up for your great info you have right here on this post. I will be returning to your site for more soon.
When I initially left a comment I seem to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and from now on whenever a comment is added I recieve 4 emails with the exact same comment. Is there an easy method you can remove me from that service? Thanks.
Pretty! This was a really wonderful post. Many thanks for providing this info.
Great web site you have here.. It’s difficult to find excellent writing like yours nowadays. I really appreciate people like you! Take care!!
I’d like to thank you for the efforts you’ve put in penning this site. I’m hoping to check out the same high-grade blog posts from you later on as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own site now 😉
Spot on with this write-up, I actually believe this website needs a great deal more attention. I’ll probably be returning to see more, thanks for the information.
Hi there! I could have sworn I’ve been to this website before but after browsing through a few of the articles I realized it’s new to me. Nonetheless, I’m definitely pleased I found it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back often!
I quite like looking through a post that can make men and women think. Also, thank you for permitting me to comment.
Hi! I could have sworn I’ve visited this web site before but after looking at many of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m certainly happy I came across it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back often!
Good post! We are linking to this great content on our site. Keep up the great writing.
This site was… how do I say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve found something that helped me. Thanks a lot!
bookmarked!!, I love your website.
Oh my goodness! Impressive article dude! Thank you, However I am experiencing problems with your RSS. I don’t know why I am unable to join it. Is there anybody getting identical RSS issues? Anyone who knows the solution can you kindly respond? Thanx.
After looking over a few of the blog posts on your blog, I really appreciate your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back in the near future. Please check out my web site as well and let me know what you think.
Hey there! I just want to give you a huge thumbs up for your great information you’ve got here on this post. I will be returning to your web site for more soon.
Excellent web site you have here.. It’s hard to find good quality writing like yours these days. I honestly appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
Aw, this was an incredibly good post. Taking the time and actual effort to create a top notch article… but what can I say… I put things off a whole lot and don’t manage to get anything done.
Aw, this was an incredibly nice post. Taking a few minutes and actual effort to make a superb article… but what can I say… I procrastinate a whole lot and don’t seem to get nearly anything done.
Greetings! Very helpful advice within this post! It is the little changes that will make the greatest changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
I’m excited to find this site. I want to to thank you for your time due to this fantastic read!! I definitely savored every part of it and i also have you saved as a favorite to look at new stuff in your blog.
I love it when folks get together and share opinions. Great blog, continue the good work.
After looking into a handful of the articles on your web page, I seriously like your way of writing a blog. I book-marked it to my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back in the near future. Please visit my web site too and let me know your opinion.
Wonderful post! We will be linking to this great article on our site. Keep up the good writing.
I like it whenever people come together and share views. Great blog, stick with it!
Your style is really unique compared to other people I’ve read stuff from. Many thanks for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I’ll just book mark this site.
Hello there! I just wish to offer you a huge thumbs up for your great info you have here on this post. I am coming back to your blog for more soon.
I love it when people get together and share opinions. Great website, stick with it.
I’d like to thank you for the efforts you’ve put in penning this site. I am hoping to see the same high-grade content by you in the future as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my very own website now 😉
This site truly has all the information and facts I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Aw, this was a really good post. Finding the time and actual effort to make a superb article… but what can I say… I put things off a whole lot and don’t manage to get nearly anything done.
You need to be a part of a contest for one of the best blogs on the internet. I will recommend this web site!
This excellent website truly has all the info I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
ремонт телефонов москва
Very good article. I absolutely love this website. Keep writing!
Good web site you have here.. It’s difficult to find high-quality writing like yours nowadays. I seriously appreciate people like you! Take care!!
May I simply just say what a comfort to find a person that actually understands what they are discussing on the internet. You actually understand how to bring an issue to light and make it important. A lot more people really need to look at this and understand this side of the story. I can’t believe you aren’t more popular since you surely possess the gift.
I would like to thank you for the efforts you have put in penning this blog. I’m hoping to check out the same high-grade content from you later on as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own, personal blog now 😉
Hi, I do think this is a great website. I stumbledupon it 😉 I may return once again since I book marked it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide others.
I could not resist commenting. Exceptionally well written!
Saved as a favorite, I really like your blog!
An interesting discussion is worth comment. I believe that you ought to publish more about this issue, it may not be a taboo matter but generally people don’t talk about these topics. To the next! All the best.
When I initially commented I appear to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now every time a comment is added I recieve 4 emails with the same comment. Is there an easy method you are able to remove me from that service? Appreciate it.
Good article! We will be linking to this great content on our website. Keep up the great writing.
Aw, this was an exceptionally nice post. Taking a few minutes and actual effort to generate a superb article… but what can I say… I put things off a whole lot and don’t manage to get anything done.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту сотовых телефонов, смартфонов и мобильных устройств.
Мы предлагаем: сервисные центры по ремонту мобильных телефонов
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
bookmarked!!, I love your site!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту сотовых телефонов, смартфонов и мобильных устройств.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт смартфона
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
There’s definately a great deal to find out about this subject. I like all the points you made.
I couldn’t resist commenting. Exceptionally well written.
Everything is very open with a really clear explanation of the challenges. It was definitely informative. Your website is very helpful. Thank you for sharing!
Greetings! Very useful advice in this particular post! It’s the little changes which will make the most important changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
Affiliate marketing is one of the most effective and powerful ways to earn money online. This type of program gives everyone the opportunity to make a profit through the Internet. Since these affiliate marketing programs are easy to join, implement and pay for the Commission on a regular basis, more people are now willing to be part of this type business.
This site truly has all the info I needed about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Oh my goodness! a fantastic write-up dude. Thanks a lot However We’re experiencing issue with ur rss . Do not know why Struggling to register for it. Could there be any person getting identical rss dilemma? Anyone who knows kindly respond. Thnkx
maintaining a healthy weight can be tricky because it revolves around genetics and some other factors*
You have noted terribly interesting points ! ps tight web web site here.
I couldn’t refrain from commenting. Perfectly written!
An impressive share! I have just forwarded this onto a co-worker who had been conducting a little research on this. And he actually ordered me lunch simply because I stumbled upon it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending the time to talk about this matter here on your website.
Aw, this was an incredibly nice post. Taking a few minutes and actual effort to generate a superb article… but what can I say… I put things off a whole lot and don’t manage to get anything done.
Took me time to read all of the feedback, but I actually loved the article. It proved to be very useful to me and I am sure to all the commenters here! It is always good when you can’t solely learn, but in addition engaged! I’m sure you had pleasure writing this article. Anyway, in my language, there aren’t a lot good source like this.
I’d need to check with you here. Which isn’t some thing It’s my job to do! I like reading an article that will get people to feel. Also, appreciate your permitting me to comment!
I like this post very much. I will definitely be back. Hope that I can go through more insightful posts then. Will likely be sharing your wisdom with all of my friends!
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – выездной ремонт бытовой техники в новосибирске
conclusion that you are absolutely right but a few require to be
After spending several hours online at last We have located an individual that seriously does know what they’re preaching about appreciate it a whole lot fantastic posting
I can objects this advice go over to two different types of humans: modern Microsoft zune masters which can be regarding an upgrade, and folks necessary . decide on from a Microsoft zune plus an apple ipod. (Additional casino players worth taking into consideration around the market, much The Walkman Times, yet unfortunately I’m hoping this you sufficient important information crank out ramifications , before final choice of their Microsoft zune vs . enthusiasts with the exception of ipod array , too.)
whoah this weblog is great i like studying your articles. Keep up the great paintings! You already know, a lot of people are searching around for this info, you could help them greatly.
Why is chaat so preferred amongst Indians? The tanginess involved is the critical tempting aspect in the numerous chaat objects you will constantly come across roadside stalls crowded with people, all getting chaat! A lot of a sweets store also sell chaat prepared the hygienic way so drawing more consumers in contrast to roadside stalls. Very few of the preferred chaat products involve dahi bhalla, paneer masala chilla, aloo tikki, kachori with sabji, paneer tikka, raj kachori, bhalla papri, lachha tokri, pani puri, bhel puri, matar kulcha, pao bhaji, and papri chaat. Most of these things are prepared from flour dough with a blend of many other ingredients these kinds of as potato items, crispy fried bread, gram or chickpeas, tangy-salty spices, chilly and tamarind sauce. Every chaat merchandise is served in a plate garnished with yogurt, fresh new green coriander leaves, and more except the pani puri. Aloo tikki is a bit various wherein boiled potatoes are smashed and designed into tiny doughs and then fried in butter. When it is accommodated in a plate, it is garnished with yogurt, onion, spices, and coriander. So, have a look at your preferred sweets store and have chaat prepared the hygienic way!
Hiya, I am really glad I’ve found this information. Nowadays bloggers publish just about gossips and net and this is actually annoying. A good web site with interesting content, this is what I need. Thanks for keeping this site, I’ll be visiting it. Do you do newsletters? Can’t find it.
Sometimes your blog is loading slowly, better find a better host.”,:-`
Do you have a spam issue on this website; I also am a blogger, and I was wondering your situation; many of us have developed some nice procedures and we are looking to exchange methods with other folks, why not shoot me an email if interested.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту стиральных машин с выездом на дом по Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт стиральных машин в москве прайс
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервис центры бытовой техники казань
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
very good post, i definitely love this website, keep on it
hinduism is a good religion, my father is hindu and also my mother.
Good article. I will be going through a few of these issues as well..
I see your site on google. I searching something about research statistic and I find it in your site. Thank a lot.
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – профи ремонт
Useful info. Hope to see more good posts in the future.
You’ve provided a nuanced view on this topic.오피
Sweet blog! I found it while browsing on Yahoo News. Do you have any tips on how to get listed in Yahoo News? I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there! Thank you
I’ve been searching for this information and at last located your post. Your own posts are aiding me in uncovering some needed specifics. Make sure you continue your writing.
Aw, this was a very good post. In notion I have to devote writing like that moreover – taking time and actual effort to manufacture a great article… but what can I say… I procrastinate alot and by no indicates apparently go accomplished.
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники в ростове на дону
Spot i’ll carry on with this write-up, I truly think this website needs considerably more consideration. I’ll probably be once more to learn far more, thank you for that info.
Your writing is both informative and engaging.오피
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту игровых консолей Sony Playstation, Xbox, PSP Vita с выездом на дом по Москве.
Мы предлагаем: сервис по ремонту игровых консолей
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту компьютерных видеокарт по Москве.
Мы предлагаем: сервис видеокарт
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Unbelievably individual friendly site. Enormous information available on few gos to.
Take a look at my web blog :: Explainer video company India (https://Explainervideo.in/explainer-video-services/)
Well i’m from Ireland, and throughout Ireland bono and the lads are unquestionably liked and also could certainly not do really much incorrect, we all love them.
I’ve just been talking to Sean Gallagher about his upcoming Instant Income Cash Machine course, and he’s been kind enough to fill me in on a few details regarding his upcoming course.
granat88
Heya i’m for the first time here. I came across this board and I find It truly helpful & it helped me out a lot. I am hoping to give one thing again and help others such as you aided me.
My buddy i have been simply speaking about this specific subject matter, the girl really is typically attempting to show us absolutely wrong! I ‘m planning to show her this web site submit as well as caress this in a very small!
bro138
Good day! This post could not be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept chatting about this. I will forward this article to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
What are you stating, man? I realize everyones got their own view, but really? Listen, your web site is neat. I like the energy you put into it, especially with the vids and the pics. But, come on. Theres gotta be a better way to say this, a way that doesnt make it seem like everyone here is stupid!
This is a topic that’s close to my heart… Many thanks! Where are your contact details though?
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту фото техники от зеркальных до цифровых фотоаппаратов.
Мы предлагаем: отремонтировать проектор
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Nice one for making the effort go over this particular, I think truly about this and consequently true love knowing more to do with that niche. Assuming would-be, any time you attain practical knowledge, would you ideas posting to any site by working with further important information? This is great for everyone.
I really like forgathering useful info, this post has got me even more info! .
I am curious to find out what blog platform you have been utilizing? I’m having some minor security problems with my latest website and I would like to find something more risk-free. Do you have any solutions?
Howdy! I could have sworn I’ve visited this site before but after going through many of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Nonetheless, I’m certainly delighted I found it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back frequently.
I liked as much as you will obtain performed proper here. The caricature is attractive, your authored subject matter stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an nervousness over that you would like be turning in the following. ill undoubtedly come further before once more as exactly the same nearly a lot ceaselessly within case you defend this hike.
Pretty! This has been an extremely wonderful article. Thanks for providing these details.
zeus138 zeus138 zeus138 zeus138
fantastic points altogether, you just received a brand new reader. What may you recommend in regards to your publish that you simply made a few days ago? Any positive?
g200m g200m g200m g200m
Hello, i feel that i saw you visited my blog thus i came to return the favor?.I am trying to find things to enhance my website!I assume its ok to use some of your concepts!!
Хочу поделиться своим опытом ремонта телефона в этом сервисном центре. Остался очень доволен качеством работы и скоростью обслуживания. Если ищете надёжное место для ремонта, обратитесь сюда: где можно починить.
ремонт бытовой техники в самаре
Hey there! I’ve been following your blog for a while now and finally got the courage to go ahead and give you a shout out from Austin Tx! Just wanted to say keep up the excellent work!
Wohh exactly what I was searching for, regards for putting up.
Hey, I appreciate you for this great article. It was very helpful to me and to the one who read this page. You truly is a genius writer!
using wooden wall decors at home is a great alternative to using those expensive metal wall decors,,
i would say that Lion King is one of the best animated films that i have ever watched..
I conceive this website has very wonderful indited content material posts .
I real glad to locate this great site on bing, just the thing I used to be seeking : D also saved to bookmarks .
Information given by you is really very useful and valuable for me. I have to write an article in my class about this theme and thanks a lot for it. I even didn’t know about Laboratory and Unarmed stick insects. Thanks a lot
I have to have made to order myspace images produced up, would you accomplish that kind of style function by any opportunity?
What a lovely weblog. I will certainly be back again. Please maintain writing!
logam777 logam777 logam777
Hello, I enjoy reading through your post. I like to write a little comment to support you.
You can definitely see your skills in the work you write. The world hopes for more passionate writers like you who are not afraid to mention how they believe. At all times follow your heart.
Good day very cool site!! Man .. Excellent .. Superb .. I will bookmark your website and take the feeds additionally¡KI’m glad to seek out numerous helpful info here in the put up, we need work out extra techniques in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
Aw, this was an extremely good post. Spending some time and actual effort to make a great article… but what can I say… I procrastinate a lot and never seem to get nearly anything done.
manhwaland
Hi there, I read your blog like every week. Your humoristic style is witty, keep it up!
anichin vip
wonderful issues altogether, you simply received a brand new reader. What could you recommend about your submit that you simply made a few days ago? Any certain?
i wish to have some diamond necklace but they are quite expensive’
sssinstagram
What’s Going down i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have discovered It absolutely helpful and it has aided me out loads. I hope to contribute & help other customers like its helped me. Great job.
Into the freshly made vacancy Gamble (Ferrell) is perfectly happy not to step: a desk-bound scourge of white-collar felons, he’ll take the paper chase over the car chase every time.
Hey! I know this is kinda off topic but I was wondering if you knew where I could locate a captcha plugin for my comment form? I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having trouble finding one? Thanks a lot!
I don’t normally check out these kinds of sites (I’m a pretty shy person) – but even though I was a bit shocked as I was reading, I was definitely a bit excited as well. Thanks for giving me a big smile for the day
beton888 beton888 beton888
This is the right site for anybody who hopes to find out about this topic. You realize a whole lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I really would want to…HaHa). You certainly put a brand new spin on a subject which has been discussed for a long time. Wonderful stuff, just wonderful!
This is a great resource for anyone interested in…오피
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – техпрофи
yandex semua film 2024
Hi there are using WordPress for your blog platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you require any html coding expertise to make your own blog? Any help would be really appreciated!
situs slot situs slot situs slot situs slot
Its not my first time to go to see this web page, i am browsing this website dailly and obtain good facts from here everyday.
I am often to blogging and that i really appreciate your content regularly. The article has truly peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your website and maintain checking for brand spanking new data.
lk21 rebahin
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here. The sketch is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish. nonetheless, you command get bought an edginess over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come further formerly again as exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this increase.
I discovered your blog site on google and verify just a few of your early posts. Continue to maintain up the very good operate. I simply further up your RSS feed to my MSN News Reader. In search of ahead to studying more from you later on!
texas88 texas88 texas88 texas88
If you are going for most excellent contents like myself, simply pay a visit this website everyday because it offers feature contents, thanks
Took me time to learn all the feedback, but I actually loved the write-up. It proved to be Very beneficial to me and I’m positive to all the commenters here! It really is always superior when you can not solely be informed, but additionally entertained! I am positive you had enjoyable penning this post.
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – выездной ремонт бытовой техники в волгограде
Great write-up, I am normal visitor of one?s blog, maintain up the excellent operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
I like this weblog so much, saved to fav.
chord resah jadi luka
Hi there, just became aware of your blog through Google, and found that it is really informative. I am gonna watch out for brussels. I will appreciate if you continue this in future. Many people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
Hello! I simply would choose to give a massive thumbs up for any great information you’ve got here within this post. I will be returning to your blog site for further soon.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервис центры бытовой техники красноярск
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
This website really has all of the information and facts I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
This is very interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I have joined your rss feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
Your post has clarified a lot for me.오피
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт техники в уфе
I’m impressed, I have to admit. Genuinely rarely should i encounter a weblog that’s both educative and entertaining, and let me tell you, you may have hit the nail about the head. Your idea is outstanding; the problem is an element that insufficient persons are speaking intelligently about. I am delighted we came across this during my look for something with this.
