Descovy
Generic name: emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide fumarate
Dosage form: tablet
Drug class: Antiviral combinations
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD. Last updated on Apr 13, 2022.
| WARNING: POST-TREATMENT ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B AND RISK OF DRUG RESISTANCE WITH USE OF Descovy FOR HIV-1 PRE-EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS (PrEP) IN UNDIAGNOSED EARLY HIV-1 INFECTION
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B (HBV) have been reported in HBV-infected individuals who have discontinued products containing emtricitabine (FTC) and/or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) and may occur with discontinuation of Descovy. Hepatic function should be monitored closely with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months in individuals who are infected with HBV and discontinue Descovy. If appropriate, anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Descovy used for HIV-1 PrEP must only be prescribed to individuals confirmed to be HIV-negative immediately prior to initiating and at least every 3 months during use. Drug-resistant HIV-1 variants have been identified with use of FTC/TDF for HIV-1 PrEP following undetected acute HIV-1 infection. Do not initiate Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP if signs or symptoms of acute HIV-1 infection are present unless negative infection status is confirmed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
Indications and Usage for Descovy
Treatment of HIV-1 Infection
Descovy is indicated, in combination with other antiretroviral agents, for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and pediatric patients weighing at least 35 kg.
Descovy is indicated, in combination with other antiretroviral agents other than protease inhibitors that require a CYP3A inhibitor, for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in pediatric patients weighing at least 14 kg and less than 35 kg.
HIV-1 Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)
Descovy is indicated in at-risk adults and adolescents weighing at least 35 kg for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to reduce the risk of HIV-1 infection from sexual acquisition, excluding individuals at risk from receptive vaginal sex. Individuals must have a negative HIV-1 test immediately prior to initiating Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Limitations of Use:
The indication does not include use of Descovy in individuals at risk of HIV-1 from receptive vaginal sex because effectiveness in this population has not been evaluated [see Clinical Studies (14.3)].
Descovy Dosage and Administration
Testing When Initiating and During Use of Descovy for Treatment of HIV-1 Infection or for HIV-1 PrEP
Prior to or when initiating Descovy, test individuals for hepatitis B virus infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Prior to or when initiating Descovy, and during use of Descovy on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein in all individuals. In individuals with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].¶
HIV-1 Screening for Individuals Receiving Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP
Screen all individuals for HIV-1 infection immediately prior to initiating Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP and at least once every 3 months while taking Descovy, and upon diagnosis of any other sexually transmitted infections (STIs) [see Indications and Usage (1.2), Contraindications (4), and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
If recent (<1 month) exposures to HIV-1 are suspected or clinical symptoms consistent with acute HIV-1 infection are present, use a test approved or cleared by the FDA as an aid in the diagnosis of acute or primary HIV-1 infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.4), and Clinical Studies (14.3)].
Recommended Dosage for Treatment of HIV-1 Infection in Adults and Pediatric Patients Weighing at Least 35 kg
Descovy is a two-drug fixed dose combination product containing emtricitabine (FTC) and tenofovir alafenamide (TAF).
The recommended dosage of Descovy for treatment of HIV-1 is one tablet containing 200 mg FTC and 25 mg of TAF taken orally once daily with or without food in:
- adults and pediatric patients with body weight at least 35 kg and estimated creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 30 mL per minute; or
- adults with creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute who are receiving chronic hemodialysis. On days of hemodialysis, administer the daily dose of Descovy after completion of hemodialysis treatment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
The safety and effectiveness of Descovy coadministered with an HIV-1 protease inhibitor that is administered with either ritonavir or cobicistat have not been established in adults with creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute, with or without hemodialysis.
For specific dosing recommendations for coadministered antiretroviral drugs, refer to their respective prescribing information [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Recommended Dosage for Treatment of HIV-1 Infection in Pediatric Patients Weighing at Least 14 kg to Less than 35 kg
The recommended dosage of Descovy in pediatric patients weighing at least 14 kg to 35 kg is based on body weight and provided in Table 1. This dosing information is applicable to pediatric patients with estimated creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 30 mL per minute [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] who are not receiving an HIV protease inhibitor that is administered with either ritonavir or cobicistat.
| Body Weight (kg) | Descovy Dose |
|---|---|
| 25 kg to less than 35 kg | One tablet containing 200 mg FTC and 25 mg of TAF taken orally once daily |
| 14 kg to less than 25 kg | One tablet containing 120 mg FTC and 15 mg TAF taken orally once daily |
The safety and effectiveness of Descovy coadministered with an HIV-1 protease inhibitor that is administered with either ritonavir or cobicistat have not been established in pediatric subjects weighing less than 35 kg.
