Fetzima
Generic name: levomilnacipran
Drug class: Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Fetzima?
Fetzima is a prescription medicine used to treat a certain type of depression called Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) in adults.
It is not known if Fetzima is safe and effective for use in children.
It is not known if Fetzima is safe and effective for the management of fibromyalgia. Fetzima is not for use for the management of fibromyalgia.
Description
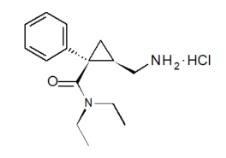
Fetzima contains levomilnacipran hydrochloride, a selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI). The chemical name of levomilnacipran hydrochloride is (1S,2R)-2-(aminomethyl)-N,N-diethyl-1-phenylcyclopropanecarboxamide hydrochloride; its empirical formula is C15H23ClN2O and its molecular weight is 282.8 g/mol. Levomilnacipran (Initial US approval: 2013) is the 1S,2R-enantiomer of milnacipran.The chemical structure of levomilnacipran hydrochloride is:
FETZIMA extended-release capsules are intended for oral administration. Each FETZIMA capsule contains extended-release beads with 23.0, 45.9, 91.8, or 137.8 mg of levomilnacipran hydrochloride equivalent to 20, 40, 80, or 120 mg of levomilnacipran, respectively.
Inactive ingredients include ethylcellulose, hypromellose, povidone, sugar spheres, talc, titanium dioxide, and triethyl citrate. Inactive ingredients also include black iron oxide, red iron oxide (80 mg and 120 mg capsules only), shellac glaze, and yellow iron oxide (20 mg and 40 mg capsules only).
Mechanism of Action
The exact mechanism of the antidepressant action of levomilnacipran is unknown, but is thought to be related to the potentiation of serotonin and norepinephrine in the central nervous system, through inhibition of reuptake at serotonin and norepinephrine transporters. Non-clinical studies have shown that levomilnacipran is a potent and selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI).
What is the most important information I should know about Fetzima?
Fetzima may cause serious side effects, including:
- Increased risk of suicidal thoughts or actions in some children, adolescents, and young adults. Fetzima and other antidepressant medicines may increase suicidal thoughts or actions in some children and young adults, especially within the first few months of treatment or when the dose is changed. Fetzima is not for use in children.
- Depression or other serious mental illnesses are the most important causes of suicidal thoughts or actions. Some people may have a higher risk of having suicidal thoughts or actions. These include people who have (or have a family history of) depression, bipolar illness (also called manic-depressive illness) or have a history of suicidal thoughts or actions.
How can I watch for and try to prevent suicidal thoughts and actions?
- Pay close attention to any changes, especially sudden changes in mood, behavior, thoughts, or feelings, or if you develop suicidal thoughts or actions. This is very important when an antidepressant medicine is started or when the dose is changed.
- Call your healthcare provider right away to report new or sudden changes in mood, behavior, thoughts, or feelings.
- Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider as scheduled. Call your healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you have concerns about symptoms.
Call your healthcare provider or get emergency medical help right away if you or your family member have any of the following symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- attempts to commit suicide
- acting on dangerous impulses
- acting aggressive, being angry or violent
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- new or worse depression
- new or worsening anxiety
- panic attacks
- feeling very agitated or restless
- new or worse irritability
- trouble sleeping
- an extreme increase in activity or talking (mania)
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
Who should not take Fetzima?
Do not take Fetzima if you:
- are allergic to levomilnacipran, milnacipran HCl, or any of the ingredients in Fetzima. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in Fetzima.
- take a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI)
- have stopped taking an MAOI in the last 14 days
- are being treated with the antibiotic linezolid or intravenous methylene blue
Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure if you take an MAOI, including the antibiotic linezolid or intravenous methylene blue.
Do not start taking an MAOI for at least 7 days after you stop treatment with Fetzima.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Fetzima?
Before taking Fetzima, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- have or have a family history of suicide, depression, bipolar disorder, mania or hypomania
- have high blood pressure
- have or had heart problems or stroke
- have or had bleeding problems
- have glaucoma (high pressure in the eye)
- have or had problems urinating (hesitation) or emptying your bladder (retention)
- have or had seizures (convulsions)
- have low sodium levels in your blood
- have or had kidney problems
- drink alcohol
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Fetzima may harm your unborn baby. Taking Fetzima during your third trimester of pregnancy may cause an increased risk of bleeding after delivery and may cause harm to your baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about the risks to you and your baby if you take Fetzima during pregnancy.
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you may be pregnant during treatment with Fetzima.
- There is a pregnancy registry for females who are exposed to Fetzima during pregnancy. The purpose of the registry is to collect information about the health of females exposed to Fetzima and their baby. If you become pregnant during treatment with Fetzima, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the National Pregnancy Registry for Antidepressants at 1-844-405-6185 or visit online at https://womensmentalhealth.org/clinical-and-research-programs/pregnancyregistry/antidepressants/.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Fetzima passes into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during treatment with Fetzima.
- If you breastfeed during treatment with Fetzima, call you healthcare provider right away if your baby develops sleepiness or fussiness, or is not feeding or gaining weight well.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Fetzima and other medicines may affect each other causing possible serious side effects.