I must to go by and convince you I enjoy reading through your website. We appreciate you every one of your valuable tips.
I discovered your blog site internet site on the search engines and appearance a few of your early posts. Keep on the very good operate. I recently extra the Rss to my MSN News Reader. Looking for toward reading more by you at a later time!…
Job scope at significant scale lies for forensic science experts at crime laboratories rub by city, county or state governments. The other region exactly where an individual looking for a career in forensic science can secure job are Federal agencies including the Departments of Justice, Federal Bureau of Investigation, Secret Service, Drug Enforcement Administration, Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms, Postal Inspection Service and other crucial departments, private labs and university laboratories is also a location of work for Forensic Science technician.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем:ремонт бытовой техники в ростове на дону
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Oh my goodness! Awesome article dude! Many thanks, However I am experiencing difficulties with your RSS. I don’t understand the reason why I can’t join it. Is there anybody getting identical RSS problems? Anybody who knows the solution can you kindly respond? Thanx.
Everyone loves it when people get together and share ideas. Great site, stick with it.
There is definately a lot to know about this issue. I really like all the points you made.
There may be noticeably a bundle to find out about this. I assume you made certain good factors in features also.
I will right away clutch your rss feed as I can not find your email subscription hyperlink or e-newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Please let me understand in order that I may just subscribe. Thanks.
Very good post! We will be linking to this particularly great article on our website. Keep up the great writing.
Hello, I had been researching the web and I ran into your own blog. Keep up the wonderful work.
Some truly terrific work on behalf of the owner of this web site , utterly great content material .
I couldn’t resist commenting. Perfectly written.
lgoace lgoace lgoace lgoace lgoace
It’s really a great and helpful piece of info. I am happy that you shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
Woah this is just an insane amount of information, must of taken ages to compile so thanx so much for just sharing it with all of us. If your ever in any need of related information, perhaps a bit of coaching, seduction techniques or just general tips, just check out my own site!
To tell you the teuth, I was passing around and come across your site. It is wonderful. I mean as a content and design. I added you to my list and decided to spent the rest of the weekend browsing. Well done!
great resources here. Ill be back for the next your posting. keep writing and happy blogging.
You are so cool! I do not think I’ve read through anything like that before. So good to discover another person with some original thoughts on this subject matter. Seriously.. many thanks for starting this up. This web site is one thing that’s needed on the web, someone with some originality.
Very nice article. I absolutely love this website. Continue the good work!
slot demo pragmatic slot demo pragmatic slot demo pragmatic slot demo pragmatic slot demo pragmatic
Great post.
maxwin89 maxwin89 maxwin89 maxwin89 maxwin89
I am truly grateful to the holder of this web page who has shared this great post at here.
rajacuan rajacuan rajacuan rajacuan rajacuan
Have you ever considered writing an e-book or guest authoring on other blogs? I have a blog centered on the same subjects you discuss and would love to have you share some stories/information. I know my viewers would appreciate your work. If you’re even remotely interested, feel free to shoot me an e mail.
Сервисный центр предлагает ремонт моноколеса rockwheel адреса ремонт моноколес rockwheel недорого
bola88 bola88 bola88 bola88 bola88
When someone writes an paragraph he/she maintains the idea of a user in his/her brain that how a user can know it. So that’s why this post is outstdanding. Thanks!
Сервисный центр предлагает мастерские ремонта сушильных машин lg срочный ремонт сушильной машины lg
Good post. I learn something totally new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon every day. It’s always helpful to read through content from other authors and use a little something from other websites.
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – сервисный центр в воронеже
the best addition on our garden that we have are those garden swings, the garden swings made our kids very very happy“
Can I just say what a comfort to discover an individual who genuinely understands what they’re discussing on the net. You certainly realize how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More and more people must look at this and understand this side of the story. I can’t believe you’re not more popular given that you definitely have the gift.
lgoace lgoace lgoace lgoace lgoace
Hey there! I simply want to give you a big thumbs up for the excellent information you’ve got here on this post. I will be coming back to your website for more soon.
There is noticeably big money to comprehend this. I assume you have made particular nice points in functions also.
Hello! I simply would wish to offer a huge thumbs up for that great info you’ve here during this post. I will be returning to your website to get more soon.
That is a good tip especially to those new to the blogosphere. Short but very precise info… Appreciate your sharing this one. A must read post!
I really like it when individuals come together and share ideas. Great site, keep it up!
I blog quite often and I seriously appreciate your content. This great article has really peaked my interest. I will book mark your website and keep checking for new details about once per week. I opted in for your Feed too.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервис центры бытовой техники тюмень
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
I seriously love your site.. Excellent colors & theme. Did you develop this web site yourself? Please reply back as I’m wanting to create my own site and would love to know where you got this from or what the theme is named. Appreciate it!
Great site you’ve got here.. It’s hard to find high-quality writing like yours nowadays. I really appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
{Tôi cực kỳ hài lòng khám phá trang web này. Tôi muốn cảm ơn bạn {vì đã|dành thời gian cho|chỉ vì điều này|vì điều này|cho bài đọc tuyệt vời này!! Tôi chắc chắn thực sự thích từng của nó và tôi đã lưu làm mục ưa thích để xem thông tin mới trên blog của bạn.|Tôi có thể chỉ nói rằng thật nhẹ nhõm để khám phá một cá nhân mà thực sự hiểu họ là gì thảo luận trên web. Bạn chắc chắn hiểu cách đưa một rắc rối ra ánh sáng và làm cho nó trở nên quan trọng. Nhiều người hơn nên xem điều này và hiểu khía cạnh này của. Tôi đã ngạc nhiên rằng bạn không nổi tiếng hơn vì bạn chắc chắn sở hữu món quà.|Rất hay bài đăng. Tôi chắc chắn yêu thích trang web này. Tiếp tục làm tốt!|Thật khó tìm những người có kinh nghiệm về điều này, tuy nhiên, bạn có vẻ bạn biết mình đang nói gì! Cảm ơn|Bạn nên là một phần của một cuộc thi dành cho một blog trực tuyến có chất lượng cao nhất. Tôi sẽ khuyến nghị trang web này!|Một động lực chắc chắn đáng giá bình luận. Tôi tin rằng bạn nên xuất bản thêm về chủ đề này, nó có thể không là một điều cấm kỵ vấn đề nhưng điển hình mọi người không nói về vấn đề những điều này. Đến phần tiếp theo! Chúc mọi điều tốt đẹp nhất!|Xin chào! Tôi chỉ muốn đề nghị rất cho thông tin tuyệt vời bạn có ở đây trên bài đăng này. Tôi sẽ là quay lại trang web của bạn để biết thêm thông tin sớm nhất.|Sau khi tôi ban đầu để lại bình luận tôi có vẻ như đã nhấp vào hộp kiểm -Thông báo cho tôi khi có bình luận mới- và từ bây giờ mỗi lần được thêm vào tôi nhận được bốn email cùng chính xác một bình luận. Phải có một phương pháp dễ dàng bạn có thể xóa tôi khỏi dịch vụ đó không? Cảm ơn rất nhiều.|Lần sau Tôi đọc một blog, Tôi hy vọng rằng nó không thất bại nhiều như bài này. Rốt cuộc, Tôi biết điều đó là sự lựa chọn của tôi để đọc, nhưng tôi thực sự tin có lẽ có điều gì đó thú vị để nói về. Tất cả những gì tôi nghe được là một loạt khóc lóc về điều gì đó mà bạn có thể sửa nếu bạn không quá bận tìm kiếm sự chú ý.|Đúng với bài viết này, tôi thực sự cảm thấy trang web này cần nhiều hơn nữa sự chú ý.
{Tôi rất vui khám phá trang này. Tôi muốn cảm ơn bạn {vì đã|dành thời gian cho|chỉ vì điều này|vì điều này|cho bài đọc tuyệt vời này!! Tôi chắc chắn yêu thích từng một phần nó và tôi đã đã lưu vào mục ưa thích để xem những thứ mới trên trang web của bạn.|Tôi có thể chỉ nói rằng thật thoải mái để tìm thấy một người mà thực sự biết họ là gì đang nói về trên internet. Bạn thực sự hiểu cách đưa một vấn đề ra ánh sáng và làm cho nó trở nên quan trọng. Nhiều người hơn phải kiểm tra điều này và hiểu khía cạnh này của. Thật ngạc nhiên bạn không nổi tiếng hơn vì bạn chắc chắn nhất sở hữu món quà.|Rất tốt bài viết trên blog. Tôi chắc chắn yêu thích trang web này. Tiếp tục với nó!|Thật khó đến những người hiểu biết cho điều này, tuy nhiên, bạn nghe có vẻ bạn biết mình đang nói gì! Cảm ơn|Bạn nên là một phần của một cuộc thi dành cho một blog trên mạng hữu ích nhất. Tôi sẽ Rất khuyến nghị trang web này!|Một động lực chắc chắn đáng giá bình luận. Tôi nghĩ rằng bạn cần xuất bản thêm về chủ đề này, nó có thể không là một điều cấm kỵ vấn đề nhưng thường xuyên mọi người không nói về những chủ đề những điều này. Đến phần tiếp theo! Chúc mọi điều tốt đẹp nhất.|Xin chào! Tôi chỉ muốn cho bạn một rất cho thông tin tuyệt vời bạn có ngay tại đây trên bài đăng này. Tôi sẽ là trở lại blog của bạn để biết thêm thông tin sớm nhất.|Khi tôi ban đầu bình luận tôi có vẻ như đã nhấp vào hộp kiểm -Thông báo cho tôi khi có bình luận mới- và bây giờ bất cứ khi nào có bình luận được thêm vào tôi nhận được 4 email có cùng nội dung. Có một phương tiện bạn có thể xóa tôi khỏi dịch vụ đó không? Cảm ơn rất nhiều.|Lần sau Tôi đọc một blog, Hy vọng rằng nó không thất bại nhiều như bài này. Ý tôi là, Vâng, đó là sự lựa chọn của tôi để đọc hết, tuy nhiên tôi thực sự nghĩ có lẽ có điều gì đó hữu ích để nói về. Tất cả những gì tôi nghe được là một loạt rên rỉ về điều gì đó mà bạn có thể sửa nếu bạn không quá bận tìm kiếm sự chú ý.|Đúng với bài viết này, tôi hoàn toàn tin trang web này cần nhiều hơn nữa sự chú ý.
{Tôi đã rất vui khám phá trang này. Tôi muốn cảm ơn bạn {vì đã|dành thời gian cho|chỉ vì điều này|vì điều này|cho bài đọc tuyệt vời này!! Tôi chắc chắn thích từng một chút nó và tôi đã đã đánh dấu trang để xem những thứ mới trong blog của bạn.|Tôi có thể chỉ nói rằng thật nhẹ nhõm để khám phá một cá nhân mà thực sự biết họ là gì đang nói về trên web. Bạn chắc chắn hiểu cách đưa một vấn đề ra ánh sáng và làm cho nó trở nên quan trọng. Nhiều người hơn nữa nên xem điều này và hiểu khía cạnh này câu chuyện của bạn. Tôi đã ngạc nhiên bạn không nổi tiếng hơn vì bạn chắc chắn có món quà.|Tốt bài viết. Tôi hoàn toàn yêu thích trang web này. Tiếp tục làm tốt!|Thật gần như không thể tìm thấy những người hiểu biết trong chủ đề cụ thể này, nhưng bạn có vẻ bạn biết mình đang nói gì! Cảm ơn|Bạn nên là một phần của một cuộc thi dành cho một trang web trực tuyến có chất lượng cao nhất. Tôi sẽ khuyến nghị trang web này!|Một hấp dẫn đáng giá bình luận. Không còn nghi ngờ gì nữa rằng bạn nên viết thêm về chủ đề này, nó có thể không là một điều cấm kỵ chủ đề nhưng thường xuyên mọi người không nói về những chủ đề như vậy. Đến phần tiếp theo! Chúc mọi điều tốt đẹp nhất!|Xin chào! Tôi chỉ muốn cho bạn một rất to cho thông tin tuyệt vời bạn có ở đây trên bài đăng này. Tôi sẽ là quay lại trang web của bạn để biết thêm thông tin sớm nhất.|Khi tôi ban đầu bình luận tôi có vẻ như đã nhấp hộp kiểm -Thông báo cho tôi khi có bình luận mới- và từ bây giờ bất cứ khi nào có bình luận được thêm vào tôi nhận được 4 email cùng chính xác một bình luận. Có một phương tiện bạn có thể xóa tôi khỏi dịch vụ đó không? Chúc mừng.|Lần sau nữa Tôi đọc một blog, Tôi hy vọng rằng nó không thất bại nhiều như bài này. Ý tôi là, Tôi biết điều đó là sự lựa chọn của tôi để đọc, nhưng tôi thực sự tin bạn sẽ có điều gì đó thú vị để nói. Tất cả những gì tôi nghe được là một loạt tiếng rên rỉ về điều gì đó mà bạn có thể sửa nếu bạn không quá bận tìm kiếm sự chú ý.|Đúng với bài viết này, tôi hoàn toàn tin trang web tuyệt vời này cần nhiều hơn nữa sự chú ý.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту гироскутеров в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: гироскутер ремонт колеса
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту моноблоков в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт экрана моноблока
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
{Tôi khá hài lòng khám phá trang web này. Tôi muốn cảm ơn bạn {vì đã|dành thời gian cho|chỉ vì điều này|vì điều này|cho bài đọc tuyệt vời này!! Tôi chắc chắn thích thú từng một chút nó và tôi cũng đã lưu làm mục ưa thích để xem điều mới trên trang web của bạn.|Tôi có thể chỉ nói rằng thật nhẹ nhõm để khám phá một cá nhân mà thực sự biết họ là gì thảo luận trực tuyến. Bạn chắc chắn hiểu cách đưa một rắc rối ra ánh sáng và làm cho nó trở nên quan trọng. Nhiều người hơn nữa nên đọc điều này và hiểu khía cạnh này của. Tôi đã ngạc nhiên bạn không nổi tiếng hơn vì bạn chắc chắn nhất có món quà.|Tốt bài viết trên blog. Tôi chắc chắn yêu thích trang web này. Tiếp tục với nó!|Thật khó tìm những người có học thức về điều này, nhưng bạn nghe có vẻ bạn biết mình đang nói gì! Cảm ơn|Bạn cần tham gia một cuộc thi dành cho một trang web trên web tuyệt vời nhất. Tôi sẽ Rất khuyến nghị blog này!|Một động lực đáng giá bình luận. Tôi nghĩ rằng bạn nên viết thêm về chủ đề này, nó có thể không là một điều cấm kỵ chủ đề nhưng điển hình mọi người không thảo luận những chủ đề những điều này. Đến phần tiếp theo! Cảm ơn rất nhiều.|Xin chào! Tôi chỉ muốn cho bạn một rất to cho thông tin xuất sắc bạn có ngay tại đây trên bài đăng này. Tôi sẽ là trở lại trang web của bạn để biết thêm thông tin sớm nhất.|Sau khi tôi ban đầu để lại bình luận tôi có vẻ như đã nhấp vào hộp kiểm -Thông báo cho tôi khi có bình luận mới- và từ bây giờ bất cứ khi nào có bình luận được thêm vào tôi nhận được 4 email cùng chính xác một bình luận. Phải có một phương tiện bạn có thể xóa tôi khỏi dịch vụ đó không? Cảm kích.|Lần sau Tôi đọc một blog, Hy vọng rằng nó sẽ không thất bại nhiều như bài này. Rốt cuộc, Tôi biết điều đó là sự lựa chọn của tôi để đọc, dù sao thì tôi thực sự tin có lẽ có điều gì đó hữu ích để nói. Tất cả những gì tôi nghe được là một loạt khóc lóc về điều gì đó mà bạn có thể sửa nếu bạn không quá bận tìm kiếm sự chú ý.|Đúng với bài viết này, tôi thực sự tin rằng trang web này cần nhiều hơn nữa sự chú ý.
Hello there, May I download that snapshot and make use of it on my personal weblog?
