Melatonin
Generic Name: melatonin
The class of drug: Miscellaneous anxiolytics, drugs that hypnotics and sedatives.
What is Melatonin?
Melatonin is a natural hormone that your body produces that aids in maintaining your circadian rhythm (also known as “biological clock”). Melatonin can also be synthesized and is available without prescription as an over-the-counter (OTC) nutritional supplements in the U.S.
Melatonin is the most frequently used to:
- helping in decreasing jet lag
- alter the sleep cycle within the blind (non 24 Hour Sleep Wake Disorder, also known as non-24)
- Treat sleep disorders caused by shift work for those who have shift-work sleep disorders
- for general insomnias
The wake-sleep-wake cycle is the process of waking and sleeping for humans. It is estimated to be 8 hours of sleep at night as well as 16 hours of activity during the day.
Supplemental Melatonin has been proven to have many benefits including sleep disorders and cancer treatment, but sufficient studies aren’t available for all applications. It is extensively researched for treating jet lag and sleep disorders.
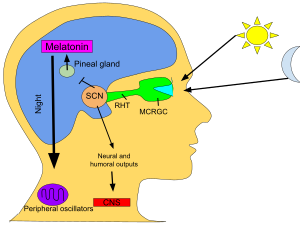
Melatonin released from the endogenous (made by the body) increases throughout the day, in response the darkness. It is at its highest from 11PM to 3AM, at approximately 200 picograms (pg) per milliliter. The levels at night are about 10 times more than the daytime. They drop dramatically before dawn and are not even noticeable during daytime hours. The rising and falling of endogenous levels indicate the times of our sleep and wake which is also known as our circadian rhythm.
Melatonin’s natural production begins from an amino acid called tryptophan with serotonin acting as an intermediary. Then, it is released to receptors within the brain, the eye and other parts to manage cycle of wake and sleep. The half-life is brief, between 20 and 50 minutes. It is processed (broken down) by the CYP450 enzyme system inside the liver, and then excreted into the feces or urine.
Production is less frequent during summer, with longer days. More extended periods of production are common during winter. Lighting at the night (such as light from smartphones or TV) interferes with production and may cause sleep disturbances. The aging process also reduces the amount of melatonin released at night. released, which could cause insomnia and early awakening that is commonly experienced by older adults.¶
How Does Melatonin Work?
Natural melatonin is a fat-soluble hormone found in the pineal gland inside the brain. It is produced from the amino acid tryptophan. It is released into cerebrospinal fluid and blood and crosses the blood-brain barrier. It communicates with the receptor agonists within the brain and various parts of the body to control cycle of wake and sleep.
Does melatonin help you sleep? When used as an supplement, its purpose is to replicate what happens to the natural hormone that sleeps. The majority of people experience drowsiness within 30 minutes following the having taken the dose.
The use of melatonin supplementation prior to bedtime might not be the ideal solution for every sleep disorder. Talk to your doctor regarding the most effective method for dosage. This medication may not be effective for everyone.
Is Melatonin a Hormone?
Exogenous Melatonin is a natural hormone produced in our bodies (the exogenous hormone). The hormone is not considered a vitamin. The supplements melatonin (exogenous hormone) are manufactured synthetically, and all the products and strengths that are available on market in the U.S. market are available without prescription in health stores, pharmacies, and at other shops for retail.
Before Taking This Medicine
Melatonin is not a good choice in case you have an allergy to it.
Before you start using this medication, consult your physician. You might not be able to take it if suffer from specific medical conditions, for example:
- Diabetes
- Heart attack
- Depression
- A blood clotting or bleeding disorder like hemophilia
- using a blood thinner such as warfarin
- blood pressure, low or high
- epilepsy or other seizure disorders
- If you are taking any medication to prevent rejection of organs for transplantation
- an autoimmune condition
- by using other sedatives, tranquilizers, or other medications.
It is unclear if this medication could cause harm to a baby who is not yet born. Do not take this medication without medical advice when you are pregnant.
Doses high of this drug could affect ovulation and make it difficult to become pregnant.