For specific dosing recommendations for coadministered antiretroviral drugs, refer to their respective prescribing information [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Recommended Dosage for HIV-1 PrEP in Adults and Adolescents Weighing at Least 35 kg
The dosage of Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP is one tablet (containing 200 mg of FTC and 25 mg of TAF) once daily taken orally with or without food in HIV-1 uninfected:
- adults and adolescents weighing at least 35 kg and with a creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 30 mL per minute; or
- adults with creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute who are receiving chronic hemodialysis. On days of hemodialysis, administer the daily dose of Descovy after completion of hemodialysis treatment [see Indications and Usage (1.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Not Recommended in Individuals with Severe Renal Impairment for Treatment of HIV-1 Infection or for HIV-1 PrEP
Descovy is not recommended in individuals with:
- severe renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance of 15 to below 30 mL per minute); or
- end stage renal disease (ESRD; estimated creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute) who are not receiving chronic hemodialysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.5) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Dosage Forms and Strengths

- 200 mg/25 mg tablets: 200 mg of emtricitabine (FTC) and 25 mg of tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) (equivalent to 28 mg of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate). These tablets are blue, rectangular-shaped, film-coated, debossed with “GSI” on one side and “225” on the other side.
- 120 mg/15 mg tablets: 120 mg of FTC and 15 mg of TAF (equivalent to 16.8 mg of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate). These tablets are white, round-shaped, film coated, debossed with “GSI” on one side and “15” on the other side.
Contraindications
Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP is contraindicated in individuals with unknown or positive HIV-1 status [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Warnings and Precautions
Severe Acute Exacerbation of Hepatitis B in Individuals with HBV Infection
All individuals should be tested for the presence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) before or when initiating Descovy [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B (e.g., liver decompensation and liver failure) have been reported in HBV-infected individuals who have discontinued products containing FTC and/or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) and may occur with discontinuation of Descovy. Individuals infected with HBV who discontinue Descovy should be closely monitored with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months after stopping treatment. If appropriate, anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted, especially in individuals with advanced liver disease or cirrhosis, since post-treatment exacerbation of hepatitis may lead to hepatic decompensation and liver failure. HBV-uninfected individuals should be offered vaccination.
Comprehensive Management to Reduce the Risk of Sexually Transmitted Infections, Including HIV-1, and Development of HIV-1 Resistance When Descovy Is Used for HIV-1 PrEP
Use Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP to reduce the risk of HIV-1 infection as part of a comprehensive prevention strategy, including adherence to daily administration and safer sex practices, including condoms, to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). The time from initiation of Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP to maximal protection against HIV-1 infection is unknown.
Risk for HIV-1 acquisition includes behavioral, biological, or epidemiologic factors including but not limited to condomless sex, past or current STIs, self-identified HIV risk, having sexual partners of unknown HIV-1 viremic status, or sexual activity in a high prevalence area or network.
Counsel individuals on the use of other prevention measures (e.g., consistent and correct condom use, knowledge of partner(s)’ HIV-1 status, including viral suppression status, regular testing for STIs that can facilitate HIV-1 transmission). Inform uninfected individuals about and support their efforts in reducing sexual risk behavior.
Use Descovy to reduce the risk of acquiring HIV-1 only in individuals confirmed to be HIV-1 negative. HIV-1 resistance substitutions may emerge in individuals with undetected HIV-1 infection who are taking only Descovy, because Descovy alone does not constitute a complete regimen for HIV-1 treatment [see Microbiology (12.4)]; therefore, care should be taken to minimize the risk of initiating or continuing Descovy before confirming the individual is HIV-1 negative.
- Some HIV-1 tests only detect anti-HIV antibodies and may not identify HIV-1 during the acute stage of infection. Prior to initiating Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP, ask seronegative individuals about recent (in past month) potential exposure events (e.g., condomless sex or condom breaking during sex with a partner of unknown HIV-1 status or unknown viremic status, or a recent STI), and evaluate for current or recent signs or symptoms consistent with acute HIV-1 infection (e.g., fever, fatigue, myalgia, skin rash).