Fetzima may affect the way other medicines work and other medicines may affect the way Fetzima works.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
- MAOIs
- medicines used to treat migraine headache known as triptans
- tricyclic antidepressants
- fentanyl
- lithium
- tramadol
- tryptophan
- buspirone
- amphetamines
- St. John’s Wort
- medicines that can affect blood clotting such as aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and warfarin
- diuretics
- medicines used to treat mood, anxiety, psychotic or thought disorders, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if you are taking any of these medicines. Your healthcare provider can tell you if it is safe to take Fetzima with your other medicines.
Do not start or stop any other medicines during treatment with Fetzima without talking to your healthcare provider first. Stopping Fetzima suddenly may cause you to have serious side effects. See, “What are the possible side effects of Fetzima?”
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get new medicine.
How should I take Fetzima?
- Take Fetzima exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it. Do not change your dose or stop taking Fetzima without first talking to your healthcare provider.
- Your healthcare provider may need to change the dose of Fetzima until it is the right dose for you.
- Take Fetzima 1 time each day at about the same time each day.
- Take Fetzima with or without food.
- Swallow Fetzima capsules whole. Do not open, chew, or crush the Fetzima capsule.
- If you miss a dose of Fetzima, take the missed dose as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and take your next dose at the regular time. Do not take 2 doses of Fetzima at the same time.
- If you take too much Fetzima, call your healthcare provider or poison control center at 1-800-222-1222, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking Fetzima?
- Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how Fetzima affects you. Fetzima can cause sleepiness or may affect your ability to make decisions, think clearly, or react quickly.
- Avoid drinking alcohol during treatment with Fetzima.
What are the possible side effects of Fetzima?
Fetzima may cause serious side effects, including:
- See, “What is the most important information I should know about Fetzima?”
- Serotonin syndrome. A potentially life-threatening problem called serotonin syndrome can happen when Fetzima is taken with certain other medicines. See, “Who should not take Fetzima?” Stop taking Fetzima and call you healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away if you have any of the following signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome:
- agitation
- seeing or hearing things that are not real (hallucinations)
- confusion
- coma
- fast heart beat
- blood pressure changes
- dizziness
- sweating
- flushing
- high body temperature (hyperthermia)
- tremors, stiff muscles, or muscle twitching
- loss of coordination
- seizures
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
- High blood pressure (hypertension). Your healthcare provider should check your blood pressure before you start and during treatment with Fetzima. If you have high blood pressure, it should be controlled before you start treatment with Fetzima.
- Increased heart rate. Your healthcare provider should check your heart rate before you start and during treatment with Fetzima. If you have heart problems or problems with an abnormal heartbeat, your problems should be treated before you start treatment with Fetzima.
- Increased risk of bleeding. Taking Fetzima with aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), warfarin or blood thinners may add to this risk. Tell your healthcare provider right away about any unusual bleeding or bruising.
- Eye problems (angle-closure glaucoma). Many antidepressant medicines, including Fetzima, may cause a certain type of eye problem called angle-closure glaucoma. Call your healthcare provider if you have changes in your vision or eye pain.
- Problems with urination. Fetzima may cause you to have problems with urination including decreased urine flow and being unable to pass any urine. Tell your healthcare provider if you develop any problems with urine flow during treatment with Fetzima.
- Manic episodes. Manic episodes may happen in people with bipolar disorder who take Fetzima. Symptoms may include:
- greatly increased energy
- severe trouble sleeping
- racing thoughts
- reckless behavior
- unusually grand ideas
- excessive happiness or irritability
- talking more or faster than usual
- Seizures (convulsions).
- Discontinuation syndrome. Suddenly stopping Fetzima may cause you to have serious side effects. Your healthcare provider may want to decrease your dose slowly. Symptoms may include:
- changes in your mood
- headache
- irritability and agitation
- tiredness
- dizziness
- problems sleeping
- electric shock sensation (paresthesia)
- hypomania
- anxiety
- ringing in your ears (tinnitus)
- confusion
- seizures
- Low sodium levels in your blood (hyponatremia). Low sodium levels in your blood may be serious and may cause death. Elderly people may be at greater risk for this. Signs and Symptoms of low sodium levels in your blood may include:
- headache
- difficulty concentrating
- memory changes
- confusion
- weakness and unsteadiness on your feet which can lead to falls
In severe or more sudden cases, signs and symptoms include:
- hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that are not real)
- fainting
- seizures
- coma
- respiratory arrest
- death
The most common side effects of Fetzima, include:
- nausea
- constipation
- sweating
- abnormal heartbeat
- erectile dysfunction
- vomiting
These are not all the possible side effects of Fetzima.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Fetzima
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Fetzima for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Fetzima to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about Fetzima that is written for healthcare professionals.
How should I store Fetzima?
- Store Fetzima at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep Fetzima and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Fetzima?
Active ingredient: levomilnacipran hydrochloride
Inactive ingredients: ethylcellulose, hypromellose, povidone, sugar spheres, talc, titanium dioxide, triethyl citrate, black iron oxide, red iron oxide (80 mg and 120 mg capsules only) shellac glaze, yellow iron oxide (20 mg and 40 mg capsules only)
Label
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- Rx Only NDC 0456-2212-30
Fetzima®
levomilnacipran
extended-release capsules
120 mg per capsule
30 capsules

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- Rx Only NDC 0456-2202-28
Fetzima®
levomilnacipran
extended-release capsules
Titration Pack
Two 20 mg Capsules
Twenty-six 40 mg capsules

SRC: NLM .