It isn’t known if the melatonin is absorbed into breast milk , or whether it can harm breastfeeding babies. Do not apply it without medical guidance when you breastfeed babies.
Don’t give health or herbal supplement to your child unless you have medical recommendation.
Melatonin Dosage
Melatonin is regarded as an effective treatment for jetlag and helps you sleep at times which you’d normally be awake.
The most effective doses of melatonin to start for jet lag vary between 0.3 up to 0.5 milligrams. 1-milligram tablet could be cut in half in order to get an 0.5-milligram dose of Melatonin in case smaller doses aren’t available to purchase. Higher doses are often advertised within the U.S. (up to 10 mg) however, higher doses could be associated with greater side consequences, such as headaches or grogginess that comes back the next day as well as vivid nightmares. Melatonin-related side effects can be more severe for older adults.
Always begin with the smallest dosage. According to an Cochrane study, dosages that exceed 5 mg seem to be not as effective as smaller doses. More doses can cause an excessively high level of physiologic melanin.
How to Use Melatonin for Jet Lag?
Jet lag is a common travel-related issue that causes trouble in sleeping, fatigue constipation, trouble concentrating and other signs. Jet lag is more likely to occur if you travel across multiple time zones, and may worsen as when there are more time zones you travel through.
Effective doses to start with for jet lag vary between 0.3 up to 0.5 mg. Lower doses can work for some , while others require a higher dosage. It might become more challenging to fly east in the event of losing time instead of flying west, once you have gained the time back. Doses that are high, such as 20 mg pills are readily available to purchase over the Internet however, these dosages aren’t normally advised or required and can significantly enhance the effects of side effects.
- eastbound When you’re traveling to the east, for example in the direction of the US to Europe Take melatonin supplemental to sleep at night 30 minutes prior to sleep time in the newly established time zone, or when you’re on the plane. Then , take it for the next four days in the time zone that you are now at night, for 30 minutes prior to going to bed. If you’re experiencing drowsiness the next day following this treatment you can try a lower dose.
- westbound When you’re traveling west, as an example in the direction of the US to Australia the dose is not necessary to start your journey however, you can use it for the following 4 nights in the newly established time zone. It is recommended to take it after dark, about 30 minutes prior to the time of bed. Melatonin might not be required for westbound travel.
If you give it adequate period of time (usually between 3 and 5 days) Jet lag tends to disappear by itself, however this may not be the best option during travel.
Other Uses
How to Take for Primary Sleep Disorders (Insomnia):
- Dosage You should take 0.1 mg up to 0.5 mg 30 minutes before the time of bed. Research suggests that melatonin supplements for sleep disorders that are primary can be effective in promoting but not keeping sleep (early early morning wake-up).
How to Take for Shift-Work Sleep Disorders
- Dosage: Consume one to three mg 30 seconds prior to time of the day Melatonin is not likely to result in increased alertness during the night time shift.
How to Take for Delayed Sleep-Wake Phase Disorder
Delayed sleep-wake cycle disorder (DSWPD) is most commonly seen in teenagers, possibly due to a decrease in production or the deficiency of melatonin at this time. The time to sleep is delaying by 3 or 6 hours when compared with normal times of sleep (10 until 11 at night). DSWPD may negatively impact the performance of students, their daily activities, and may lead to morning drowsiness that could be dangerous for teens driving. Any sleep-related disorder in an adolescent needs to be examined by a doctor.
- Dosage: There is no consensus available on the proper dosage for DSWPS. Some doctors suggest 3 to 5 mg of the drug in the evening, at minimum 1.5 hours prior to time of bed. The use of bright lights and behavior management can improve outcomes. Be aware that drowsiness could develop following the melatonin dose Therefore, avoid dangerous actions like driving.
How to Take for Non-24-Hour Sleep Wake Disorder (Non-24)
Over 70% of those who are blind suffer from Non-24 which is a condition that affects the circadian rhythm. For those who are completely blind, there aren’t any lights to aid in resetting our biological clock. The time of sleep and wake-up time of those with Non-24-Hour Sleep Wake Disorder change slightly later each day. Sleep times change and go out of alignment with the normal sleep-wake cycle. The extra minutes accumulate day and alter the normal pattern of wake-sleep.
