Overview
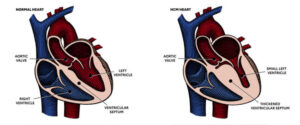
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a condition that causes the heart muscle to get unusually thick (hypertrophied). The thickened heart muscle may make it difficult for your heart muscle to circulate blood.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is often not diagnosed since many patients with the disease show very few if any symptoms and lead normal lives without any difficulties. However, it is found in a small percentage of patients, the thick heart muscle may lead to breathlessness or chest pain. It can also cause issues with the electrical system, which can lead to life-threatening heart rhythm abnormalities (arrhythmias) and sudden deaths.
Symptoms
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can comprise any or all of these:
- The chest can be painful, especially when you exercise.
- The appearance of tinnitus, in particular when exercising or exercise
- Heart murmurs that doctors may detect when monitoring your heart
- The sensation of rapid, fluttering, or beating heartbeats (palpitations)
- Breathing shortness, particularly when exercising
When is the best time to seek medical help?
Certain conditions may result in shortness of breath or heart palpitations. It’s crucial to get an immediate, accurate diagnosis and the appropriate treatment. Consult your physician if you have any family background of HCM, or any other symptoms that are associated with or any symptoms that are associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Contact 911 or your area emergency contact number in the case are suffering from any of the following symptoms that last more than a couple of minutes:
- A rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Breathing difficulties
- Chest pain
Causes
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is typically caused by genetic abnormalities (gene mutations) which causes the muscle of your heart to become abnormally thick.
In the majority of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, the muscle wall (septum) between the two chambers on the bottom of the heart (ventricles) gets larger than normal. This means that the wall that is thicker can block blood flow from the heart. This is known as obstructive Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
If there’s not a significant obstruction or obstructing of circulation the situation is known as non-obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. But, the heart’s primary chamber for pumping (left ventricle) can become stiff. This causes the heart’s muscle to loosen and decreases the amount of blood it can be able to hold and deliver to the body each heartbeat.
People suffering from hypertrophic cardiomyopathy suffer from an irregular arrangement of the heart muscles (myofiber in disarray). The arrhythmias can occur in certain people.
Risk factors
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy usually passes via the families (inherited).
If you are a child of a person who suffers from hypertrophic cardiomyopathy you stand an opportunity of 50% of inheriting the genetic mutation responsible for the condition.
Children, parents, or siblings of someone suffering from hypertrophic cardiomyopathy should inquire with their physicians about the possibility of screening for the disease.
Complications
A lot of people suffering from hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) do not have major health issues. The complications of hypertrophic cardiovascular disease may be:
- atrial fibrillation. Thickened heart muscle and the abnormality in the structure of the heart cells could cause changes to the electrical circuits of the heart, which can cause irregular or fast heartbeats. Atrial fibrillation may also increase the risk to develop blood clots that can spread into your brain and cause stroke.
- Blood flow is blocked. In many people, the heart muscle that is thickened hinders blood flow from the heart, which causes breathing problems with exercise and heart pain dizziness, and fainting episodes.
- Mitral valve issues. If the thickened heart muscle restricts blood flow that leaves in the heart, then the valve that connects the left ventricle and the left atrium (mitral valve) might not be closing correctly. As a result, blood may leak back through the left atrium (mitral valve regurgitation) and could cause worsening symptoms.
- Dilated cardiomyopathy. In a small percentage of people who have HCM, The thickened heart muscle could weaken and become ineffective. The ventricle is enlarged (dilated) and the pumping capacity decreases.
- Heart Failure. The thickened heart muscle may eventually become stiff enough to efficiently pump blood to the heart. This means that your heart isn’t able to pump enough blood to supply your body’s requirements.
- Death of a sudden heart. Rarely, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can lead to heart-related sudden death in anyone of all age groups. Since many people with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy do not realize that they suffer from it sudden cardiac death can be the first indication of a health issue. It can happen to seemingly healthy young people, such as high school athletes as well as active, young adults.
Prevention
There’s no cure for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. It is crucial to detect the condition as soon as you can to help guide the treatment process and prevent any complications.
If you’re a family member in the first degree -parents, siblings, or child with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), doctors might suggest genetic testing to test for this condition. But, not all people with HCM There is a mutation that can be detected. Additionally, certain insurance companies do not be able to cover the genetic test.
If genetic testing hasn’t been done or the results aren’t beneficial the doctor might suggest echocardiograms on a frequent basis, especially if you have relatives who suffer from hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Athletes and adolescents should be checked at least once a year. Adults who do not compete in athletics should be tested at least every 5 years.
Diagnosis
Tests
Your physician will most likely request tests to diagnose hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) or to rule out any conditions that may cause similar symptoms.
- Echocardiogram. Echocardiograms are commonly used to identify hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The test makes use of sounds (ultrasound) to determine whether your heart’s muscle is excessively heavy. It also shows how your heart’s valves and chambers have been pumping blood.