{Tôi đã hạnh phúc hơn cả vui khám phá trang này. Tôi muốn cảm ơn bạn {vì đã|dành thời gian cho|chỉ vì điều này|vì điều này|cho bài đọc tuyệt vời này!! Tôi chắc chắn thích từng của nó và tôi cũng đã lưu làm mục ưa thích để xem điều mới trên blog của bạn.|Tôi có thể chỉ nói rằng thật nhẹ nhõm để tìm thấy một cá nhân mà thực sự hiểu họ là gì đang nói về trên web. Bạn thực sự nhận ra cách đưa một vấn đề ra ánh sáng và làm cho nó trở nên quan trọng. Nhiều người hơn nữa phải đọc điều này và hiểu khía cạnh này câu chuyện của bạn. Tôi không thể tin bạn không nổi tiếng hơn cho rằng bạn chắc chắn có món quà.|Tốt bài viết. Tôi chắc chắn yêu thích trang web này. Tiếp tục làm tốt!|Thật khó tìm những người hiểu biết về điều này, nhưng bạn có vẻ bạn biết mình đang nói gì! Cảm ơn|Bạn nên tham gia một cuộc thi dành cho một trang web trên internet tốt nhất. Tôi sẽ Rất khuyến nghị blog này!|Một hấp dẫn chắc chắn đáng giá bình luận. Không còn nghi ngờ gì nữa rằng bạn cần xuất bản thêm về vấn đề này, nó có thể không là một điều cấm kỵ chủ đề nhưng nói chung mọi người không nói về vấn đề những điều này. Đến phần tiếp theo! Trân trọng.|Xin chào! Tôi chỉ muốn cho bạn một rất cho thông tin tuyệt vời bạn có ngay tại đây trên bài đăng này. Tôi sẽ là trở lại trang web của bạn để biết thêm thông tin sớm nhất.|Khi tôi ban đầu để lại bình luận tôi có vẻ như đã nhấp hộp kiểm -Thông báo cho tôi khi có bình luận mới- và bây giờ mỗi lần được thêm vào tôi nhận được bốn email cùng chính xác một bình luận. Có một cách bạn có thể xóa tôi khỏi dịch vụ đó không? Cảm ơn bạn.|Lần sau nữa Tôi đọc một blog, Tôi hy vọng rằng nó sẽ không làm tôi thất vọng nhiều như bài này. Ý tôi là, Tôi biết điều đó là sự lựa chọn của tôi để đọc hết, tuy nhiên tôi thực sự tin bạn sẽ có điều gì đó hữu ích để nói về. Tất cả những gì tôi nghe được là một loạt phàn nàn về điều gì đó mà bạn có thể sửa nếu bạn không quá bận tìm kiếm sự chú ý.|Đúng với bài viết này, tôi thành thật cảm thấy trang web tuyệt vời này cần nhiều hơn nữa sự chú ý.
Will you care and attention essentially write-up most of the following in my webpage in essence your website mention of this blog?
Youre so cool! I dont suppose Ive read anything like this before. So nice to find somebody with some original thoughts on this subject. realy thank you for starting this up. this website is something that is needed on the web, someone with a little originality. useful job for bringing something new to the internet!
{Tôi đã rất vui khám phá trang web này. Tôi cần cảm ơn bạn {vì đã|dành thời gian cho|chỉ vì điều này|vì điều này|cho bài đọc tuyệt vời này!! Tôi chắc chắn thích thú từng của nó và tôi cũng đã lưu làm mục ưa thích để xem những thứ mới trong trang web của bạn.|Tôi có thể chỉ nói rằng thật nhẹ nhõm để tìm thấy một người mà thực sự biết họ là gì thảo luận trên internet. Bạn chắc chắn nhận ra cách đưa một vấn đề ra ánh sáng và làm cho nó trở nên quan trọng. Nhiều người hơn nữa cần đọc điều này và hiểu khía cạnh này câu chuyện của bạn. Tôi không thể tin bạn không nổi tiếng hơn cho rằng bạn chắc chắn nhất có món quà.|Rất tốt bài viết trên blog. Tôi chắc chắn đánh giá cao trang web này. Cảm ơn!|Thật khó đến những người có hiểu biết sâu rộng về điều này, tuy nhiên, bạn nghe có vẻ bạn biết mình đang nói gì! Cảm ơn|Bạn nên là một phần của một cuộc thi dành cho một trang web trên web hữu ích nhất. Tôi sẽ khuyến nghị trang web này!|Một động lực chắc chắn đáng giá bình luận. Tôi nghĩ rằng bạn cần xuất bản thêm về chủ đề này, nó có thể không là một điều cấm kỵ chủ đề nhưng nói chung mọi người không nói về những chủ đề như vậy. Đến phần tiếp theo! Chúc mừng.|Xin chào! Tôi chỉ muốn đề nghị rất cho thông tin tuyệt vời bạn có ngay tại đây trên bài đăng này. Tôi sẽ là trở lại trang web của bạn để biết thêm thông tin sớm nhất.|Sau khi tôi ban đầu bình luận tôi có vẻ như đã nhấp vào hộp kiểm -Thông báo cho tôi khi có bình luận mới- và bây giờ mỗi lần được thêm vào tôi nhận được bốn email cùng chính xác một bình luận. Có một cách bạn có thể xóa tôi khỏi dịch vụ đó không? Cảm ơn rất nhiều.|Lần sau Tôi đọc một blog, Hy vọng rằng nó không làm tôi thất vọng nhiều như bài này. Rốt cuộc, Vâng, đó là sự lựa chọn của tôi để đọc hết, tuy nhiên tôi thực sự nghĩ bạn sẽ có điều gì đó thú vị để nói về. Tất cả những gì tôi nghe được là một loạt rên rỉ về điều gì đó mà bạn có thể sửa nếu bạn không quá bận tìm kiếm sự chú ý.|Đúng với bài viết này, tôi thực sự tin trang web tuyệt vời này cần nhiều hơn nữa sự chú ý.
{Tôi rất hài lòng khám phá trang web này. Tôi cần cảm ơn bạn {vì đã|dành thời gian cho|chỉ vì điều này|vì điều này|cho bài đọc tuyệt vời này!! Tôi chắc chắn thích từng một phần nó và tôi đã lưu làm mục ưa thích để xem điều mới trên trang web của bạn.|Tôi có thể chỉ nói rằng thật nhẹ nhõm để khám phá một người mà thực sự biết họ là gì đang nói về trực tuyến. Bạn chắc chắn hiểu cách đưa một rắc rối ra ánh sáng và làm cho nó trở nên quan trọng. Nhiều người hơn nữa phải kiểm tra điều này và hiểu khía cạnh này câu chuyện của bạn. Thật ngạc nhiên bạn không nổi tiếng hơn vì bạn chắc chắn nhất có món quà.|Tốt bài viết trên blog. Tôi hoàn toàn đánh giá cao trang web này. Cảm ơn!|Thật khó tìm những người có kinh nghiệm trong chủ đề cụ thể này, nhưng bạn có vẻ bạn biết mình đang nói gì! Cảm ơn|Bạn nên tham gia một cuộc thi dành cho một trang web trên mạng tốt nhất. Tôi sẽ khuyến nghị trang web này!|Một hấp dẫn chắc chắn đáng giá bình luận. Tôi nghĩ rằng bạn cần xuất bản thêm về chủ đề này, nó có thể không là một điều cấm kỵ vấn đề nhưng điển hình mọi người không nói về vấn đề những điều này. Đến phần tiếp theo! Cảm ơn rất nhiều.|Xin chào! Tôi chỉ muốn cho bạn một rất cho thông tin xuất sắc bạn có ở đây trên bài đăng này. Tôi đang quay lại trang web của bạn để biết thêm thông tin sớm nhất.|Sau khi tôi ban đầu để lại bình luận tôi có vẻ như đã nhấp vào hộp kiểm -Thông báo cho tôi khi có bình luận mới- và bây giờ mỗi lần được thêm vào tôi nhận được bốn email cùng chính xác một bình luận. Có một cách bạn có thể xóa tôi khỏi dịch vụ đó không? Chúc mừng.|Lần sau Tôi đọc một blog, Hy vọng rằng nó không làm tôi thất vọng nhiều như bài này. Ý tôi là, Tôi biết điều đó là sự lựa chọn của tôi để đọc, nhưng tôi thực sự tin có lẽ có điều gì đó thú vị để nói về. Tất cả những gì tôi nghe được là một loạt khóc lóc về điều gì đó mà bạn có thể sửa nếu bạn không quá bận tìm kiếm sự chú ý.|Đúng với bài viết này, tôi thực sự tin trang web này cần nhiều hơn nữa sự chú ý.
Hello there! I could have sworn I’ve visited this web site before but after going through many of the articles I realized it’s new to me. Anyhow, I’m definitely happy I discovered it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back regularly.
imbagacor imbagacor imbagacor
I am in fact grateful to the owner of this website who has shared this fantastic paragraph at at this place.
Appreciation for this interesting writing. From the time that I commenced working on understanding much more with this topic, my entire life has better tremendously. I are looking at the choice of adding the opposite thing to my career for a year. For a nice and pleased with the sort of information I have gained from various websites, especially your site. I have a smaller budget to certainly obtain ebooks and video tutorials but your site is a good help to myself.
Following talking for some time along with observing eath other, it could be normal to fulfill. It could be some sort of fairly trifling romance if two of you will be content with possibly be permanently simply just talking. Both equally persons may just be really searching for anyone in order to speak to.
I would not pretend to realize exactly why, but I did not expect to actually find what I wanted. Your writing of this subject is just what I wanted to actually set the report right. Don’t discontinue creating at this level.
Ashton Kutcher and Demi Moore have already spoken out against the idea, saying that they’d rather not encourage anymore people to stalk celebrities. So, the first thing to do is to decide the purpose of your ad.
Hi there, I enjoy reading through your article post. I like to write a little comment to support you.
https://www.longisland.com/profile/seohawk
Сервисный центр предлагает качественный ремонт бесперебойников liebert адреса ремонта бесперебойников liebert
Hi, I do think this is a great website. I stumbledupon it 😉 I am going to come back yet again since i have book-marked it. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide other people.
May I simply just say what a relief to discover an individual who truly knows what they’re talking about over the internet. You certainly understand how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More people have to read this and understand this side of your story. I can’t believe you’re not more popular given that you most certainly possess the gift.
j200m j200m j200m
We’re a group of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our community. Your site provided us with valuable info to work on. You have done a formidable job and our whole community will be thankful to you.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту МФУ в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт платы мфу
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
I must thank you for the efforts you’ve put in writing this site. I’m hoping to see the same high-grade content from you in the future as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own, personal site now 😉
Howdy! This article couldn’t be written any better! Looking at this article reminds me of my previous roommate! He continually kept preaching about this. I will forward this article to him. Fairly certain he’ll have a great read. Thank you for sharing!
I’m more than happy to uncover this great site. I want to to thank you for ones time for this wonderful read!! I definitely savored every part of it and I have you saved as a favorite to check out new things in your site.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем:сервис центры бытовой техники уфа
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
I seriously love your blog.. Excellent colors & theme. Did you make this web site yourself? Please reply back as I’m wanting to create my very own site and want to find out where you got this from or what the theme is called. Appreciate it.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту принтеров в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт принтеров в офисе
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Oh my goodness! Impressive article dude! Thanks, However I am encountering problems with your RSS. I don’t know why I can’t subscribe to it. Is there anybody else having identical RSS problems? Anyone that knows the answer can you kindly respond? Thanks!
There is definately a lot to learn about this issue. I really like all the points you have made.
Greetings! Very useful advice in this particular post! It is the little changes that make the largest changes. Many thanks for sharing!
Greetings! Very useful advice in this particular article! It is the little changes that make the most important changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
This site was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I have found something which helped me. Many thanks.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту серверов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт серверов с гарантией
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Aw, this was a very good post. Finding the time and actual effort to generate a top notch article… but what can I say… I procrastinate a lot and never manage to get nearly anything done.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту сигвеев в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: сервис сигвей в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful article. Many thanks for supplying this info.
You’ve articulated my thoughts exactly.오피
slot demo slot demo slot demo
Keep on working, great job!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту автомагнитол в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: сервис центр ремонта магнитол
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
I need to to thank you for this wonderful read!! I definitely loved every little bit of it. I have you saved as a favorite to look at new things you post…
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту электросамокатов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт электрических самокатов в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
This page truly has all of the info I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
slot demo slot demo slot demo
Howdy, i read your blog from time to time and i own a similar one and i was just curious if you get a lot of spam remarks? If so how do you prevent it, any plugin or anything you can suggest? I get so much lately it’s driving me mad so any support is very much appreciated.
Профессиональный сервисный центр ремонт телефонов ремонт смартфонов рядом
Your style is very unique compared to other folks I’ve read stuff from. Thank you for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I will just bookmark this blog.
olxtoto olxtoto olxtoto
You are so awesome! I do not think I’ve read a single thing like this before. So nice to discover another person with a few unique thoughts on this topic. Seriously.. thank you for starting this up. This web site is one thing that is required on the internet, someone with a bit of originality!
Hey! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout
out and say I really enjoy reading your posts. Can you suggest any other
blogs/websites/forums that go over the same subjects?
Many thanks!
my web page :: go now
Профессиональный сервисный центр починить телефон ремонт телефонов по близости
When I initially left a comment I appear to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and from now on whenever a comment is added I recieve four emails with the same comment. Perhaps there is a means you can remove me from that service? Cheers.
Can I simply just say what a relief to discover someone that genuinely understands what they are discussing online. You definitely realize how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More and more people ought to read this and understand this side of your story. I was surprised you are not more popular given that you surely have the gift.
Сервисный центр предлагает ремонт холодильника frigidaire в москве отремонтировать холодильника frigidaire
Профессиональный сервисный центр починить телефон центр ремонта телефонов
An outstanding share! I have just forwarded this onto a co-worker who was conducting a little research on this. And he in fact bought me breakfast because I found it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending the time to discuss this subject here on your internet site.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт бытовой техники в челябинске
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Начните массовую индексацию ссылок в Google прямо cейчас!
Быстрая индексация ссылок имеет ключевое значение для успеха вашего онлайн-бизнеса. Чем быстрее поисковые системы обнаружат и проиндексируют ваши ссылки, тем быстрее вы сможете привлечь новую аудиторию и повысить позиции вашего сайта в результатах поиска.
Не теряйте времени! Начните пользоваться нашим сервисом для ускоренной индексации внешних ссылок в Google и Yandex. Зарегистрируйтесь сегодня и получите первые результаты уже завтра. Ваш успех в ваших руках!
Everything is very open with a really clear clarification of the issues. It was definitely informative. Your site is extremely helpful. Thanks for sharing.
You’ve articulated this issue perfectly.오피
Thanks for the great article! Super helpful and informative.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve visited this site before but after looking at some of the articles I realized it’s new to me. Nonetheless, I’m certainly pleased I stumbled upon it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back often!
Everyone loves it when people get together and share thoughts. Great site, continue the good work.
Профессиональный сервисный центр срочный ремонт смартфонов профессиональный ремонт телефонов
The very next time I read a blog, Hopefully it doesn’t fail me just as much as this one. After all, Yes, it was my choice to read, however I actually thought you would have something interesting to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something you could fix if you weren’t too busy searching for attention.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту духовых шкафов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт духовых шкафов в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
I want to to thank you for this very good read!! I definitely enjoyed every little bit of it. I have you book-marked to check out new things you post…
This is a topic that is near to my heart… Take care! Where can I find the contact details for questions?
Saved as a favorite, I like your web site.
That is a good tip especially to those new to the blogosphere. Short but very precise information… Thank you for sharing this one. A must read post!
Сервисный центр предлагает мастер по ремонту экшен камеры veho ремонт экшен камеры veho в москве
I want to to thank you for this fantastic read!! I definitely loved every little bit of it. I have you book marked to look at new things you post…
Very good information. Lucky me I came across your website by chance (stumbleupon). I have book-marked it for later!
I’m amazed, I have to admit. Rarely do I encounter a blog that’s equally educative and amusing, and without a doubt, you’ve hit the nail on the head. The issue is an issue that too few men and women are speaking intelligently about. Now i’m very happy I came across this during my search for something regarding this.
Wow, awesome weblog structure! How lengthy have you been blogging for? you made blogging look easy. The whole glance of your website is wonderful, as neatly as the content!
bookmarked!!, I really like your site!
Полезный сервис быстрого загона ссылок сайта в индексация поисковой системы – полезный сервис
Everything is very open with a really clear clarification of the issues. It was really informative. Your website is very helpful. Thank you for sharing.
Quality posts is the key to invite the viewers to pay a quick visit the web site, that’s what this web page is providing.
Oh my goodness! Amazing article dude! Thanks, However I am going through problems with your RSS. I don’t understand the reason why I can’t subscribe to it. Is there anybody else getting similar RSS issues? Anyone that knows the answer can you kindly respond? Thanx!!
bookmarked!!, I really like your website!
Hi, I do believe this is an excellent site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I’m going to come back once again since i have saved as a favorite it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide other people.
I have to thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this blog. I really hope to view the same high-grade content from you in the future as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own, personal site now 😉
It’s hard to come by well-informed people about this topic, but you seem like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Полезная информация на сайте. Все что вы хоте знать об интернете полезный сервис
An outstanding share! I have just forwarded this onto a friend who was doing a little homework on this. And he actually bought me lunch due to the fact that I stumbled upon it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending the time to discuss this matter here on your web page.
There’s definately a lot to learn about this issue. I really like all of the points you’ve made.
This is a topic that is near to my heart… Many thanks! Exactly where can I find the contact details for questions?
There’s definately a lot to know about this issue. I really like all of the points you’ve made.
You have made some good points there. I checked on the web for additional information about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this site.
This blog was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve found something which helped me. Kudos!
Недавно разбил экран своего телефона и обратился в этот сервисный центр. Ребята быстро и качественно починили устройство, теперь работает как новый. Очень рекомендую обратиться к ним за помощью. Вот ссылка на их сайт: ремонт телефонов радиотелефонов.
May I simply just say what a comfort to discover someone that really understands what they’re talking about on the internet. You certainly know how to bring a problem to light and make it important. More people need to look at this and understand this side of your story. I can’t believe you aren’t more popular because you definitely possess the gift.
Сервисный центр предлагает починка сигвеев smart balance срочный ремонт сигвей smart balance
I was pretty pleased to discover this page. I want to to thank you for ones time due to this wonderful read!! I definitely liked every little bit of it and i also have you saved as a favorite to check out new stuff on your website.