- If recent (<1 month) exposures to HIV-1 are suspected or clinical symptoms consistent with acute HIV-1 infection are present, use a test approved or cleared by the FDA as an aid in the diagnosis of acute or primary HIV-1 infection.
While using Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP, HIV-1 testing should be repeated at least every 3 months, and upon diagnosis of any other STIs.
- If an HIV-1 test indicates possible HIV-1 infection, or if symptoms consistent with acute HIV-1 infection develop following a potential exposure event, convert the HIV-1 PrEP regimen to an HIV treatment regimen until negative infection status is confirmed using a test approved or cleared by the FDA as an aid in the diagnosis of acute or primary HIV-1 infection.
Counsel HIV-1 uninfected individuals to strictly adhere to the once daily Descovy dosing schedule. The effectiveness of Descovy in reducing the risk of acquiring HIV-1 is strongly correlated with adherence, as demonstrated by measurable drug levels in a clinical trial of Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP. Some individuals, such as adolescents, may benefit from more frequent visits and counseling to support adherence [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4), Microbiology (12.4), and Clinical Studies (14.3)].
Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in HIV-1 infected patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including FTC, a component of Descovy. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, HIV-1 infected patients whose immune system responds may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (such as Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia [PCP], or tuberculosis), which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
Autoimmune disorders (such as Graves’ disease, polymyositis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and autoimmune hepatitis) have also been reported to occur in the setting of immune reconstitution; however, the time to onset is more variable, and can occur many months after initiation of treatment.
New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment
Postmarketing cases of renal impairment, including acute renal failure, proximal renal tubulopathy (PRT), and Fanconi syndrome have been reported with TAF-containing products; while most of these cases were characterized by potential confounders that may have contributed to the reported renal events, it is also possible these factors may have predisposed patients to tenofovir-related adverse events [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)]. Descovy is not recommended in individuals with estimated creatinine clearance of 15 to below 30 mL per minute, or in individuals with estimated creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute who are not receiving chronic hemodialysis.
Individuals taking tenofovir prodrugs who have impaired renal function and those taking nephrotoxic agents including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are at increased risk of developing renal-related adverse reactions.
Prior to or when initiating Descovy, and during treatment with Descovy on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein in all individuals. In individuals with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorus. Discontinue Descovy in individuals who develop clinically significant decreases in renal function or evidence of Fanconi syndrome.
Lactic Acidosis/Severe Hepatomegaly with Steatosis
Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogs, including emtricitabine, a component of Descovy, and tenofovir DF, another prodrug of tenofovir, alone or in combination with other antiretrovirals. Treatment with Descovy should be suspended in any individual who develops clinical or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity (which may include hepatomegaly and steatosis even in the absence of marked transaminase elevations).
Adverse Reactions
The following adverse reactions are discussed in other sections of the labeling:
- Severe Acute Exacerbations of Hepatitis B [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Immune Reconstitution Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Lactic Acidosis/Severe Hepatomegaly with Steatosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug (or a drug given in various combinations with other concomitant therapy) cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug (or drug given in the same or different combination therapy) and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials of FTC+TAF with Elvitegravir (EVG) plus Cobicistat (COBI) in Treatment-Naïve Adults with HIV-1 Infection
In pooled 48-week trials of antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected adult subjects, the most common adverse reaction in subjects treated with FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI (N=866) (incidence greater than or equal to 10%, all grades) was nausea (10%). In this treatment group, 0.9% of subjects discontinued FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI due to adverse events during the 48-week treatment period [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. The safety profile was similar in virologically-suppressed adults with HIV-1 infection who were switched to FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI (N=799). Antiretroviral treatment-naïve adult subjects treated with FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI experienced mean increases of 30 mg/dL of total cholesterol, 15 mg/dL of LDL cholesterol, 7 mg/dL of HDL cholesterol, and 29 mg/dL of triglycerides after 48 weeks of use.
Renal Laboratory Tests
In two 48-week trials in antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected adults treated with FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI (N=866) with a median baseline eGFR of 115 mL per minute, mean serum creatinine increased by 0.1 mg per dL from baseline to Week 48. Median urine protein-to-creatinine ratio (UPCR) was 44 mg per gram at baseline and at Week 48. In a 48-week trial in virologically-suppressed TDF-treated adults who switched to FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI (N=959) with a mean baseline eGFR of 112 mL per minute, mean serum creatinine was similar to baseline at Week 48; median UPCR was 61 mg per gram at baseline and 46 mg per gram at Week 48. Across these trials, renal serious adverse events or discontinuations due to renal adverse reactions were encountered in less than 1% of participants treated with FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI.