In some cases, the echocardiogram can be carried out while you exercise normally on the treadmill. This is known as the exercise stress test. Treadmill stress tests are often employed to detect people suffering from hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. - Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). Sensors (electrodes) that are attached to adhesive pads are put on your chest, and occasionally your legs. They detect electrical signals coming emanating from the heart. An ECG may show irregular heart rhythms as well as symptoms of heart thickening. In certain cases, A device, also known as a Holter monitoring device, is essential. The device tracks the heart’s activity over the course of one day to 2 days.
- Cardiac MRI A cardiac MRI utilizes powerful radio waves and magnets to produce images of the heart. It provides your doctor with details about your heart’s muscles and illustrates the way your heart and valves function. The test is usually carried out using an echocardiogram.
Treatment
The aim of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy treatment is to alleviate symptoms and to prevent sudden cardiac death for those at risk. The treatment you receive is contingent upon the degree of the symptoms. Together you and your physician will discuss the best treatment for your situation.
Medications
The use of medicines can reduce the amount of muscle that the heart squeezes, and also slow down the heart rate so that the heart is able to move blood more effectively. The treatment for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and its signs can include:
- Beta blockers like metoprolol (Lopressor Toprol-XL, Toprol) and propranolol (Inderal, Innopran XL) or atenolol (Tenormin)
- Calcium channel blockers, such as verapamil (Verelan, Calan SR,) or diazepam (Cardizem, Tiazac)
- Heart rhythm drugs like amiodarone (Pacerone) and disopyramide (Norpace)
- Blood thinners like warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven), dabigatran (Pradaxa), and Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) or Apixaban (Eliquis) to reduce the risk of blood clots in the event of atrial fibrillation.
Surgery or other procedures
A variety of different procedures or surgeries are available to treat the condition of cardiomyopathy or the symptoms. They range from open-heart surgery to the placement of a device to regulate your heart’s rhythm.
- Septal myectomy. The open-heart procedure may be suggested if your medications fail to help the symptoms. The procedure involves the removal of part of the overgrown, thickened wall (septum) connecting the chambers of the heart. Septal myectomy assists in improving blood flow through the heart and decreases the flow of blood backward via the valve in your mitral (mitral regurgitation). The procedure can be performed with different methods, based on the site of the thickened heart muscle. In one kind, called Apical Myectomy, surgeons cut off the thickened heart muscle near the heart’s apex. Sometimes, the mitral valve is repaired as well.
- Septal ablation. This procedure destroys the heart muscle that is thickened using alcohol. Alcohol is delivered via an extremely thin, long tubing (catheter) through the coronary artery that supplies blood to this region. The potential for complications is interruption of the electrical system of the heart (heart block) that requires the placement of pacemakers.
- Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). It is a tiny device that monitors your heartbeat continuously. It’s placed in the chest similar to an implanted pacemaker. If a serious arrhythmia develops it will be treated. ICD provides precise electrical shocks that are precisely calibrated that restore a normal heartbeat. It has been proven to stop sudden cardiac deaths, which occur in a tiny percentage of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Lifestyle and home solutions for home and lifestyle
Lifestyle modifications can lower the chance of complications related to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes, including:
- Be cautious when participating in games. Competitive sports are generally not recommended for those suffering from hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with the possibility of exceptions to lower-intensity sports. It is possible to engage in low- to moderate-intensity exercises as part of your healthy lifestyle. Discuss specific guidelines with your physician.
- A healthy diet is essential to keep your heart healthy. A healthy diet is an essential part of keeping your heart healthy.
- Maintaining the right body weight. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce strain on your heart, and will reduce the risk of complications from surgical procedures or others.
- Reduced alcohol consumption. If you have symptoms or have a history of irregular heart rhythms caused by alcohol, talk to your physician for advice on appropriate levels of alcohol consumption. Consuming excessive amounts of alcohol could create irregular heart rhythms, and may cause an obstruction of blood flow to the heart.
- Do not forget to take your medications. Make sure to adhere to the prescribed dosage.
- Regularly attend appointments with your doctor. Your doctor may suggest regular follow-up appointments to check your condition. Inform your doctor whether you are experiencing any new or more severe symptoms.
Pregnancy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy sufferers are typically able to have normal pregnancies. If you do have hypertrophic cardiomyopathy your doctor may suggest you see an expert in caring for women who have high-risk conditions in the course of pregnancy.
Support and Coping
The diagnosis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can bring about a variety of emotional turmoil. As with many patients suffering from this condition, you could feel grief anger, fear, and sadness. These reactions are normal to the changes in your lifestyle which are a result of the diagnosis.
To manage your situation:
- Reduce anxiety. Find ways to lower stress.
- Get help. Get support from your family and friends.
- Make lifestyle changes that the doctor suggests. Making healthy lifestyle modifications, like eating a healthy diet, and keeping a healthy weight can assist you in coping with the challenges of living with your illness.

Wow, marvelous weblog layout! How lengthy have you been blogging for?
you made running a blog look easy. The entire look of your
web site is fantastic, as neatly as the content material!
You can see similar here dobry sklep