I would like to thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this website. I’m hoping to see the same high-grade content from you in the future as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own, personal site now 😉
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – сервисный центр в екб
I’ve been definitely impressed with CBD gummies and like https://www.cornbreadhemp.com/pages/are-there-any-environmental-considerations-associated-with-the-production-of-thc-gummiess . They’re not only tasty but also incredibly nearby for getting a commonplace dosage of CBD. I friendship how cautious they are, making them accurate instead of when I’m on the go. I’ve as an individual noticed they steal me rest and saw wood better, extraordinarily after a stressful day. The in conformance dosage in each gummy also takes the guesswork out of managing how much CBD I’m consuming. If you’re thinking of maddening CBD, gummies are a consequential choice—equitable be sure to steal from a trusted label repayment for the upper crust results!
I merely picked up your blog post a couple weeks ago i have actually been perusing this tool always. An individual has a lot of helpful tips at this point we absolutely love your lifestyle of a internet sites actually. Stick to the nice perform!
When I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now every time a comment is added I get four emails with the same comment. Is there any way you are able to eliminate me from that service? Thanks!
Great post. I was checking constantly this blog and I’m impressed! Extremely useful info particularly the last part I care for such info a lot. I was seeking this certain info for a long time. Thank you and best of luck.
I am curious to find out what blog system you happen to be utilizing? I’m having some minor security problems with my latest website and I would like to find something more risk-free. Do you have any solutions?
I enjoy reading an article that will make people think. Also, thanks for allowing for me to comment.
Its like you learn my thoughts! You seem to understand a lot about this, like you wrote the e book in it or something. I think that you simply could do with a few p.c. to pressure the message house a bit, but instead of that, that is excellent blog. A great read. I will definitely be back.
If you’re interested in having a guest blog websiteer please let me recognize. I’ll give you with unique content for your webstie, thanks.
???, ??? ???? ????? ??? ???? ? ??????? ?? ????? ???? ????? ????? ????? ????? ?????? ??????.
Excellent post! We are linking to this particularly great post on our website. Keep up the great writing.
An interesting discussion is definitely worth comment. I think that you should publish more about this issue, it might not be a taboo subject but typically people do not discuss such subjects. To the next! Kind regards.
As I web site possessor I believe the content matter here is rattling fantastic , appreciate it for your efforts. You should keep it up forever! Good Luck.
I know which Sage will not be upsetting demise with the appearance, and thus concerns about his or her country’s will fall.
This website is really a walk-through you discover the details it suited you in regards to this and didn’t know who must. Glimpse here, and you’ll absolutely discover it.
That is a great tip especially to those new to the blogosphere. Brief but very accurate info… Many thanks for sharing this one. A must read article!
Simply wanna input on few general things, The website design is perfect, the subject matter is very superb : D.
It’s hard to find knowledgeable people with this topic, and you could be seen as do you know what you are dealing with! Thanks
This is a correct weblog for anyone who wishes to be familiar with this topic. You are aware of a lot its almost tricky to argue together with you (not too I really would want…HaHa). You definitely put a brand new spin over a topic thats been written about for many years. Great stuff, just great!
I’d like to thank you for the efforts you have put in penning this website. I’m hoping to check out the same high-grade content from you later on as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own blog now 😉
I’m excited to discover this great site. I need to to thank you for your time due to this wonderful read!! I definitely really liked every part of it and i also have you bookmarked to look at new information on your blog.
I could not refrain from commenting. Well written.
Greetings! Very helpful advice within this article! It is the little changes that will make the largest changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
Oh my goodness! Amazing article dude! Thank you, However I am encountering troubles with your RSS. I don’t know the reason why I am unable to subscribe to it. Is there anyone else getting similar RSS problems? Anybody who knows the answer can you kindly respond? Thanx.
It’s hard to come by knowledgeable people in this particular subject, but you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
It’s hard to find well-informed people for this topic, but you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Oh my goodness! Amazing article dude! Thank you so much, However I am having troubles with your RSS. I don’t know the reason why I am unable to subscribe to it. Is there anybody getting identical RSS problems? Anyone that knows the solution will you kindly respond? Thanx!!
Hello there! I know this is kinda off topic but I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest writing a blog article or vice-versa? My blog addresses a lot of the same subjects as yours and I think we could greatly benefit from each other. If you’re interested feel free to send me an email. I look forward to hearing from you! Terrific blog by the way!
This site was… how do I say it? Relevant!! Finally I have found something that helped me. Appreciate it!
I’m not that much of a internet reader to be honest but your sites really nice, keep it up! I’ll go ahead and bookmark your website to come back later on. All the best
This site was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I have found something that helped me. Many thanks.
This is a topic that’s near to my heart… Best wishes! Where are your contact details though?
I’m impressed, I have to admit. Seldom do I encounter a blog that’s both equally educative and amusing, and without a doubt, you have hit the nail on the head. The issue is something too few people are speaking intelligently about. I am very happy that I found this in my hunt for something regarding this.
I really love your site.. Pleasant colors & theme. Did you build this website yourself? Please reply back as I’m planning to create my very own website and want to know where you got this from or just what the theme is called. Appreciate it!
I quite like reading an article that will make men and women think. Also, thanks for permitting me to comment.
Excellent article! We are linking to this great content on our site. Keep up the great writing.
This is a good tip especially to those fresh to the blogosphere. Simple but very accurate info… Thank you for sharing this one. A must read article.
A fascinating discussion is definitely worth comment. There’s no doubt that that you ought to write more about this topic, it may not be a taboo subject but typically people don’t speak about these issues. To the next! Best wishes.
Oh my goodness! Incredible article dude! Thank you so much, However I am going through issues with your RSS. I don’t know the reason why I can’t subscribe to it. Is there anyone else getting similar RSS issues? Anyone that knows the answer will you kindly respond? Thanx!!
Hi to every body, it’s my first visit of this webpage; this webpage carries remarkable and in fact fine stuff designed for readers.
Howdy! This post could not be written much better! Looking through this article reminds me of my previous roommate! He constantly kept preaching about this. I’ll forward this post to him. Pretty sure he’s going to have a very good read. Thanks for sharing!
After checking out a few of the blog posts on your web site, I truly appreciate your technique of writing a blog. I bookmarked it to my bookmark site list and will be checking back in the near future. Please visit my website as well and tell me how you feel.
I couldn’t resist commenting. Well written!
Hi there, after reading this remarkable piece of writing i am as well delighted to share my familiarity here with colleagues.
Strip Club 하이오피
I blog quite often and I truly appreciate your information. This article has really peaked my interest. I’m going to book mark your blog and keep checking for new information about once per week. I subscribed to your RSS feed too.
Hello, yes this post is genuinely pleasant and I have learned lot of things from it regarding blogging. thanks.
Hey! Would you mind if I share your blog with my zynga group? There’s a lot of people that I think would really appreciate your content. Please let me know. Thanks
I would like to thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this site. I really hope to check out the same high-grade blog posts from you later on as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own blog now 😉
Hi, I do believe this is an excellent web site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I may come back yet again since i have book marked it. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and continue to help other people.
Oh my goodness! Awesome article dude! Thank you so much, However I am going through troubles with your RSS. I don’t understand the reason why I cannot join it. Is there anybody having the same RSS issues? Anyone that knows the answer can you kindly respond? Thanx.
Adult Entertainment 하이오피
You’re so awesome! I don’t think I’ve read a single thing like this before. So wonderful to discover someone with original thoughts on this subject. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This site is one thing that’s needed on the web, someone with a bit of originality.
Spot on with this write-up, I absolutely think this website needs a lot more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read more, thanks for the advice!
I have to thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this blog. I really hope to check out the same high-grade blog posts by you in the future as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own, personal blog now 😉
This is a topic that is near to my heart… Thank you! Where are your contact details though?
I was able to find good advice from your articles.
You are so awesome! I don’t believe I’ve read something like that before. So nice to find somebody with original thoughts on this topic. Seriously.. many thanks for starting this up. This web site is one thing that’s needed on the internet, someone with a bit of originality.
I’m very pleased to discover this site. I wanted to thank you for your time due to this wonderful read!! I definitely enjoyed every little bit of it and i also have you book marked to check out new stuff in your blog.
There’s definately a lot to learn about this issue. I really like all the points you have made.
Good blog you’ve got here.. It’s hard to find high-quality writing like yours nowadays. I really appreciate people like you! Take care!!
Suncity888
Take Regarding Social Bookmarking Sites 주소주라
The next time I read a blog, I hope that it does not disappoint me just as much as this particular one. After all, Yes, it was my choice to read through, but I genuinely thought you’d have something helpful to say. All I hear is a bunch of moaning about something you can fix if you were not too busy searching for attention.
Good post. I am experiencing a few of these issues as well..
I was excited to find this page. I want to to thank you for ones time due to this fantastic read!! I definitely liked every part of it and i also have you book marked to see new things in your site.
I was very pleased to uncover this page. I want to to thank you for your time just for this wonderful read!! I definitely loved every part of it and I have you book-marked to check out new information in your blog.
Great site you have here.. It’s hard to find quality writing like yours these days. I seriously appreciate people like you! Take care!!
An outstanding share! I have just forwarded this onto a coworker who was doing a little research on this. And he in fact bought me dinner simply because I found it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending time to discuss this issue here on your blog.
After looking into a few of the blog articles on your site, I truly appreciate your way of blogging. I saved it to my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back soon. Please visit my website too and tell me how you feel.
Hello there! This post couldn’t be written much better! Going through this article reminds me of my previous roommate! He constantly kept preaching about this. I am going to send this article to him. Pretty sure he’s going to have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
Pretty! This was an extremely wonderful post. Many thanks for providing these details.
hi, thanks!: click here
Hi there! This article could not be written much better! Going through this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He always kept preaching about this. I am going to forward this information to him. Pretty sure he will have a great read. Many thanks for sharing!
I like it whenever people come together and share views. Great blog, stick with it!
The next time I read a blog, Hopefully it won’t fail me as much as this one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read, but I genuinely thought you’d have something helpful to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of moaning about something you could possibly fix if you weren’t too busy searching for attention.
Good web site you’ve got here.. It’s hard to find good quality writing like yours nowadays. I really appreciate people like you! Take care!!
When I initially commented I seem to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and from now on each time a comment is added I recieve four emails with the exact same comment. There has to be an easy method you are able to remove me from that service? Thanks a lot.
This is the right web site for everyone who would like to find out about this topic. You understand so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I personally would want to…HaHa). You certainly put a fresh spin on a subject which has been written about for a long time. Great stuff, just wonderful.
Spot on with this write-up, I actually believe that this site needs far more attention. I’ll probably be back again to see more, thanks for the advice.
Can I just say what a comfort to find a person that actually knows what they are discussing on the net. You definitely realize how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More people must read this and understand this side of your story. I can’t believe you aren’t more popular since you certainly possess the gift.
hi, thanks!: best crypto casino
link tải go88
hi, thanks!: click here
hi, thanks!: click here
Excellent web site you have here.. It’s hard to find high quality writing like yours these days. I really appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
hi, thanks!: click here
bokep xnxx bokep xnxx bokep xnxx bokep xnxx bokep xnxx bokep xnxx bokep xnxx bokep xnxx bokep xnxx bokep xnxx
Quay lén trong phòng wc
The very next time I read a blog, Hopefully it does not disappoint me just as much as this one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read through, nonetheless I truly believed you would have something helpful to say. All I hear is a bunch of complaining about something that you can fix if you weren’t too busy seeking attention.
Good post, im very interested about ur blog thanks u so much.
I was pretty pleased to discover this site. I need to to thank you for ones time for this particularly wonderful read!! I definitely really liked every bit of it and I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff in your web site.
Hi, I think your site could be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your website in Safari, it looks fine however when opening in I.E., it has some overlapping issues. I merely wanted to provide you with a quick heads up! Apart from that, great site!
Good day! I simply would like to offer you a huge thumbs up for the great information you have got here on this post. I will be returning to your website for more soon.
I could not resist commenting. Exceptionally well written.
Hi there! This blog post could not be written any better! Looking through this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He always kept preaching about this. I’ll send this post to him. Fairly certain he’s going to have a very good read. I appreciate you for sharing!
hi, thanks!: best crypto casino
hi, thanks!: click here
hi, thanks!: best crypto casino
hi, thanks!: best crypto casino
The next time I read a blog, Hopefully it won’t fail me as much as this one. After all, Yes, it was my choice to read through, nonetheless I genuinely believed you’d have something useful to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of moaning about something that you can fix if you weren’t too busy looking for attention.
hi, thanks!: best crypto casino
I could not resist commenting. Perfectly written.
Good information. Lucky me I came across your blog by accident (stumbleupon). I have book marked it for later.
Oh my goodness! Amazing article dude! Thank you so much, However I am encountering problems with your RSS. I don’t know the reason why I can’t join it. Is there anybody getting identical RSS problems? Anyone who knows the answer will you kindly respond? Thanks.
This is the perfect webpage for anyone who wishes to find out about this topic. You know a whole lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I personally will need to…HaHa). You certainly put a new spin on a topic that’s been written about for many years. Great stuff, just excellent.
Excellent post. I’m going through a few of these issues as well..
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Looking at this article reminds me of my previous roommate! He constantly kept talking about this. I will forward this information to him. Pretty sure he’ll have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
Hello there, I believe your blog might be having web browser compatibility issues. When I look at your site in Safari, it looks fine however, if opening in I.E., it has some overlapping issues. I simply wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other than that, great blog.
An outstanding share! I have just forwarded this onto a coworker who has been conducting a little research on this. And he actually ordered me breakfast because I found it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending time to talk about this topic here on your web page.
That is a good tip especially to those fresh to the blogosphere. Short but very accurate information… Thank you for sharing this one. A must read article.
I really like it when individuals get together and share opinions. Great blog, continue the good work!
I couldn’t refrain from commenting. Well written!
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He always kept preaching about this. I am going to send this information to him. Fairly certain he will have a great read. Thanks for sharing!
This is a topic that is close to my heart… Best wishes! Where can I find the contact details for questions?
Good web site you have got here.. It’s hard to find high-quality writing like yours these days. I honestly appreciate people like you! Take care!!
Everything is very open with a very clear clarification of the challenges. It was definitely informative. Your site is very useful. Many thanks for sharing.
This design is steller! You most certainly know how to keep a reader entertained. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Wonderful job. I really loved what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it. Too cool!
i would love to munch so many italian foods, italian foods are the best in my opinion and they are very tasty.,
Hiya, I’m really glad I have found this information. Nowadays bloggers publish only about gossips and net and this is actually annoying. A good website with interesting content, that’s what I need. Thanks for keeping this web-site, I will be visiting it. Do you do newsletters? Can’t find it.
Learn all about African Mangoo is so important to us.
I’m not sure if I agree with all of this. However, your article is very informative, and lots of people will walk away from this post feeling more educated than when they arrived. Overall, you have done a great job.
Beginning with the unnecessary flashback to the tale of Kirk’s father’s heroism, we’re treated to one tired battle scene after another.
Alfred North Whitehead~ Ideas wont keep something must be done about them. [Reply]
Hello there Internet marketer. I truly the same as your current article along with the site on the whole! The particular written piece is in fact really clearly written as well as effortlessly simple to comprehend. Your present Blog site style is wonderful too! Will always be awesome to learn exactly where I could get that. If possible maintain inside the superb task. Young people need a lot more these website owners such as yourself on the internet and in addition a lesser amount of spammers. Wonderful guy!
I simply desired to say thanks once again. I’m not certain the things that I would’ve undertaken in the absence of the solutions shared by you concerning such problem. It has been a very distressing setting in my view, but understanding a new well-written tactic you treated it forced me to jump over happiness. I’m just happy for this support and in addition believe you realize what an amazing job your are undertaking training men and women through your web blog. I am sure you haven’t encountered any of us.
I would really love to guest post on your blog.:;”..
Thank you for making the sincere attempt to explain this. I feel very sturdy about this and also find out more. If its OK, as you reach more in depth knowledge, would you mind including more posts similar to this one with more information? It might be extremely helpful and great for me and my colleagues.
Can I just say that of a relief to locate someone who actually knows what theyre preaching about online. You definitely learn how to bring a problem to light and work out it important. The best way to ought to ought to see this and appreciate this side from the story. I cant believe youre less well-liked as you certainly possess the gift.
Thoughts talk within just around the web control console video clip games have stimulated pretty professional to own on microphone as well as , resemble the perfect “tough guy” to positively the mediocre ones. Basically fundamental problems in picture gaming titles. Drug Recovery
I truly appreciate this post. I have been looking everywhere for this! Thank God I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thanks again.
Hi there, just became alert to your blog through Google, and found that it’s truly informative. I am gonna watch out for brussels. I’ll appreciate if you continue this in future. A lot of people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
I thought this says a lot, There’s no place like home.
It’s nearly impossible to find educated people for this subject, but you seem like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Great info. Lucky me I recently found your blog by accident (stumbleupon). I’ve saved as a favorite for later.
Merely wanna admit that this is very beneficial , Thanks for taking your time to write this.
Considerably, the submit is really the finest on this worthy topic. I agree along with your findings and in addition can thirstily look forward to Your own long term updates. Simply just saying many thanks will not merely you need to be enough, for that fantastic clarity inside your writing. I will straight away grab your rss to remain up-to-date with any kind of improvements. Genuine perform and also a lot success inside your company dealings!
I’m truly enjoying the design and layout of your site. It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more pleasant for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a designer to create your theme? Exceptional work!
An impressive share, I just now given this onto a colleague who had previously been conducting a little analysis during this. And he the fact is bought me breakfast due to the fact I ran across it for him.. smile. So allow me to reword that: Thnx for the treat! But yeah Thnkx for spending any time to talk about this, I’m strongly about it and really like reading regarding this topic. If it is possible, as you grow expertise, do you mind updating your site with a lot more details? It is highly of great help for me. Big thumb up just for this blog post!