Melatonin’s role the Non-24 is to assist in stimulation that resets the biological clock by having an extended sleep time at night , and one long awake time during the day.
- Dosage: Studies of people who are blind recommend 0.5 mg/day, taken at a set time before going to bed or an hour prior to going to bed.
Hetlioz is a prescription-only melatonin antagonist, has been licensed for use in the non-24-hour sleeping Wake Disorder in adults and for treating nighttime sleep Disturbances in Smith-Magenis Disorder (SMS) for patients who are who are 3 years old or older.
- Hetlioz (tasimelteon)
Rozerem (ramelteon) is also known as a melatonin-agonist, is approved for treating insomnia that is characterized by difficulties with the onset of sleep in adults.
- Hetlioz (tasimelteon)Rozerem (ramelteon)
Fast-dissolving Tablets
There are a few melatonin tablets available in quick-dissolving forms available in the U.S. To consume the tablet by mouth:
- Dry hands are the best way to remove the tablet from the packaging and then put it into your mouth.
- Don’t take the tablet completely. Let it dissolve in your mouth, without chewing. If you wish, you can take a drink to help you swallow the tablet that has disintegrated.
Contact your physician to discuss your condition if the one you’re treating with this medication fails to improve or gets worse when you use this medication.
Place in a cool, dry place far from heat and moisture.
Melatonin for Children
Parents might think about using melatonin for their child who is having difficulty sleeping. Use this drug only for children under supervision of a pediatrician, or any other medical sleep expert. Insomnia or other sleep disorders in children must be assessed by a physician.
Melatonin is not recommended to replace good routine schedules for bedtimes in children. Based on Yale sleep expert Dr. Craig Canapari, use of this drug results in less trouble sleeping, a quicker the time to sleep and more rest in the night.
The products that contain lower doses of melatonin for children are available in market in the U.S. market. The long-term usage of this medication is not studied in clinical trials conducted for children, and any possible adverse reactions when used for a long time aren’t identified. Melatonin’s use in children who suffer from autistic spectrum disorder, or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder should be accompanied by the use of behavioral therapies and be guided by a physician.
Sleep-related sleep disorder is a common problem that is seen in adolescents or young adults which could be due to changes in the endogenous production. The time to sleep is extended by 3 to 6 hours when compared with the normal time of 10-11 PM. It is essential to ensure that you are without electronics for at least an hour prior to bedtime is crucial for sleeplessness in children and teenagers.
Melatonin Side Effects in Children
The most frequently reported melatonin-related side effect among children is morning drowsiness. Other typical side effects seen in children are:
- Bedwetting
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- A higher risk of seizures in children with neurological disorders.
Melatonin supplements from diets can contain potential health or drug interactions when you suffer from specific medical conditions, an upcoming surgery, or any other health issues.
What should you be aware of to
- Avoid operating machinery or driving for at most 4 hours following the taking of melatonin or until the effects of drowsiness have gone away.
- Do not take this medication in conjunction with other prescription or over-the-counter medications, or nutritional supplements without consulting your physician or pharmacist or another healthcare professional.
- Avoid drinking alcohol when taking this medication.
- Beware of tea, coffee and cola, as well as energy drinks, and other drinks that contain caffeine since it could interfere with the effects of melatonin.
What Happens if I Miss a Dose?
If you don’t take the dose, there’s no reason to worry, however Melatonin can affect your thinking or reaction times. If you plan on driving or engaging in any risky exercise, you should avoid the dose since melatonin may cause sleepiness.
In the event of a missed dose, you should take the dose missed as soon as you can remember. Do not take any missed doses if it’s nearing the time for the next dose. Don’t take extra medication or increase your dosage to make up for the missed medication.
Can You Overdose?