In a 24-week trial in adults with renal impairment (baseline eGFR 30 to 69 mL per minute) who received FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI (N=248), mean serum creatinine was 1.5 mg per dL at both baseline and Week 24. Median UPCR was 161 mg per gram at baseline and 93 mg per gram at Week 24. FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI was permanently discontinued due to worsening renal function in two of 80 (3%) subjects.
Bone Mineral Density Effects
In the pooled analysis of two 48-week trials of antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected adult subjects, bone mineral density (BMD) from baseline to Week 48 was assessed by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). Mean BMD decreased from baseline to Week 48 −1.30% with FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI at the lumbar spine and −0.66% at the total hip. BMD declines of 5% or greater at the lumbar spine were experienced by 10% of FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI subjects. BMD declines of 7% or greater at the femoral neck were experienced by 7% of FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI subjects. The long-term clinical significance of these BMD changes is not known.
In 799 virologically-suppressed TDF-treated adult subjects that switched to FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI, at Week 48 mean BMD increased (1.86% lumbar spine, 1.95% total hip). BMD declines of 5% or greater at the lumbar spine were experienced by 1% of FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI subjects. BMD declines of 7% or greater at the femoral neck were experienced by 1% of FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI subjects.
Adverse Reactions in a Clinical Trial of FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI in Virologically-Suppressed Adults with End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) Receiving Chronic Hemodialysis
In a 48-week trial of virologically-suppressed HIV-1 infected adult subjects with end stage renal disease (ESRD) (estimated creatinine clearance of less than 15 mL/min) on chronic hemodialysis treated with FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI (N=55), the most commonly reported adverse reaction (adverse event assessed as causally related by investigator and all grades) was nausea (7%). Serious adverse events were reported in 53% of subjects and the most common serious adverse events were pneumonia (13%), fluid overload (7%), hyperkalemia (7%) and osteomyelitis (7%). Overall 5% of subjects permanently discontinued treatment due to an adverse event.
Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials in Pediatric Subjects with HIV-1 Infection
Pediatric Subjects Weighing at Least 25 kg:
The safety profile of FTC+TAF in pediatric subjects weighing at least 25 kg is informed by an open-label trial of antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected pediatric subjects between the ages of 12 to less than 18 years weighing at least 35 kg through 48 weeks (N=50; Cohort 1) and virologically-suppressed subjects between the ages of 6 to less than 12 years weighing at least 25 kg (N=52; Cohort 2). Subjects received FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI through 48 weeks. With the exception of a decrease in the mean CD4+ cell count observed in cohort 2, the safety of this combination was similar to that in adults.
Bone Mineral Density Effects
Cohort 1: Treatment-naïve adolescents (12 to less than 18 years; at least 35 kg)
Among the subjects in cohort 1 receiving FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI, mean BMD increased from baseline to Week 48, +4.2% at the lumbar spine and +1.3% for the total body less head (TBLH). Mean changes from baseline BMD Z-scores were −0.07 for lumbar spine and −0.20 for TBLH at Week 48. One subject had significant (at least 4%) lumbar spine BMD loss at Week 48.
Cohort 2: Virologically-suppressed children (6 to less than 12 years; at least 25 kg)
Among the subjects in cohort 2 receiving FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI, mean BMD increased from baseline to Week 48, +3.9% at the lumbar spine and +4.2% for TBLH. Mean changes from baseline BMD Z-scores were -0.24 for lumbar spine and -0.19 for TBLH at Week 48. Six subjects had significant (at least 4%) lumbar spine BMD loss at Week 48 and 2 subjects also had at least 4% TBLH BMD loss at Week 48.