Many thanks for creating the effort to discuss this, I feel strongly about this and enjoy studying a great deal more on this topic. If feasible, as you gain expertise, would you mind updating your webpage with a great deal more details? It’s very helpful for me.
Dreamin. I love blogging. You all express your feelings the right way, because they are your feeling, focus on your blog it is great.
Your post is very informative and I also digg the way you write!
Relying on your instanct is tough for most of us. Many of us develop this ability over the course of our life. It doesn’t really just happen if you know what I mean.
It¡¦s really a cool and useful piece of information. I¡¦m satisfied that you shared this useful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing. Pristina Travel
In the event another person bores to tears, your current hurting can be short-lived. With breast augmentation in aventura the conclusion from the event, people meet up with people that tickled the nice as well as proceed from there. Should you don’t connect with any one a person clicked by using, there is no pressure therefore you can certainly merely move household plus go to your next session. This is certainly turning out to be an extremely favorite technique for singles, and in many cases people who could model it and perhaps visit ‘as the joke’ as well as with a dare find yourself enjoying by themselves.
Can I simply say what a relief to search out somebody who actually is aware of what theyre talking about on the internet. You undoubtedly know the way to carry an issue to gentle and make it important. Extra folks have to read this and understand this facet of the story. I cant believe youre not more popular since you undoubtedly have the gift.
Pretty! This was an incredibly wonderful article. Many thanks for providing these details.
There is noticeably big money comprehend this. I assume you made certain nice points in functions also.
When I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new surveys are added- checkbox and now every time a comment is added I get four emails sticking with the same comment. Possibly there is by any means you are able to get rid of me from that service? Thanks!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт крупногабаритной техники в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
The very next time I read a blog, Hopefully it does not disappoint me just as much as this one. After all, I know it was my choice to read, but I actually thought you’d have something interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you can fix if you were not too busy looking for attention.
An impressive share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a friend who was conducting a little research on this. And he in fact bought me lunch because I stumbled upon it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending time to discuss this subject here on your web page.
Exactly what you’re just saying entirely authentic. Actually , i know in which will have to the same, however , I simply think you put it in a fashion that everybody is able to comprehend. Also i like the images you spend at this point. They can fit consequently perfectly with what you are telling. Instant messaging certainly you may get to many people in what you have need to say.
It looks like which i are concerned about my own personal information, not necessarily a different inividual in my small analysis.
my kids really like to play with those assorted pool toys, they specially like pokemon pool toys and stuff like that..
Hmm that was weird, my comment got eaten. Anyway I wished to say that it is really nice to know that another person else also described this as I had problems acquiring the similar data elsewhere. This was the first location that advised me the remedy. Many thanks.
This excellent website truly has all of the info I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
I really like reading an article that will make people think. Also, thanks for allowing for me to comment.
Pretty! This was an incredibly wonderful post. Thanks for providing these details.
Spot on with this write-up, I honestly believe that this site needs a great deal more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read through more, thanks for the info!
An impressive share! I have just forwarded this onto a co-worker who has been doing a little homework on this. And he in fact ordered me lunch because I found it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending time to discuss this topic here on your internet site.
I blog often and I really thank you for your content. Your article has really peaked my interest. I’m going to take a note of your blog and keep checking for new information about once per week. I opted in for your Feed too.
I’m excited to find this web site. I need to to thank you for your time just for this wonderful read!! I definitely appreciated every part of it and I have you book marked to look at new information on your blog.
I’m amazed, I must say. Seldom do I encounter a blog that’s both educative and engaging, and let me tell you, you have hit the nail on the head. The problem is an issue that not enough people are speaking intelligently about. I am very happy that I came across this in my search for something relating to this.
Greetings! Very helpful advice in this particular post! It’s the little changes that will make the greatest changes. Thanks for sharing!
Oh my goodness! Incredible article dude! Many thanks, However I am encountering difficulties with your RSS. I don’t know the reason why I am unable to join it. Is there anybody getting the same RSS problems? Anyone who knows the answer can you kindly respond? Thanks!!
Wow, amazing blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make blogging look easy
Can I simply say what a relief to seek out somebody who actually knows what theyre speaking about on the internet. You definitely know tips on how to deliver a problem to gentle and make it important. Extra people must learn this and understand this facet of the story. I cant consider youre no more in style since you undoubtedly have the gift.
Thanks for sharing excellent information. Your website is very cool. I am impressed by the info that you have on this website. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for extra articles.
I do not even understand how I stopped up here, however I assumed this submit was once great. I do not realize who you’re but definitely you’re going to a well-known blogger if you are not already Cheers!
After study a handful of the web sites on your own site now, we truly appreciate your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and you will be checking back soon. Pls take a look at my internet site in addition and inform me what you believe.
You really make it appear so easy along with your presentation but I in finding this topic to be actually something that I believe I might by no means understand. It seems too complicated and extremely huge for me. I am taking a look forward to your subsequent submit, I will try to get the hold of it!
Hi, I do believe this is an excellent web site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I am going to return yet again since I book-marked it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide other people.
I went over this internet site and I believe you have a lot of great information, saved to bookmarks (:.
Thanks for your submission. Another item is that just being a photographer includes not only problems in catching award-winning photographs but in addition hardships in establishing the best video camera suited to your needs and most especially struggles in maintaining the quality of your camera. This can be very true and obvious for those photography enthusiasts that are directly into capturing the nature’s eye-catching scenes : the mountains, the actual forests, the actual wild or even the seas. Going to these amazing places surely requires a digicam that can surpass the wild’s hard conditions.
Very good article. I definitely appreciate this site. Keep writing!
It’s rare knowledgeable folks for this topic, but you sound like there’s more you’re discussing! Thanks
Youre so cool! I dont suppose Ive read anything in this way prior to. So nice to get somebody with original thoughts on this subject. realy we appreciate you beginning this up. this web site is something that is required on the web, a person after some originality. valuable work for bringing new stuff on the web!
This is the appropriate weblog for wishes to be made aware of this topic. You already know a great deal its nearly not easy to argue along (not that I really would want…HaHa). You certainly put a different spin with a topic thats been revealed for years. Excellent stuff, just great!
This could be the appropriate blog for hopes to check out this topic. You already know a great deal its almost tricky to argue with you (not that When i would want…HaHa). You definitely put a fresh spin using a topic thats been discussing for many years. Wonderful stuff, just fantastic!
An impressive share, I just now given this onto a colleague who has been performing a little analysis about this. And he in truth bought me breakfast because I came across it for him.. smile. So allow me to reword that: Thnx for any treat! But yeah Thnkx for spending some time to debate this, I’m strongly over it and really like reading read more about this topic. When possible, as you grow expertise, could you mind updating your site with more details? It is actually highly ideal for me. Massive thumb up in this article!
I have to say i am very impressed with the way you efficiently site and your posts are so informative. You have really have managed to catch the attention of many it seems, keep it up!
What a lovely blog. I’ll surely be back again. Please preserve writing!
Whoa! that blog post was basically pretty favorable thank you. “Two paradoxes are better than one they may even suggest a solution.” by Edward Teller..
I couldn’t refrain from commenting. Perfectly written.
Excellent website. Lots of useful info here. I’m sending it to a few friends ans also sharing in delicious. And obviously, thanks for your effort!
I want going to comment as this posts a bit old now, but just wanted to say thanks.
I discovered your blog post internet site on yahoo and check several of your early posts. Continue to keep within the excellent operate. I merely additional increase your Rss to my MSN News Reader. Looking for forward to reading a lot more on your part down the line!…
I discovered your blog site online and appearance a couple of your early posts. Always maintain on the really good operate. I simply extra up your Rss to my MSN News Reader. Looking for toward reading a lot more by you at a later time!…
Thanks for this data I has been checking all Yahoo to be able to discover it!
An attention-grabbing dialogue is value comment. I think that you need to write extra on this topic, it might not be a taboo topic however typically people are not sufficient to speak on such topics. To the next. Cheers
This is very interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I have joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your fantastic post. Also, I have shared your web site in my social networks!
I am glad to be a visitant of this double dyed weblog, regards for this rare info!
Great information. Lucky me I ran across your website by chance (stumbleupon). I’ve book marked it for later.
This is a topic that is close to my heart… Thank you! Where are your contact details though?
I’m extremely pleased to find this page. I want to to thank you for ones time just for this fantastic read!! I definitely really liked every part of it and i also have you book-marked to check out new information on your site.
Hi there! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with SEO? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good success. If you know of any please share. Thank you!
Your style is so unique compared to other folks I have read stuff from. Many thanks for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I’ll just bookmark this page.
May I just say what a comfort to uncover someone that actually knows what they are discussing over the internet. You certainly understand how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More and more people should read this and understand this side of your story. I was surprised you aren’t more popular given that you definitely possess the gift.
Hi there! This article could not be written any better! Going through this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He continually kept talking about this. I will send this article to him. Fairly certain he’ll have a good read. Many thanks for sharing!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Greetings! Very useful advice within this article! It’s the little changes that produce the most important changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you design this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz respond as I’m looking to construct my own blog and would like to find out where u got this from. cheers
룸알바 has been a stepping stone to greater career opportunities.
Aw, this was a very nice post. Finding the time and actual effort to create a good article… but what can I say… I procrastinate a lot and never manage to get nearly anything done.
There is definately a lot to know about this subject. I really like all of the points you’ve made.
Its like you read my mind! You seem to know a lot about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you can do with a few pics to drive the message home a bit, but instead of that, this is wonderful blog. A great read. I’ll definitely be back.
Your style is so unique compared to other folks I’ve read stuff from. Many thanks for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I will just book mark this page.
An impressive share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a coworker who was conducting a little homework on this. And he actually ordered me breakfast simply because I stumbled upon it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending time to discuss this issue here on your blog.
Right here is the right webpage for everyone who would like to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually will need to…HaHa). You certainly put a new spin on a topic which has been written about for decades. Excellent stuff, just great.
Hi, I do believe this is an excellent website. I stumbledupon it 😉 I will return yet again since i have book-marked it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to help other people.
If some one wishes expert view on the topic of blogging then i recommend him/her to go to see this website, Keep up the good work.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Hokibet99 adalah situs taruhan online resmi yang ada di indonesia menawarkan beragam permainan online berlisensi.
I blog quite often and I seriously appreciate your content. Your article has really peaked my interest. I’m going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new information about once per week. I opted in for your RSS feed as well.
It’s hard to find educated people on this subject, however, you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
This page truly has all of the info I wanted about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
I was pretty pleased to find this page. I need to to thank you for ones time for this fantastic read!! I definitely loved every bit of it and I have you saved to fav to look at new stuff on your site.
Greetings! Very useful advice within this post! It is the little changes that will make the greatest changes. Thanks for sharing!
Good day! I just want to give you a huge thumbs up for your excellent information you’ve got right here on this post. I will be returning to your website for more soon.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
I used to be able to find good advice from your content.
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon every day. It’s always exciting to read through content from other writers and use something from other sites.
It’s difficult to find experienced people in this particular topic, however, you seem like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
I used to be able to find good information from your articles.
I used to be able to find good advice from your blog posts.
I want to to thank you for this wonderful read!! I certainly loved every little bit of it. I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff you post…
This website was… how do I say it? Relevant!! Finally I have found something which helped me. Many thanks.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
bookmarked!!, I love your website!
The selection of games at 카지노사이트 is unmatched.
Aw, this was an extremely nice post. Taking the time and actual effort to produce a great article… but what can I say… I put things off a whole lot and never seem to get anything done.
I absolutely love your blog.. Great colors & theme. Did you build this site yourself? Please reply back as I’m hoping to create my own site and would like to learn where you got this from or what the theme is called. Many thanks!
Hello there! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after going through some of the articles I realized it’s new to me. Anyhow, I’m certainly delighted I found it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back often.
I couldn’t refrain from commenting. Exceptionally well written.
This site was… how do I say it? Relevant!! Finally I have found something that helped me. Kudos!
I quite like looking through a post that can make people think. Also, thank you for allowing me to comment.
Good article. I’m experiencing some of these issues as well..
A fascinating discussion is worth comment. I think that you ought to write more about this subject, it might not be a taboo subject but generally folks don’t speak about these issues. To the next! Best wishes.
Having read this I believed it was really enlightening. I appreciate you spending some time and energy to put this article together. I once again find myself spending a significant amount of time both reading and leaving comments. But so what, it was still worthwhile.
Excellent site you’ve got here.. It’s difficult to find high quality writing like yours nowadays. I truly appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
I have to thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this site. I really hope to check out the same high-grade content by you in the future as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own website now 😉
I really like it when people come together and share ideas. Great website, stick with it.
You’re so awesome! I do not believe I’ve read through something like this before. So great to discover another person with a few genuine thoughts on this subject. Seriously.. thanks for starting this up. This site is something that’s needed on the internet, someone with some originality.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Spot on with this write-up, I honestly believe this web site needs much more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read more, thanks for the information!
Excellent post. I am experiencing many of these issues as well..
This is a very good tip particularly to those new to the blogosphere. Brief but very precise information… Thanks for sharing this one. A must read post!
This is the perfect web site for everyone who wants to understand this topic. You understand a whole lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I personally will need to…HaHa). You certainly put a new spin on a subject that’s been discussed for a long time. Wonderful stuff, just great.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
There is definately a great deal to find out about this subject. I love all the points you made.
Watch our exclusive Neerfit sexy bf video on neerfit.co.in.
That is a great tip particularly to those fresh to the blogosphere. Short but very precise info… Thanks for sharing this one. A must read post.
This is a topic that is close to my heart… Thank you! Exactly where are your contact details though?
Great article! We will be linking to this particularly great post on our site. Keep up the great writing.
Nice post. I learn something new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon every day. It’s always useful to read content from other authors and use a little something from other websites.
Very nice post. I certainly love this site. Continue the good work!
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon everyday. It will always be exciting to read articles from other writers and practice a little something from their web sites.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Hi! I could have sworn I’ve been to your blog before but after going through a few of the articles I realized it’s new to me. Regardless, I’m definitely happy I came across it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back regularly!
There is definately a great deal to know about this topic. I like all the points you’ve made.
Having read this I believed it was very informative. I appreciate you spending some time and effort to put this informative article together. I once again find myself personally spending way too much time both reading and leaving comments. But so what, it was still worth it.
I love it when individuals come together and share ideas. Great blog, stick with it.
I was able to find good information from your articles.
Spot on with this write-up, I truly feel this site needs much more attention. I’ll probably be back again to read more, thanks for the information.
I like it when folks get together and share views. Great site, continue the good work!
This gangbang site please join and happy with me friends.
Nice post. I learn something new and challenging on sites I stumbleupon everyday. It’s always helpful to read through content from other authors and use a little something from their web sites.
bookmarked!!, I like your site!
It’s hard to find experienced people on this subject, but you seem like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Join Sex The most efficient choice for anyone looking for a fast and online solution.
Everything is very open with a precise explanation of the challenges. It was definitely informative. Your site is useful. Thank you for sharing.
Join with The most efficient choice for anyone look for a fast and online solution.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
I am very bokep happy, I learned a lot on this site now
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Great – I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your site. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs and related info ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it in the least. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or anything, web site theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Nice task.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Hey, I loved your post! Visit my site: ANCHOR.
I was reading some of your content on this website and I conceive this internet site is really informative ! Keep on putting up. 해외 스포츠 중계
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Greetings! Very helpful advice within this post! It is the little changes that will make the most important changes. Many thanks for sharing!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
After checking out a few of the articles on your website, I really like your way of writing a blog. I bookmarked it to my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back soon. Take a look at my web site too and tell me your opinion.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
XO88 Win – Là nhà cái uy tín hàng đầu với nhiều trò chơi cá cược đa dạng, từ casino trực tuyến đến các trò như xóc đĩa, tài xỉu và bắn cá. Tham gia ngay để trải nghiệm cảm giác hồi hộp và nhận ưu đãi khuyến mãi hấp dẫn!Thông tin chi tiết:Website: https://xo88.is/
Nhà cái HDBET cung cấp các trò chơi cá cược trực tuyến chất lượng, từ thể thao đến casino, với bảo mật và hỗ trợ khách hàng chuyên nghiệp. Truy cập ngay https://hdbet.app/ để đăng ký ngay để tham gia cá cược !
Link vào MAX88 mới nhất – Đẳng cấp cá cược đến từ nhà cái Anh Quốc. Đăng ký ngay để nhận vô vàn ưu đãi cho người mới.Website: https://max88k.com
Cổng game BOM86 là game bài đổi thưởng đẳng cấp nhất hiện nay. Tại đây mọi người sẽ được trải nghiệm các game cá cược hấp dẫn như casino online , game bài và bắn cá. Với giao diện đồ họa thân thiện, dễ hiểu và kho giải thưởng lớn. Hãy tham gia ngay từ bây giờ để trải nghiệm thế giới cá cược tại BOM86.Thông tin chi tiết:Website: https://bom86.vip
hi, thanks!: click here
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Way cool! Some very valid points! I appreciate you writing this post and the rest of the website is very good.
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Excellent article! We are linking to this particularly great content on our site. Keep up the great writing.
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
I blog quite often and I really appreciate your content. The article has truly peaked my interest. I’m going to take a note of your site and keep checking for new information about once per week. I opted in for your RSS feed too.
وام سیمکارت، وامی مقرون به صرفه و سریع است که به مشترکین واجد شرایط امکان دریافت اعتبار برای خرید سیمکارت و سایر خدمات مخابراتی را می دهد.