Melatonin is believed to be extremely secure in the short term, with a low danger of overdose. If you suspect that you have taken too much or other serious adverse reactions and allergic reactions, get immediate medical assistance from your health care doctor or contact the Poison Help Line at 1-800-222-1222.
Is Melatonin Safe?
Melatonin is a fairly safe supplement in short-term use and side effects are rare. Its long-term safety isn’t known through controlled, randomized studies. It is generally believed to be safe even in higher doses such as 3 or 5 mg once daily.
There are people who experience adverse consequences from melatonin. These include:
- daytime drowsiness, dizziness, weakness, or confusion
- vivid dreams nightmares
- feeling depressed, anxious, irritable
- headache
- Inability to eat nausea, diarrhea, stomach discomfort
- changes in blood pressure
- back or joint discomfort
- increased risk of seizures
More powerful doses of external doses(>1 milligram up to 10 mg) could cause more severe adverse effects such as fatigue during the day, diminished mental or physical performance and body temperature drop, and elevated levels of prolactin.
Related: Melatonin: Worth Losing Sleep Over?
Melatonin and Pregnancy
The majority of dietary supplements, including melatonin, have not been tested in women who are pregnant, during breastfeeding, or even in infants. Get advice from your doctor prior to using any nutritional supplement if you are nursing, pregnant or thinking about using this product for children under 18 years old.
Melatonin Drug Interactions
A number of important drug interactions may occur with melatonin despite the fact that it is a nutritional supplement. Always check the potential for food, drug and health interactions with your physician when you begin or stop taking any medication.
Always inform your pharmacist and doctor about every medication you are taking, including prescription and over-the counter medicines as well as herbal supplements and vitamins. Don’t stop taking any medications until you have spoken with your physician.
Discuss with your doctor prior to using melatonin in the event that you are taking Warfarin, a blood thinner. Melatonin has been shown to boost those effects caused by warfarin for certain patients. This is not a comprehensive list of the drug interactions that could be associated with melatonin.
Is Melatonin Approved by the FDA?
Melatonin is not recognized from the FDA for use in any way. It is a violation of the regulations of FDA’s Dietary Health and Education Act as a nutritional supplement. Dietary supplements can include minerals, vitamins amino acids, botanicals or herbs, as well as other substances to aid in the supplementation of the diet. Like other supplements to the diet the FDA has not approved melatonin. FDA. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its safety or effectiveness.
Manufacturers are required to inform FDA about any new ingredients before introducing them to the market. Once the supplement is placed available for sale the FDA will keep track of any adverse event or events which are reported to them by the consumer, the manufacturer or health experts. If a product manufacturer makes a claim about health that is not substantiated or the supplement proves to be unfit for human consumption, the FDA can take it off the market. OTC out of the market.
Avoid purchasing dietary supplements on the Internet or from pharmacies online that are not able to verify their authenticity. It is crucial to keep in mind that the OTC label that states “natural” supplement does not necessarily mean that it’s “safe” for consumption. Products with a label that is United America Pharmacopeia (USP) Convention Verified are considered to be the most reliable in this regard. The indication “USP” is found on the label on the outside of the bottle. For instance the majority of Nature Made products are verified by the USP. The most secure way to purchase prescriptions online is to use pharmacies that are accredited with the Verification of Internet Pharmacy Practice Sites (VIPPS) programs.
Do Electronic Devices Alter Melatonin Levels?
Nighttime light blocks Melatonin’s production and has been proven to cause sleep disturbances for people who are using electronic devices that emit light during the night. Researchers have discovered that the light emitted by electronic devices may block the release of the natural hormone called melatonin in the nighttime. This was the most noticeable effect in children who were younger as levels at night decreased by as much as 37 percent in some cases. This could be a problem for children aged 9 to 16.
Research suggests that lighting after dark decreases melatonin levels that can result in difficulties in establishing sleep. Electronic light-emitting devices like the laptop, television smartphones, tablets and other devices frequently find their way into the bedroom during the night or are used in the evening after the darkness has gone. Children should not be using electronics such as TVs in their bedrooms before bed, and everybody should be aware of screens and light-emitting devices at a time for at least an hour prior to bedtime.