Change from Baseline in CD4+ cell counts
Cohort 2: Virologically-suppressed children (6 to less than 12 years; at least 25 kg)
Cohort 2 evaluated pediatric subjects (N=52) who were virologically-suppressed and who switched from their antiretroviral regimen to FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI. Although all subjects had HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL, there was a decrease from baseline in CD4+ cell count at Weeks 24 and 48. The mean baseline and mean change from baseline in CD4+ cell count and in CD4% from Week 2 to Week 48 are presented in Table 2. All subjects maintained their CD4+ cell counts above 400 cells/mm3 [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
| Mean Change from Baseline | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Week 2 | Week 4 | Week 12 | Week 24 | Week 32 | Week 48 | |
|
|||||||
| CD4+ Cell Count (cells/mm3) | 961 (275.5)* | -117 | -114 | -112 | -118 | -62 | -66 |
| CD4% | 38 (6.4)* | +0.3% | -0.1% | -0.8% | -0.8% | -1.0% | -0.6% |
Pediatric Subjects Weighing at Least 14 to Less Than 25 kg:
In a separate open-label trial of virologically-suppressed subjects at least 2 years of age and weighing at least 14 to less than 25 kg (N=22; Cohort 3) who received FTC+TAF with bictegravir through 24 weeks, no new adverse reactions or laboratory abnormalities were identified compared to those observed in adults. In this trial, the mean (SD) change from baseline to Week 24 in CD4+ cell count was −126 (264) cells per mm3 and the mean (SD) change in CD4% from baseline to Week 24 was 0.2% (4.4%).
Adverse Reactions from Clinical Trial Experience in HIV-1 Uninfected Individuals Taking Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP
The safety profile of Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP was comparable to that observed in clinical trials of HIV-infected subjects based on a double-blind, randomized, active-controlled trial (DISCOVER) in which a total of 5,387 HIV-1 uninfected adult men and transgender women who have sex with men received Descovy (N=2,694) or TRUVADA (N=2,693) once daily for HIV-1 PrEP [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. Median duration of exposure was 86 and 87 weeks, respectively. The most common adverse reaction in participants who received Descovy (incidence greater than or equal to 5%, all grades) was diarrhea (5%). Table 3 provides a list of the most common adverse reactions that occurred in 2% or more of participants in either treatment group. The proportion of participants who discontinued treatment with Descovy or TRUVADA due to adverse events, regardless of severity, was 1.3% and 1.8%, respectively.
| Descovy (N=2,694) |
TRUVADA (N=2,693) |
|
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Diarrhea | 5% | 6% |
| Nausea | 4% | 5% |
| Headache | 2% | 2% |
| Fatigue | 2% | 3% |
| Abdominal pain* | 2% | 3% |
Renal Laboratory Tests
Changes from baseline to Week 48 in renal laboratory data are presented in Table 4. The long-term clinical significance of these renal laboratory changes on adverse reaction frequencies between Descovy and TRUVADA is not known.
| Descovy (N=2,694) |
TRUVADA (N=2,693) |
|
|---|---|---|
| eGFRCG=estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate by Cockcroft-Gault; UPCR=urine protein/creatinine ratio | ||
|
||
| Serum Creatinine (mg/dL)* | ||
| Change at Week 48 | −0.01 (0.107) | 0.01 (0.111) |
| eGFRCG (mL/min)† | ||
| Change at Week 48 | 1.8 (−7.2, 11.1) | −2.3 (−10.8, 7.2) |
| Percentage of Participants who Developed UPCR >200 mg/g‡ | ||
| At Week 48 | 0.7% | 1.5% |
Bone Mineral Density Effects
In the DISCOVER trial, mean increases from baseline to Week 48 of 0.5% at the lumbar spine (N=159) and 0.2% at the total hip (N=158) were observed in participants receiving Descovy, compared to mean decreases of 1.1% at the lumbar spine (N=160) and 1.0% at the total hip (N=158) in participants receiving TRUVADA. BMD declines of 5% or greater at the lumbar spine and 7% or greater at the total hip were experienced by 4% and 1% of participants, respectively, in both treatment groups at Week 48. The long-term clinical significance of these BMD changes is not known.