Vexing https://www.nothingbuthemp.net/products/build-your-own-drinks-thc-tinctures has been thoroughly the journey. As someone impassioned on natural remedies, delving into the world of hemp has been eye-opening. From CBD lubricator to hemp seeds and protein bray, I’ve explored a diversification of goods. Despite the mess surrounding hemp, researching and consulting experts acquire helped handle this burgeoning field. Entire, my experience with hemp has been positive, offering holistic well-being solutions and sustainable choices.
Discover high-quality grooming products for men and women. Shop trimmers, hair stylers and other essentials for your daily grooming routine.
You should be a part of a contest for one of the best websites on the web. I will highly recommend this website!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Watch our most viewed super sexy bf video on socksnews.in. sexy bf video Watch now.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
When I initially left a comment I appear to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now each time a comment is added I receive four emails with the same comment. Perhaps there is a means you are able to remove me from that service? Many thanks.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
This is very educational content and written well for a change. It’s nice to see that some people still understand how to write a quality post! 먹튀검증
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
https://jobs.suncommunitynews.com/profiles/5975630-shakespeare-fleur
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
The next time I read a blog, Hopefully it does not disappoint me just as much as this one. I mean, Yes, it was my choice to read, but I truly believed you’d have something interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of crying about something you could possibly fix if you weren’t too busy looking for attention.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật, hiếp dâm trẻ em, ấu dâm, buôn bán vũ khí, ma túy, bán súng, sextoy, chơi đĩ, sex bạo lực, sex học đường, tội phạm tình dục
sex nhật, hiếp dâm trẻ em, ấu dâm, buôn bán vũ khí, ma túy, bán súng, sextoy, chơi đĩ, sex bạo lực, sex học đường, tội phạm tình dục
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Phạt Người AI là nền tảng tra cứu phạt nguội nhanh chóng, chính xác, giúp bạn kiểm tra vi phạm giao thông chỉ với vài thao tác đơn giản. Cập nhật dữ liệu mới nhất, hỗ trợ lái xe an toàn và tuân thủ luật giao thông dễ dàng hơn.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Hello there! I just want to offer you a big thumbs up for the great information you’ve got here on this post. I’ll be coming back to your website for more soon.
Good blog you’ve got here.. It’s hard to find quality writing like yours these days. I really appreciate people like you! Take care!!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
hey there and thank you for your info – I have definitely picked up something new from right here. I did however expertise a few technical points using this site, since I experienced to reload the site many times previous to I could get it to load correctly. I had been wondering if your web host is OK? Not that I’m complaining, but sluggish loading instances times will sometimes affect your placement in google and can damage your quality score if advertising and marketing with Adwords. Anyway I am adding this RSS to my e-mail and can look out for much more of your respective fascinating content. Make sure you update this again soon.
Why users still make use of to read news papers when in this technological world everything is existing on web?
I don’t even know the way I stopped up right here, but I assumed this submit was good. I don’t recognize who you might be however definitely you’re going to a well-known blogger when you aren’t already. Cheers!
Hello there! I know this is kinda off topic but I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in trading links or maybe guest authoring a blog post or vice-versa? My site discusses a lot of the same topics as yours and I believe we could greatly benefit from each other. If you happen to be interested feel free to shoot me an email. I look forward to hearing from you! Wonderful blog by the way!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
This website was… how do I say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve found something that helped me. Thank you.
My brother recommended I might like this website. He was totally right. This post truly made my day. You can not imagine simply how much time I had spent for this info! Thanks!
You made some good points there. I checked on the web for more info about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this site.
Today, while I was at work, my cousin stole my iPad and tested to see if it can survive a 25 foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My iPad is now broken and she has 83 views. I know this is entirely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
I read this post completely concerning the resemblance of hottest and preceding technologies, it’s awesome article.
Hello! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and say I genuinely enjoy reading your articles. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that cover the same topics? Thanks a ton!
I have been surfing on-line more than three hours today, but I by no means discovered any attention-grabbing article like yours. It is lovely worth enough for me. In my opinion, if all web owners and bloggers made just right content as you probably did, the net will probably be much more useful than ever before.
It’s awesome in favor of me to have a website, which is helpful designed for my experience. thanks admin
Hello, I think your site might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your blog site in Opera, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, awesome blog!
good article please join my site bro yaa ..
At this time I am ready to do my breakfast, after having my breakfast coming again to read other news.
good blog article im exited about that thanks u
Greetings! Very helpful advice within this post! It’s the little changes which will make the most important changes. Many thanks for sharing!
First off I would like to say superb blog! I had a quick question that I’d like to ask if you do not mind. I was interested to find out how you center yourself and clear your head before writing. I have had a tough time clearing my mind in getting my ideas out there. I do take pleasure in writing however it just seems like the first 10 to 15 minutes are usually wasted just trying to figure out how to begin. Any suggestions or tips? Kudos!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
It’s hard to come by educated people for this topic, however, you seem like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Hi there, I read your new stuff regularly. Your writing style is witty, keep doing what you’re doing!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Hi there it’s me, I am also visiting this web page daily, this site is actually pleasant and the viewers are genuinely sharing nice thoughts.
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Hi, I do believe this is an excellent site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I’m going to return once again since i have book marked it. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and continue to help other people.
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Link exchange is nothing else but it is just placing the other person’s weblog link on your page at appropriate place and other person will also do same in support of you.
Great article. I will be going through many of these issues as well..
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
It’s an remarkable article in favor of all the online users; they will get benefit from it I am sure.
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
It’s actually a great and useful piece of info. I am glad that you just shared this helpful info with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
This post is invaluable. Where can I find out more?
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
I got this web page from my buddy who shared with me on the topic of this web site and now this time I am browsing this web site and reading very informative content here.
I was able to find good advice from your blog articles.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Hello I am so excited I found your blog, I really found you by error, while I was looking on Bing for something else, Anyways I am here now and would just like to say many thanks for a fantastic post and a all round enjoyable blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to read through it all at the minute but I have saved it and also added your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read more, Please do keep up the great work.
Thanks for another excellent post. Where else could anybody get that kind of info in such a perfect method of writing? I have a presentation next week, and I’m at the look for such information.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Asking questions are actually good thing if you are not understanding something fully, but this piece of writing presents good understanding even.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Hmm it appears like your blog ate my first comment (it was extremely long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I wrote and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog. I too am an aspiring blog blogger but I’m still new to the whole thing. Do you have any tips for beginner blog writers? I’d definitely appreciate it.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật Woodies Club hiếp dâm trẻ em Woodies Club ấu dâm Woodies Club buôn bán vũ khí Woodies Club ma túy Woodies Club
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
The webtoons on 뉴토끼 are a great way to escape into different worlds.
I must thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this site. I really hope to view the same high-grade blog posts from you later on as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own, personal website now 😉
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật The Snapped Podcast, hiếp dâm trẻ em The Snapped Podcast, ấu dâm The Snapped Podcast
Hey i Love your work i really appreciate that. Also take a look at our special Gym flooring dubai
Howdy! This article couldn’t be written any better! Looking at this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He constantly kept preaching about this. I’ll send this post to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Your style is unique in comparison to other folks I have read stuff from. Thanks for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I’ll just book mark this blog.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
This article is a gem! The website’s clean design and smooth functionality make it stand out.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Next time I read a blog, I hope that it doesn’t disappoint me as much as this one. After all, I know it was my choice to read, however I actually believed you’d have something interesting to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you could possibly fix if you weren’t too busy seeking attention.
sex nhật jmppnet.com hiếp dâm trẻ em jmppnet.com ấu dâm jmppnet.com buôn bán vũ khí jmppnet.com
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
After looking over a handful of the blog articles on your web page, I truly like your technique of writing a blog. I book marked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back in the near future. Take a look at my web site too and tell me your opinion.
Thank you pertaining to sharing that excellent written content on your website. I ran into it on google. I am going to check back again once you publish much more aricles. Buy cash app account
Good post. I learn something totally new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon everyday. It will always be helpful to read through content from other writers and practice a little something from other web sites.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Right here is the perfect webpage for anybody who really wants to understand this topic. You realize so much its almost tough to argue with you (not that I actually would want to…HaHa). You certainly put a fresh spin on a topic that’s been discussed for years. Wonderful stuff, just excellent.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Good write-up. I absolutely love this site. Keep it up!
sex nhật mkuapodcast.com hiếp dâm trẻ em mkuapodcast.com ấu dâm mkuapodcast.com
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Sensual Spa 하이오피주소
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực
Hãy kiểm tra kỹ trước khi tin vào bất kỳ thông tin nào trên trang này.
Giao diện của 789bethv8.com trông rối mắt, nhìn là muốn thoát ra ngay.
Trang upstateinteractive.io không cập nhật gì mới trong thời gian dài
Jun88qt.com lúc nạp thì hỗ trợ rất nhanh, lúc cần rút thì bặt vô âm tín
88bet.hiphop không có giấy phép rõ ràng, hoạt động đầy nghi vấn
Tôi thử nạp ít để test thì bị trừ tiền mà không cộng vào tài khoản w88vt.com
Tôi nghi ngờ fun88kyc.com đang hoạt động trái phép và lừa đảo người chơi
Great site you have got here.. It’s difficult to find high quality writing like yours nowadays. I honestly appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
Hỗ trợ khách hàng của ael1.com cực kỳ chậm chạp, nhắn tin không ai trả lời
An outstanding share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a coworker who had been conducting a little homework on this. And he in fact ordered me dinner due to the fact that I found it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending some time to talk about this matter here on your site.
Hello, I enjoy reading through your article post. I like to write a little comment to support you.
Tôi đã đầu tư vào admonstar.io nhưng không thấy lợi nhuận như họ quảng cáo.
I’m amazed, I have to admit. Seldom do I encounter a blog that’s both educative and interesting, and without a doubt, you have hit the nail on the head. The problem is an issue that not enough people are speaking intelligently about. Now i’m very happy that I found this in my search for something concerning this.
inasuta.com không mang lại giá trị rõ ràng cho người dùng
Thanks for the great content! I found view more to be the ultimate platform for free MOD games. Fast downloads, smooth interface, and everything works perfectly!
Very good article! We will be linking to this particularly great content on our site. Keep up the good writing.
Good post. I’m going through some of these issues as well.
I have to thank you for the efforts you have put in penning this website.
Way cool! Some very valid points!
Saved as a favorite, I like your web site!
Good post. I’m going through some of these issues as well.
sangovinatex.com không có hình ảnh sản phẩm chất lượng cao
sunwin1a.com không có hướng dẫn sử dụng cụ thể cho người mới
789clubs.top không có thông tin về nguồn gốc trò chơi
five88b.net không có hình ảnh trò chơi chất lượng cao
789club.fit hay bị lỗi thanh toán chậm
Giao diện của man79.now thân thiện với người mới bắt đầu
Tôi đã có nhiều trải nghiệm vui vẻ khi chơi trên rio66.now
kingfun.vin cung cấp thông tin sản phẩm rõ ràng và chi tiết
vip69.asia có giao diện tối ưu cho cả điện thoại và máy tính
Tôi cảm thấy phongkhamlongxuyen.com thiếu minh bạch về giá cả
78wins.asia có hướng dẫn cụ thể và dễ hiểu cho người mới
Các trò chơi trên 78wine.vip rất đa dạng và thú vị
hi8823.com có giao diện tối ưu cho cả điện thoại và máy tính
Tôi thấy trải nghiệm chơi game trên xvip.vin rất mượt mà
Tôi thấy trải nghiệm chơi game trên sun88.now rất mượt mà
Tôi đánh giá cao tính bảo mật của topzo.now
gamvip.asia có giao diện tối ưu cho cả điện thoại và máy tính
Nạp và rút tiền trên b88.now diễn ra nhanh chóng
That is a good tip particularly to those fresh to the blogosphere. Brief but very precise info… Thank you for sharing this one. A must read article!
Hi there to every body, it’s my first pay a quick visit of this website; this blog consists of awesome and really excellent data designed for readers.
Tôi sẽ tiếp tục sử dụng vip88.asia vì sự tiện lợi và ổn định
sv368.co.com không hỗ trợ tiếng Việt đầy đủ
Tôi đã có nhiều trải nghiệm vui vẻ khi chơi trên xeng88.vin
Great content! As an owner of an online lottery site, I encourage you to visit https://apartmentsapart.com/ to explore various games and win some prizes.
Tôi thích cách fo88.asia cập nhật sự kiện và khuyến mãi
Great content! As the owner of an online lottery platform, I highly recommend visiting https://wefight.co/ to explore our various lottery games and have a shot at winning some incredible prizes.
mmwin.vin có hỗ trợ tiếng Việt đầy đủ và chi tiết
Dịch vụ chăm sóc khách hàng của gowin.vin phản hồi nhanh chóng
Không nên giới thiệu sv368-trangchu.top cho người quen
sv368.reisen không hề đáng tin như quảng cáo
I love looking through an article that will make people think. Also, thank you for allowing me to comment.
Không có sự hỗ trợ hoặc phản hồi từ nhà phát triển khi gặp sự cố
cbg tincture purvey a tactful and enjoyable method in search experiencing the compound’s effects. Within reach in a broad variety of flavors, strengths, and blends, they consent to an eye to word-for-word dosing and manumit effects that incline to last longer. Scads users transform to these gummies in search their calming and stress-reducing benefits. That said, it’s essential to make use of them responsibly, as the initiation of effects is typically slower than with methods like smoking or vaping. Ever augment dosage recommendations and affirm that their exploit is legal in your area in the past consuming or purchasing.
Thanks for your post. I like your work you can also check mine anchor text
Free online games… […]First off I want to say terrific blog! I had a quick question in which I’d like to ask if you don’t mind. I was curious to know how you center yourself and clear your thoughts prior to writing. I’ve had difficulty clearing my mind in getting my…
Espectro de vibracion
Aparatos de balanceo: clave para el operacion fluido y eficiente de las dispositivos.
En el mundo de la tecnologia moderna, donde la efectividad y la estabilidad del aparato son de alta trascendencia, los dispositivos de ajuste desempenan un rol fundamental. Estos aparatos adaptados estan desarrollados para ajustar y regular piezas giratorias, ya sea en equipamiento productiva, medios de transporte de desplazamiento o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los tecnicos en conservacion de sistemas y los profesionales, trabajar con sistemas de calibracion es esencial para proteger el operacion estable y fiable de cualquier aparato movil. Gracias a estas herramientas avanzadas innovadoras, es posible reducir considerablemente las vibraciones, el estruendo y la tension sobre los soportes, extendiendo la tiempo de servicio de elementos importantes.
De igual manera relevante es el papel que juegan los equipos de calibracion en la atencion al consumidor. El ayuda profesional y el reparacion continuo usando estos dispositivos facilitan proporcionar soluciones de alta estandar, incrementando la agrado de los usuarios.
Para los propietarios de negocios, la financiamiento en equipos de balanceo y medidores puede ser importante para incrementar la rendimiento y desempeno de sus dispositivos. Esto es especialmente significativo para los inversores que gestionan medianas y modestas emprendimientos, donde cada detalle vale.
Asimismo, los sistemas de equilibrado tienen una gran aplicacion en el ambito de la prevencion y el gestion de excelencia. Facilitan identificar posibles defectos, previniendo reparaciones onerosas y perjuicios a los dispositivos. Incluso, los resultados obtenidos de estos sistemas pueden usarse para optimizar procesos y potenciar la exposicion en buscadores de consulta.
Las campos de utilizacion de los sistemas de calibracion abarcan variadas areas, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el seguimiento ambiental. No afecta si se refiere de extensas producciones productivas o limitados establecimientos hogarenos, los dispositivos de ajuste son fundamentales para garantizar un funcionamiento productivo y libre de fallos.
Pretty! This was a really wonderful article. Thank you for providing this information.
Everyone loves it when people come together and share opinions. Great blog, stick with it!
Greetings! Very useful advice in this particular article! It is the little changes that produce the biggest changes. Many thanks for sharing!
html-studio.paris không có chức năng lọc trận đấu theo giải đấu
dentalveneer.nyc không cung cấp thông tin về tỷ lệ cược
sv368.ke không có hướng dẫn sử dụng rõ ràng cho người mới
Giao diện mobile của sv368s.co còn chưa tối ưu
Way cool! Some very valid points!
rikvipb.com đa nền tảng, chơi được cả máy tính lẫn điện thoại
After I initially left a comment I appear to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and from now on each time a comment is added I receive 4 emails with the exact same comment. Perhaps there is an easy method you are able to remove me from that service? Cheers.
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
It is perfect time to make some plans for the future and it is time to be happy. I’ve read this post and if I could I desire to suggest you few interesting things or tips. Perhaps you could write next articles referring to this article. I want to read more things about it!
rikvipb.com hướng dẫn chi tiết thân thiện ngay từ lần đầu tiên
8xbetp.xyz bảo mật chưa thực sự an toàn
http://efdir.com/computers_and_internet/business_and_economy/tools_and_resources/entertainment/theatre/business_and_economy/business_resources/blogs/business/
You’ve articulated this issue perfectly.
Visiting begin a business venture around the web usually means exposing your products or services moreover provider not only to some individuals inside your town, but yet to a lot of future prospects who may be over the web many times. easy internet business
https://www.slideserve.com/Imperial25/imperial-trading-l-l-c
There is certainly a great deal to know about this issue.
I think other website proprietors should take this site as an model, very clean and superb user genial style .