Melatonin Reviews and Studies
For Primary Sleep Disorders
Researchers have conducted a variety of studies on the use of melatonin supplements to treat various health issues. The majority of studies have been conducted on sleep disorders such as jet time and sleep disorders that result from shift work and delayed sleep phase disorders and insomnia. The results of studies are not always consistent in their findings and there are many there are still questions about its effectiveness, dosage, duration of treatment, and the longevity of safety for certain sleep disorders.
Melatonin is a good option in treating jet lag for numerous people when it is administered at the correct timing. Studes investigating the efficacy of melatonin in the treatment of insomnia have shown a slight decrease in the time required to fall asleep however, it is not likely to enhance the overall quantity of rest. It appears to be safe to use for insomnia that is primary (less than 3 months).
For Other Conditions
Melatonin uses in a variety of areas have been studied, however not all applications are approved or have enough research to establish the the most appropriate clinical application. They include:
- Cancer
- Increase the strength of your immune system
- Sunburn
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Fibromyalgia
- Systemic sclerosis
- Scavenger of free radicals and antioxidants
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Ocular disorders
- Sleep aids for children with Autism spectrum disorders or ADHD or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
- Blood pressure control at night
- The disorder is known as seasonal affective disorder (SAD)
How Does Melatonin Come at the Store?
Within the U.S., melatonin pills can be bought without a prescription at the supermarket, pharmacy or health food stores. The strength of the pills varies between 1-milligram (mg) and up to 10 mg. However, you should begin with the lowest dosage to determine its effects. Some experts recommend starting by taking 0.3 or 0.5 mg 30 minutes prior to going to bed instead of more powerful doses. Cut a one-mg Instant Release tablet by half to obtain an 0.5 mg dose, if lower doses aren’t available. Don’t try this with products that release time. Be sure to avoid drinking alcohol while taking the preparation for time-release since it may interfere with the time-release mechanism.
Does Food Contain Melatonin?
An article published in Food and Nutrition Research indicates that certain foods contain different quantities of melatonin, as determined by chromatographic and immunological lab methods. The way in which consumption of these foods could impact endogenous production sleep, or not even evaluated:
- Tomatoes
- Walnuts
- Rice/barley cereal
- Strawberries tart cherries, tart
- Olive oil
- Beer, wine
- Milk from cows
Studies have revealed that melatonin synthesizing depends on the availability of the amino acid tryptophan. It is which is a vital component of our diet. If tryptophan consumption is severely limited, the production of melatonin decreases significantly in humans.
Within the Nurses Health Study There was no correlation discovered between the intake of different nutrients, like folate and vitamin B6 or zinc, as well as increased urinary excretion.
A diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and grains will have significant amounts of dietary melatonin. The impact of dietary consumption on levels at night of melatonin is quite minimal. Melatonin production is caused by the effects of darkness and light and also by age, which decreases as we age.
How Much Does Melatonin Cost?
A 120-count bottle cost about $10.00 However, prices can differ based on the brand and strength that are purchased. Insurance typically does not pay for non-prescription (OTC) items, but certain plans might allow them to use savings accounts for health.
Bottom Line: Pros and Cons
Benefits:
- Available throughout The U.S. over-the-counter (OTC) without prescription
- Use for short periods (less than three months) is fairly safe and has no evidence of toxicity.
- Generics and inexpensive products with store brand products are available
- Orally-dissolvable and lower dose products for children are readily available.
- It is available in a variety of dosage forms and dosages
Downsides:
- It is not approved for use by the FDA (over-the-counter nutritional supplement)
- Certain products’ quality cannot be guaranteed
- Research studies on less popular use aren’t consistent.
- Doses can vary among patients. Always ask a physician or health care provider for dose guidance for children.
- Effective doses lower in dosage (0.1 or 1 mg) aren’t always available commercially.
- The higher dosages (2 up to 10 mg) that are used for a long time frame can trigger relapse insomnia, and they aren’t well researched.