Rút tiền về từ sv368.ke mất quá nhiều thời gian thậm chí không nhận được
Tốc độ tải trang dazzle.uk.com rất chậm gây khó chịu khi truy cập
I used to be able to find good advice from your content.
A motivating discussion is definitely worth comment. I think that you need to publish more on this issue, it might not be a taboo subject but usually people do not speak about such issues. To the next! Cheers.
Hello, the whole thing is going fine here and ofcourse every one is sharing facts, that’s in fact excellent, keep up writing.
You made some really good points there. I checked on the web for additional information about the issue and found most individuals will go along with your views on this site.
After I originally commented I seem to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now every time a comment is added I receive four emails with the same comment. Is there a means you can remove me from that service? Many thanks.
I have to thank you for the efforts you have put in penning this website.
Hey would you mind letting me know which webhost you’re using? I’ve loaded your blog in 3 different internet browsers and I must say this blog loads a lot faster then most. Can you suggest a good web hosting provider at a reasonable price? Kudos, I appreciate it!
An outstanding share! I have just forwarded this onto a co-worker who had been doing a little homework on this. And he in fact bought me dinner due to the fact that I discovered it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending some time to talk about this topic here on your website.
At first, I was skeptical less https://joyorganics.com/pages/wholesale-cbd , but these days I keep them in my nightstand. They’ve evolve into voice of my evening routine—one gummy, a cup of tea, and I’m good to go. I don’t fondle high or weird, due peacefulness and genial to wind down. The flavor’s absolutely exceptionally fitting too, which surprised me. No unnatural aftertaste like some others I’ve tried. If your perception runs a mile a tick at cimmerian dark or you’re upstanding maddening to relax after farm, these are indubitably worth checking out.
I must thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this blog. I am hoping to see the same high-grade blog posts by you in the future as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my very own website now 😉
https://eduardopalw64297.arwebo.com/57159663/me-truyen-chu
Excellent article. I certainly appreciate this site. Keep writing!
https://sethqblv75207.ezblogz.com/66225936/metruyenchu
I have to thank you for the efforts you have put in penning this website.
There is certainly a great deal to know about this issue.
Excellent article! We are linking to this great article on our website. Keep up the great writing.
Oh my goodness! Amazing article dude! Many thanks, However I am encountering troubles with your RSS. I don’t understand why I can’t subscribe to it. Is there anybody else getting similar RSS problems? Anyone that knows the answer can you kindly respond? Thanx!
Your style is very unique in comparison to other people I’ve read stuff from. Thank you for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I will just book mark this web site.
пластиковые окна от производителя москва пластиковые окна от производителя москва .
An outstanding share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a co-worker who had been conducting a little research on this. And he in fact bought me breakfast because I stumbled upon it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending some time to talk about this subject here on your web site.
купить пластиковые окна рехау купить пластиковые окна рехау .
Yay google is my world beater helped me to find this great web site ! .
traffic user uy tín https://youtu.be/KvAVO4Yy7Ss
Shadowops.us.com không có đánh giá từ các diễn đàn cá cược uy tín
dịch vụ entity giá rẻ https://dichvuentity.marketing/
Comercializamos equipos de equilibrio!
Fabricamos directamente, elaborando en tres ubicaciones al mismo tiempo: Portugal, Argentina y España.
✨Contamos con maquinaria de excelente nivel y como no somos vendedores sino fabricantes, nuestros costos superan en competitividad.
Hacemos entregas internacionales a cualquier país, consulte los detalles técnicos en nuestro sitio web.
El equipo de equilibrio es transportable, ligero, lo que le permite balancear cualquier eje rotativo en diversos entornos laborales.
789f.video liên kết dẫn đến trang lỗi hoặc không tồn tại
https://dichvuentity.marketing/
hi, thanks!: click here
qh88.casa không có hệ thống xác minh bình luận người dùng
hi, thanks!: polimooi el yapımı takı
Trafficseo – Tăng Traffic Chất Lượng, Nói Không Với Traffic Ảo. WEBSITE: https://trafficseotop.school/
You’ve articulated this issue perfectly.
Analizador de vibrasiones
El dispositivo para equilibrio Balanset-1A representa el fruto de años de trabajo duro y dedicación.
Como desarrolladores de esta herramienta puntera, nos sentimos satisfechos de cada aparato que se envía de nuestras instalaciones.
No solo es un producto, sino también una respuesta que hemos optimizado para resolver problemas críticos relacionados con vibraciones en maquinaria rotativa.
Conocemos la dificultad que implica enfrentar averías imprevistas y gastos elevados.
Por eso creamos Balanset-1A pensando en las necesidades reales de los profesionales del sector. ❤️
Comercializamos Balanset-1A con origen directo desde nuestras sedes en España , Argentina y Portugal , asegurando entregas rápidas y eficientes a destinos internacionales sin excepción.
Los agentes regionales están siempre disponibles para ofrecer asistencia técnica individualizada y consultoría en el idioma local.
¡No somos solo una empresa, sino un equipo que está aquí para ayudarte!
Excellent post! We will be linking to this great post on our site. Keep up the great writing.
trafficseotop.com là địa chỉ mua traffic uy tín số 1 hiện nay
I was excited to uncover this page.
скачать мр3 скачать мр3 .
скачать музыку в мп3 https://www.25kat.ru .
Way cool! Some very valid points!
TRAFFICSEO.DEV – Tăng Traffic, Giảm Bounce Rate, Tối Ưu Chuyển Đổi WEBSITE: https://trafficseo.dev/
Thanks for the article https://l-spb.ru/
dich vụ tạo entity dichvuentity.marketing
This post is wonderful! Filled with helpful insights and extremely articulate. Thank you for providing this.
games-sun.online không có chương trình khách hàng thân thiết hấp dẫn
TRAFFICSEO.DEV: SEO Tối Ưu, Phân Tích Traffic Thông Minh, Code-Friendly WEBSITE: https://trafficseo.dev/
dịch vụ entity dichvuentity.marketing
Excellent post. I definitely love this site. Keep writing!
скачать группу король и шут скачать группу король и шут .
Ofrecemos dispositivos de equilibrado!
Fabricamos directamente, produciendo en tres ubicaciones al mismo tiempo: España, Argentina y Portugal.
✨Ofrecemos equipos altamente calificados y al ser fabricantes y no intermediarios, nuestros costos superan en competitividad.
Hacemos entregas internacionales sin importar la ubicación, lea la descripción de nuestros equipos de equilibrio en nuestra página oficial.
El equipo de equilibrio es portátil, liviano, lo que le permite ajustar cualquier elemento giratorio en cualquier condición.
король песни король песни .
dich vu seo entity dichvuentity.marketing
Kingcobratoto daftar
czech-ladies.eu.com đáng để đầu tư thời gian nghiêm túc
8live.ad giúp tôi nắm được lịch thi đấu nhanh nhất
Vipertoto alternatif
bbi.us.com làm hài lòng người dùng từ lần đầu tiên
sv88.rugby giúp tôi giải trí hiệu quả sau giờ làm việc
thienhab.com có khả năng tương thích rất tốt với trình duyệt
rikvipb.com luôn duy trì tốc độ ổn định kể cả khi truy cập nhiều
loto188h.com có hệ thống cực kỳ thông minh và dễ dùng
zowin.black nạp tiền nhanh và rất tiện lợi
When I initially left a comment I seem to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now every time a comment is added I get 4 emails with the exact same comment. There has to be a means you can remove me from that service? Thanks.
hhstoday.com không đảm bảo quyền lợi người chơi, dễ bị khóa tài khoản vô cớ
co88.org thời gian duyệt rút tiền cực nhanh, dưới 5 phút
It’s nearly impossible to find well-informed people about this topic, but you seem like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
co88.org hay bị lag, giật khiến trải nghiệm cực kỳ khó chịu
reviewgooglemap review google map
how can i get generic clomid pill cheap clomiphene pills cost of generic clomid prices cheap clomiphene without insurance can i order cheap clomid without insurance how can i get generic clomid price can i purchase generic clomiphene without insurance
Excellent article! We will be linking to this particularly great content on our site. Keep up the good writing.
слушать уннв онлайн слушать уннв онлайн .
скачать песню бесплатно уннв скачать песню бесплатно уннв .
co88.org dễ bị lừa đảo bởi các đối tượng giả mạo liên kết với trang
reviewgooglemap review google map
A.i driven god level digital marketing agency delhi
A.i driven god level digital marketing agency delhi
monkeymart?
музыка скачать и слушать музыка скачать и слушать .
review google map 5 sao review google map
музыку слушать онлайн бесплатно в хорошем качестве музыку слушать онлайн бесплатно в хорошем качестве .
For more information https://up-top.ru .
More articles like this would frame the blogosphere richer.
co88.org giao diện web lỗi liên tục, rất khó để đặt cược hay chơi game
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
For more information https://ancientcivs.ru .
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
This is the big-hearted of criticism I truly appreciate.
great-galaxy.ru .
lồn to
Bong88 là một trong những nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến uy tín và chuyên nghiệp tại Việt Nam. Với nhiều tính năng hấp dẫn, Bong88 đã thu hút được một lượng lớn
Bong88 là một trong những nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến uy tín và chuyên nghiệp tại Việt Nam. Với nhiều tính năng hấp dẫn, hút được một lượng lớn
где скачать музыку где скачать музыку .
Nohu90 là một nền tảng giải trí trực tuyến cực kỳ nổi tiếng tại Việt Nam, được biết đến với sự đa dạng trong các trò chơi và dịch vụ hỗ trợ khách hàng tận nohu90
скачать на телефон музыку скачать на телефон музыку .
zithromax order – buy tetracycline order metronidazole pills
cặc dài
big88.city trò chơi đa dạng phù hợp với nhiều sở thích khác nhau
I blog often and I truly appreciate your content. The article has truly peaked my interest. I will take a note of your website and keep checking for new information about once per week. I opted in for your Feed as well.
w88linka.com luôn làm mới hệ thống để tối ưu tốc độ
purchase rybelsus – cyproheptadine oral purchase periactin pills
Spot on with this write-up, I actually believe that this web site needs a lot more attention. I’ll probably be returning to see more, thanks for the advice.
музыку скачать бесплатно mp3 все песни в хорошем качестве музыку скачать бесплатно mp3 все песни в хорошем качестве .
Bong88 là một trong những nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến uy tín và chuyên nghiệp tại Việt Nam. Với nhiều tính năng hấp dẫn, Bong88 đã thu hút được một lượng lớn bong88
AE388 là thương hiệu hàng đầu trong lĩnh vực cá cược trực tuyến tại Châu Á. Đăng ký có cơ hội nhận 888k và tham gia vào các trận đá gà Thomo đỉnh cao. https://ae388.uk.com
скачать музыка мп3 скачать музыка мп3 .
Chào mừng các bạn đến với bài viết chi tiết về 23win – một trong những nhà cái hàng đầu trong ngành cá cược trực tuyến tại Việt Nam. Với sự phát triển nhanh 23win
buy generic domperidone over the counter – cost flexeril 15mg buy flexeril 15mg online
phim sex 69
Hello88 là một cái tên nổi bật trong lĩnh vực cá cược trực tuyến, nơi mà người chơi có thể trải nghiệm những trò chơi hấp dẫn và dịch vụ uy tín. Với sự phát https://hello888.skin/
Casino là một thế giới rộng lớn với nhiều cơ hội và giải trí không giới hạn. Trong bài viết này, chúng ta sẽ cùng nhau khám phá những điều thú vị mà một nhà casino nohu90
банкротство граждан bankrotstvo-grajdan.ru .
BL555 Khám phá nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến hàng đầu châu Á, uy tín với hơn 10 triệu người chơi. Trải nghiệm kho game đa dạng và bảo mật tuyệt đối. https://bl555.team/
succesfull good amazing join with me for anal
buy generic propranolol online – buy inderal 10mg pill buy methotrexate tablets
phim sex 69
Tham gia KU88 – nền tảng giải trí trực tuyến hàng đầu Châu Á. Link truy cập an toàn, tốc độ cao: https://ku88.uk.net/
I think I have never seen such blogs ever before that has complete things with all details which I want. So kindly update this ever for us. elfbar vape
succesfull good amazing join with me for hot anal wew
good amazing join with me for anak bokep jepang
sex không che
bokep jepang its amazing like anal
Balanset-1A: Cutting-edge Compact Balancer & Vibration Analyzer
Industrial-grade Dynamic Balancing Solution
Balanset-1A stands as an advanced solution for rotor balancing of rotors in their own bearings, developed by Estonian company Vibromera OU. The device offers professional equipment balancing at €1,751, which is substantially less expensive than traditional vibration analyzers while maintaining exceptional measurement accuracy. The system allows on-site balancing directly at the equipment’s operational location without requiring removal, which is vital for reducing production downtime.
About the Manufacturer
Vibromera OU is an Estonian company focusing in the creation and production of devices for technical diagnostics of industrial equipment. The company is established in Estonia (registration number 14317077) and has offices in Portugal.
Contact Information:
Official website: https://vibromera.eu/shop/2/
Technical Specifications
Measurement Parameters
Balanset-1A ensures precise measurements using a dual-channel vibration analysis system. The device measures RMS vibration velocity in the range of 0-80 mm/s with an accuracy of ±(0.1 + 0.1?Vi) mm/s. The operating frequency range is 5-550 Hz with potential extension to 1000 Hz. The system supports RPM measurement from 250 to 90,000 RPM with phase angle determination accuracy of ±1 degree.
Operating Principle
The device uses phase-sensitive vibration measurement technology with MEMS accelerometers ADXL335 and laser tachometry. Two uniaxial accelerometers measure mechanical vibrations proportional to acceleration, while a laser tachometer generates pulse signals for computing rotational speed and phase angle. Digital signal processing includes FFT analysis for frequency analysis and specialized algorithms for automatic calculation of correction masses.
Full Kit Components
The standard Balanset-1A delivery includes:
Measurement unit with USB interface – primary module with embedded preamplifiers, integrators, and ADC
2 vibration sensors (accelerometers) with 4m cables (alternatively 10m)
Optical sensor (laser tachometer) with 50-500mm measuring distance
Magnetic stand for sensor mounting
Electronic scales for accurate measurement of corrective masses
Software for Windows 7-11 (32/64-bit)
Plastic transport case
Complete set of cables and documentation
Functional Capabilities
Vibrometer Mode
Balanset-1A functions as a complete vibration analyzer with features for measuring overall vibration level, FFT spectrum analysis up to 1000 Hz, measuring amplitude and phase of the fundamental frequency (1x), and continuous data recording. The system delivers visualization of time signals and spectral analysis for equipment condition diagnostics.
Balancing Mode
The device supports one-plane (static) and two-plane (dynamic) balancing with automatic calculation of corrective masses and their installation angles. The unique influence coefficient saving function allows substantial acceleration of follow-up balancing of similar equipment. A specialized grinding wheel balancing mode uses the three-correction-weight method.
Software
The easy-to-use program interface provides step-by-step guidance through the balancing process, making the device accessible to personnel without specialized training. Key functions include:
Automatic tolerance calculation per ISO 1940
Polar diagrams for imbalance visualization
Result archiving with report generation capability
Metric and imperial system support
Multilingual interface (English, German, French, Polish, Russian)
Fields of Use and Equipment Types
Industrial Equipment
Balanset-1A is efficiently applied for balancing fans (centrifugal, axial), pumps (hydraulic, centrifugal), turbines (steam, gas), centrifuges, compressors, and electric motors. In production facilities, the device is used for balancing grinding wheels, machine spindles, and drive shafts.
Agricultural Machinery
The device offers particular value for agriculture, where reliable operation during season is vital. Balanset-1A is used for balancing combine threshing drums, shredders, mulchers, mowers, and augers. The capability to balance on-site without equipment disassembly permits avoiding costly downtime during critical harvest periods.
Specialized Equipment
The device is effectively used for balancing crushers of various types, turbochargers, drone propellers, and other high-speed equipment. The RPM frequency range from 250 to 90,000 RPM covers practically all types of industrial equipment.
Benefits Over Alternatives
Economic Efficiency
At a price of €1,751, Balanset-1A delivers the functionality of devices costing €10,000-25,000. The investment recovers costs after preventing just 2-3 bearing failures. Savings on outsourced balancing specialist services totals thousands of euros annually.
Ease of Use
Unlike complicated vibration analyzers requiring months of training, mastering Balanset-1A takes 3-4 hours. The step-by-step guide in the software allows professional balancing by personnel without special vibration diagnostics training.
Portability and Autonomy
The complete kit weighs only 4 kg, with power supplied through the laptop’s USB port. This enables balancing in outdoor conditions, at isolated sites, and in difficult-access locations without additional power supply.
Universal Application
One device is appropriate for balancing the broadest spectrum of equipment – from small electric motors to large industrial fans and turbines. Support for one and two-plane balancing covers all typical tasks.
Real Application Results
Drone Propeller Balancing
A user achieved vibration reduction from 0.74 mm/s to 0.014 mm/s – a 50-fold improvement. This demonstrates the remarkable accuracy of the device even on small rotors.
Shopping Center Ventilation Systems
Engineers successfully balanced radial fans, achieving reduced energy consumption, eliminated excessive noise, and increased equipment lifespan. Energy savings recovered the device cost within several months.
Agricultural Equipment
Farmers note that Balanset-1A has become an essential tool preventing costly breakdowns during peak season. Decreased vibration of threshing drums led to decreased fuel consumption and bearing wear.
Cost and Delivery Terms
Current Prices
Complete Balanset-1A Kit: €1,751
OEM Kit (without case, stand, and scales): €1,561
Special Offer: €50 discount for newsletter subscribers
Bulk Discounts: up to 15% for orders of 4+ units
Acquisition Options
Official Website: vibromera.eu (recommended)
eBay: certified sellers with 100% rating
Industrial Distributors: through B2B channels
Payment and Shipping Terms
Payment Methods: PayPal, bank cards, bank transfer
Shipping: 10-20 business days by international mail
Shipping Cost: from $10 (economy) to $95 (express)
Warranty: manufacturer’s warranty
Technical Support: included in price
Summary
Balanset-1A constitutes an optimal solution for organizations aiming to establish an effective equipment balancing system without significant capital expenditure. The device opens up access to professional balancing, permitting small enterprises and service centers to deliver services at the level of large industrial companies.
The mix of accessible price, ease of use, and professional features makes Balanset-1A an essential tool for modern technical maintenance. Investment in this device is an investment in equipment dependability, decreased operating costs, and improved competitiveness of your business.
You need to be a part of a contest for one of the greatest blogs on the internet. I am going to recommend this blog!
Khám phá KU88 – nhà cái có mặt trên thị trường quốc tế với giao diện thân thiện và nhiều tính năng hiện đại: https://ku88.uk.net/
good post really good and amazing im really happys..
hiếp dâm tập thể
Không cần lo bị chặn link, vào W88 nhanh qua đường dẫn mới nhất tại đây https://w88linkb.com/
188BET là lựa chọn tuyệt vời cho những ai đam mê cá cược thể thao và casino trực tuyến, giao diện thân thiện và nhiều khuyến mãi hấp dẫn + https://188betlinka.com
Thanks for sharing such valuable information, it was a very engaging read…
hiếp dâm tập thể
phim khiêu dâm miễn phí
ипотека под материнский капитал crediteurasia.ru .
hey good post. This was super helpful! Do you have any other good job.
crochet bags?
KU88 mang đến sân chơi cá cược trực tuyến chất lượng, hỗ trợ người chơi 24/7. Truy cập chính thức: https://ku88.uk.net/
amoxil pills – diovan 160mg ca combivent 100mcg ca
Great post! I really enjoyed reading this and found it very informative. Thanks for sharing!
Great post! I really enjoyed reading your insights on this topic. Keep up the amazing work!
Great site you have here.. It’s hard to find high-quality writing like yours nowadays. I really appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
plastic surgery in turkey
Transform Your Look with Cosmetic Surgery in Istanbul
Looking for a discreet, professional, and affordable way to enhance your appearance? Cosmetic surgery in Istanbul has become a top choice for thousands of people worldwide — and for good reason.
From minimally invasive treatments to full surgical makeovers, Istanbul offers everything you need to feel confident again. Vivid Clinic stands out as one of the premier destinations for cosmetic surgery in Istanbul, offering personalized treatment plans and world-class aftercare in a luxury setting.
Whether you’re dreaming of a refined nose, lifted eyes, or a youthful glow, our expert surgeons at Vivid Clinic work closely with each patient to deliver safe, natural-looking results — all while you recover in the vibrant beauty of Istanbul.
Very good info. Lucky me I found your site by accident (stumbleupon). I have saved as a favorite for later!
Great post! Thanks for sharing such valuable insights.
Great post! I really enjoyed reading it. Thanks for sharing your insights.
cặc dài lồn to
скачать музыку mp3 скачать музыку mp3 .
phim khiêu dâm hay
песни новые скачать песни новые скачать .
azithromycin oral – buy nebivolol pills for sale bystolic 5mg ca
окна пвх окна пвх .
hong88.uk.net không khóa tài khoản vô cớ, bảo vệ quyền lợi người chơi
bec88.us.com hỗ trợ nhiều hình thức thanh toán tiện lợi và bảo mật
hdbet.eu.com giao dịch tài chính an toàn, không gặp sự cố hay lỗi hệ thống
пластиковые окна москва пластиковые окна москва .
vibet88.uk.com tỷ lệ trả thưởng minh bạch và luôn ở mức cao
hi, thanks!: Altrops Trade
Spot on with this write-up, I actually feel this site needs a great deal more attention. I’ll probably be back again to read through more, thanks for the info.
cosmetic surgery istanbul
Why Cosmetic Surgery Istanbul Is the New Global Standard
Cosmetic surgery istanbul isn’t just a trend — it’s a movement. Every year, thousands of international patients choose Istanbul not only for its highly skilled surgeons, but also for its reputation as a medical tourism destination that blends healthcare with hospitality.
Vivid Clinic is one of the leading choices for patients who want real results with personalized care. Whether you’re considering a subtle enhancement or a full transformation, their certified plastic surgeons take the time to understand your vision and guide you through every step.
Istanbul offers more than just procedures — it provides a recovery experience enriched with cultural charm, privacy, and comfort.
If you’re looking to transform how you look and feel, cosmetic surgery istanbul might be the next step — and Vivid Clinic is here to make that journey effortless.
Thank you for sharing your story. It really touched me and gave me a new moments.
пластиковые окна пластиковые окна .
окна в москве http://www.okna177.ru .
phim sex học sinh
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Углубиться в тему – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-1.ru/
cặc dài lồn to
Awesome issues here. I am very glad to look your article. Thanks a lot and I am having a look ahead to touch you. Will you kindly drop me a mail?
tadalafil abc 5 mg
buy clavulanate generic – atbio info brand acillin
Very good article. I certainly love this site. Thanks!
Good post. I learn something totally new and challenging on sites I stumbleupon everyday. It will always be helpful to read through content from other writers and practice something from other websites.
tra cuu phat nguoi Tra cứu phạt nguội
Immigration Lawyers… […]here are some links to sites that we link to because we think they are worth visiting[…]…
buy esomeprazole for sale – https://anexamate.com/ esomeprazole 20mg over the counter
phạtnguội.com Tra cứu phạt nguội
cặc dài lồn to
cặc dài lồn to
Greetings! Very helpful advice in this particular article! It is the little changes that make the most significant changes. Thanks for sharing!
tracuuphatnguoi.vn kiểm tra phạt nguội phạt nguội
kiểmtraphạtnguội Tra cứu phạt nguội
where can i buy medex – https://coumamide.com/ losartan price
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://fotonons.ru/
plastic surgery turkey
Why More People Choose Plastic Surgery Turkey
When it comes to beauty, precision, and patient care, plastic surgery turkey is setting the bar high. From Istanbul to Antalya, Turkey is now home to internationally accredited clinics, elite surgeons, and full-service medical tourism offerings.
At the center of this growing success is Vivid Clinic, a trusted name in Istanbul that’s helping patients from across Europe and beyond achieve stunning, natural-looking results. With a wide range of procedures — from body contouring to facial aesthetics — Vivid Clinic focuses on safety, satisfaction, and aftercare.
Affordable prices don’t mean compromise. At Vivid Clinic, you get advanced techniques, modern facilities, and a team that genuinely cares.
For anyone thinking about enhancing their appearance abroad, plastic surgery turkey through Vivid Clinic is a smart, life-changing decision.
Hi there! I just wish to offer you a huge thumbs up for your great information you’ve got right here on this post. I am coming back to your website for more soon.
Hiếp dâm trẻ em, loạn luân, ấu dâm
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://cultureinthecity.ru/
meloxicam 7.5mg ca – tenderness where can i buy mobic
lồn to
lồn to
Hello there! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and say I really enjoy reading your articles. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that deal with the same topics? Many thanks!
https://seal.dp.ua/vybir-skla-dlya-fary-audi-porady-vid-ekspertiv
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://imgtube.ru/
tra cuu phat nguoi camera phạt nguội
tracuuphatnguoi.com.vn Tra cứu phạt nguội
phạt nguội giao thông Hà Nội
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://imgtube.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://40-ka.ru/
Here’s more on the topic https://upsskirt.ru/
Here’s more on the topic https://upsskirt.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here is a website on the topic – https://40-ka.ru/
prednisone 5mg usa – https://apreplson.com/ purchase prednisone for sale
decomania
Voici un spin-tax de haute qualité pour votre texte en français, respectant toutes vos consignes :
Dans un contexte où le média spécialisé Decomania analyse les avancées dans le domaine fintech, une question se pose : Quantum AI 2025 représente-t-il une véritable innovation ou uniquement une initiative prometteuse ?
Mécanisme et Promesses : Que Propose Cette Plateforme ?
Quantum AI 2025 se présente comme un outil de trading automatisé intégrant IA et calcul quantique. D’après ses concepteurs, cette technologie rendrait possible :
Une analyse avancée des marchés (crypto, valeurs mobilières, Forex).
Une régulation intelligente du risque pour améliorer les résultats.
Une interface intuitive, adapté pour les investisseurs de différents niveaux.
Néanmoins, aucune étude indépendante ne corrobore publiquement ces allégations, et les feedbacks d’utilisateurs restent partagés.
Éléments à Contrôler Selon Decomania
Notre étude révèle différents points à évaluer avant de investir :
Différentes plateformes locales (opulence-mirage.com) – Une pratique courante, mais qui peut complexifier la vérification.
Transparence limitée – Des données techniques insuffisantes sont disponibles sur les systèmes mis en œuvre.
Expériences variées – Une partie des clients mentionnent des performances satisfaisantes, tandis que certains signalent des difficultés techniques.
Conseils pour les Investisseurs
Privilégier les solutions agréées (AMF) pour une meilleure protection.
Essayer en mode démo avant toute mise de fonds.
Mettre en parallèle avec d’autres solutions (à l’image de les plateformes proposés par d’autres brokers réputés).
Conclusion : Un Projet à Suivre avec Circnospection
Quantum AI 2025 présente une méthode novatrice, mais ses résultats tangibles nécessitent encore des preuves concrètes. En attendant de une meilleure visibilité, une stratégie prudente est conseillée.
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://great-galaxy.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://great-galaxy.ru/
cakhiatv.lifestyle bảo trì hệ thống nhanh, không gây gián đoạn trải nghiệm người chơi
I am in fact thankful to the holder of this web page who has shared this fantastic post at here.
скачать песни бесплатно в хорошем качестве без регистрации скачать песни бесплатно в хорошем качестве без регистрации .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://shvejnye.ru/
buy erectile dysfunction drugs over the counter – https://fastedtotake.com/ how to get ed pills without a prescription
That is a really good tip particularly to those new to the blogosphere. Brief but very accurate information… Thanks for sharing this one. A must read post.
I love what you guys are usually up too. This sort of clever work and reporting! Keep up the fantastic works guys I’ve added you guys to my blogroll.
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://shvejnye.ru/
decomania
Voici un spin-tax de haute qualité pour votre texte en français, respectant toutes vos consignes :
Dans un contexte où Decomania explore les innovations des secteurs financiers et technologiques, une interrogation émerge : Quantum AI 2025 représente-t-il un progrès tangible ou seulement une initiative prometteuse ?
Fonctionnement et Perspectives : Quel est le Principe de Cette Plateforme ?
Quantum AI 2025 se présente comme une solution de trading algorithmique intégrant smart tech et calcul quantique. D’après ses concepteurs, cette technologie offrirait :
Une analyse avancée des places boursières (actifs numériques, titres, marché des changes).
Un contrôle algorithmique du risque pour améliorer les résultats.
Une prise en main aisée, adapté pour les investisseurs de différents niveaux.
Cependant, aucune recherche tierce ne confirme formellement ces allégations, et les témoignages s’avèrent contrastés.
Points à Contrôler Pour Decomania
Notre analyse souligne plusieurs éléments à considérer avant de investir :
Plusieurs URLs géolocalisées (opulence-mirage.com) – Une méthode habituelle, mais qui peut complexifier l’authentification.
Transparence limitée – Peu d’informations techniques sont accessibles sur les algorithmes utilisés.
Expériences variées – Certains utilisateurs indiquent des performances satisfaisantes, tandis qu’ plusieurs rapportent des complications pratiques.
Recommandations pour les Opérateurs
Privilégier les plateformes régulées (AMF) pour un cadre plus sûr.
Tester en version démonstration avant chaque investissement.
Comparer avec d’autres options (comme les plateformes proposés par eToro).
Conclusion : Une Solution à Surveiller avec Réserve
Quantum AI 2025 avance une technologie de pointe, mais ses résultats tangibles nécessitent encore des preuves concrètes. En attendant de une meilleure visibilité, une stratégie prudente est préconisée.
Your style is very unique compared to other folks I have read stuff from. Many thanks for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I’ll just bookmark this blog.
песни на телефон песни на телефон .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://voenoboz.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://voenoboz.ru/
Hiếp dâm trẻ em, loạn luân, ấu dâm
Hiếp dâm trẻ em, loạn luân, ấu dâm
Hiếp dâm trẻ em, loạn luân, ấu dâm
UP X — обзор официальной платформы Ап Икс
Сегодня абсолютно каждый житель Российской Федерации может сыграть в увлекательные игровые автоматы, и при этом не покидая собственное жилище. Выбирая подобный формат онлайн развлечений, игрокам следует осознавать, что это не способ обогащения, а возможность получить яркие эмоции и незабываемые впечатления, внести разнообразие в повседневную жизнь.
https://mymcu.ru/
order amoxicillin pills – https://combamoxi.com/ buy amoxil generic
https://bongdalu7.com/ ít trò chơi, thiếu đa dạng
decomania
Voici un spin-tax de haute qualité pour votre texte en français, respectant toutes vos consignes :
Tandis que Decomania analyse les avancées dans le domaine fintech, une interrogation émerge : Quantum AI 2025 représente-t-il une véritable innovation ou seulement une initiative prometteuse ?
Mécanisme et Perspectives : Qu’Offre Cette Plateforme ?
Quantum AI 2025 se positionne comme un outil de investissement algorithmique combinant intelligence artificielle et informatique quantique. Pour ses développeurs, cette technologie permettrait :
Une évaluation poussée des marchés (crypto, titres, devises).
Une régulation intelligente des risques pour optimiser les rendements.
Une prise en main aisée, pensé pour les traders aux profils variés.
Cependant, aucune recherche tierce ne confirme formellement ces allégations, et les témoignages restent partagés.
Éléments à Vérifier D’après Decomania
Notre examen met en lumière différents points à évaluer avant de investir :
Multiples sites régionaux (etc.) – Une pratique courante, mais qui peut complexifier la vérification.
Opacité relative – Peu d’informations techniques sont accessibles sur les algorithmes utilisés.
Résultats divergents – Plusieurs investisseurs rapportent des performances satisfaisantes, tandis qu’ plusieurs rapportent des difficultés techniques.
Suggestions pour les Investisseurs
Privilégier les interfaces contrôlées (etc.) pour un cadre plus sûr.
Essayer en version démonstration avant chaque investissement.
Comparer avec d’autres solutions (comme les plateformes offerts par eToro).
Conclusion : Une Solution à Surveiller avec Réserve
Quantum AI 2025 présente une méthode novatrice, mais son efficacité réelle nécessitent encore des confirmations pratiques. Dans l’attente de une meilleure visibilité, une méthode mesurée est conseillée.
Here’s more on the topic https://my-caffe.ru/
скачать музыка мп3 скачать музыка мп3 .
moomoo.uk.com rút tiền chậm, đôi khi bị giữ lâu mà không có lý do
rami.uk.com bảo mật kém, có nguy cơ lộ thông tin cá nhân
скачать песни новинки бесплатно скачать песни новинки бесплатно .
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://adventime.ru/
jordanofficial.eu.com giá cả không cạnh tranh, cao hơn so với thị trường
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://kaizen-tmz.ru/
Here’s more on the topic https://my-caffe.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://kaizen-tmz.ru/
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://adventime.ru/
купить пластиковые окна дешево купить пластиковые окна дешево .
заказать окна пвх http://www.02stroika.ru .
Quantum Prime Profit 2025
Voici un spin-tax de haute qualité pour votre texte en français, respectant toutes vos consignes :
Tandis que Decomania analyse les nouveautés des secteurs financiers et technologiques, une interrogation émerge : Quantum AI 2025 constitue-t-il un progrès tangible ou uniquement un projet ambitieux ?
Mode opératoire et Perspectives : Quel est le Principe de Cette Plateforme ?
Quantum AI 2025 se définit comme un outil de trading algorithmique intégrant intelligence artificielle et calcul quantique. Selon ses créateurs, cette technologie rendrait possible :
Une analyse avancée des marchés (cryptomonnaies, actions, marché des changes).
Un contrôle algorithmique des risques pour optimiser les rendements.
Une prise en main aisée, adapté pour les traders de différents niveaux.
Néanmoins, aucun audit externe ne valide publiquement ces allégations, et les retours utilisateurs restent partagés.
Aspects à Contrôler D’après Decomania
Notre étude souligne différents points à prendre en compte avant de investir :
Différentes plateformes locales (opulence-mirage.com) – Une pratique courante, mais qui peut rendre difficile le contrôle.
Manque de clarté – Peu d’informations techniques sont disponibles sur les modèles employés.
Performances inégales – Plusieurs investisseurs rapportent des rendements intéressants, alors que plusieurs rapportent des difficultés techniques.
Recommandations pour les Opérateurs
Favoriser les plateformes régulées (CySEC) pour un cadre plus sûr.
Tester en compte test avant tout engagement financier.
Comparer avec d’autres options (telles que les systèmes proposés par d’autres brokers réputés).
Conclusion : Une Technologie à Observer avec Prudence
Quantum AI 2025 avance une technologie de pointe, mais ses performances concrètes demandent toujours des confirmations pratiques. En attendant de plus de transparence, une stratégie prudente est préconisée.