Serum Lipids
Changes from baseline to Week 48 in total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, triglycerides, and total cholesterol to HDL ratio are presented in Table 5.
| Descovy (N=2,694) |
TRUVADA (N=2,693) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Week 48 | Baseline | Week 48 | |
| mg/dL | Change† | mg/dL | Change† | |
|
||||
| Total Cholesterol (fasted) | 176 ‡ | 0 ‡ | 176 § | -12 § |
| HDL-Cholesterol (fasted) | 51 ‡ | -2 ‡ | 51 § | -5 § |
| LDL-Cholesterol (fasted) | 103 ¶ | 0 ¶ | 103 # | -7 # |
| Triglycerides (fasted) | 109 ‡ | +9 ‡ | 111 § | -1 § |
| Total Cholesterol to HDL ratio | 3.7 ‡ | 0.2 ‡ | 3.7 § | 0.1 § |
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of products containing TAF. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Angioedema, urticaria, and rash
Renal and Urinary Disorders
Acute renal failure, acute tubular necrosis, proximal renal tubulopathy, and Fanconi syndrome
Drug Interactions
Potential for Other Drugs to Affect One or More Components of Descovy
TAF, a component of Descovy, is a substrate of P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1, and OATP1B3. Drugs that strongly affect P-gp and BCRP activity may lead to changes in TAF absorption (see Table 5). Drugs that induce P-gp activity are expected to decrease the absorption of TAF, resulting in decreased plasma concentration of TAF, which may lead to loss of therapeutic effect of Descovy and development of resistance. Coadministration of Descovy with other drugs that inhibit P-gp and BCRP may increase the absorption and plasma concentration of TAF. TAF is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, or UGT1A1. TAF is a weak inhibitor of CYP3A in vitro. TAF is not an inhibitor or inducer of CYP3A in vivo.
Drugs Affecting Renal Function
Because FTC and tenofovir are primarily excreted by the kidneys by a combination of glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion, coadministration of Descovy with drugs that reduce renal function or compete for active tubular secretion may increase concentrations of FTC, tenofovir, and other renally eliminated drugs and this may increase the risk of adverse reactions. Some examples of drugs that are eliminated by active tubular secretion include, but are not limited to, acyclovir, cidofovir, ganciclovir, valacyclovir, valganciclovir, aminoglycosides (e.g., gentamicin), and high-dose or multiple NSAIDs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Established and Other Potentially Significant Interactions
Table 6 provides a listing of established or potentially clinically significant drug interactions with recommended steps to prevent or manage the drug interaction (the table is not all inclusive). The drug interactions described are based on studies conducted with either Descovy, the components of Descovy (emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide) as individual agents, or are predicted drug interactions that may occur with Descovy. For magnitude of interaction, see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3).
| Concomitant Drug Class: Drug Name | Effect on Concentration† | Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Antiretroviral Agents: Protease Inhibitors (PI) | ||
| tipranavir/ritonavir | ↓ TAF | Coadministration with Descovy is not recommended. |
| Other Agents | ||
| Anticonvulsants: carbamazepine oxcarbazepine phenobarbital phenytoin |
↓ TAF | Consider alternative anticonvulsant. |
| Antimycobacterials: rifabutin rifampin rifapentine |
↓ TAF | Coadministration of Descovy with rifabutin, rifampin, or rifapentine is not recommended. |
| Herbal Products: St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum) |
↓ TAF | Coadministration of Descovy with St. John’s wort is not recommended. |
Drugs without Clinically Significant Interactions with Descovy
Based on drug interaction studies conducted with the components of Descovy, no clinically significant drug interactions have been either observed or are expected when Descovy is combined with the following antiretroviral agents: atazanavir with ritonavir or cobicistat, darunavir with ritonavir or cobicistat, dolutegravir, efavirenz, ledipasvir, lopinavir/ritonavir, maraviroc, nevirapine, raltegravir, rilpivirine, and sofosbuvir. No clinically significant drug interactions have been either observed or are expected when Descovy is combined with the following drugs: buprenorphine, itraconazole, ketoconazole, lorazepam, methadone, midazolam, naloxone, norbuprenorphine, norgestimate/ethinyl estradiol, and sertraline.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in individuals exposed to Descovy during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients by calling the Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry (APR) at 1-800-258-4263.
Risk Summary
Available data from the APR show no statistically significant difference in the overall risk of major birth defects for emtricitabine (FTC) or tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) compared with the background rate for major birth defects of 2.7% in a U.S. reference population of the Metropolitan Atlanta Congenital Defects Program (MACDP) (see Data). The rate of miscarriage for individual drugs is not reported in the APR. The estimated background rate of miscarriage in the clinically recognized pregnancies in the U.S. general population is 15–20%.
In animal studies, no adverse developmental effects were observed when the components of Descovy were administered separately during the period of organogenesis at exposures 60 and 108 times (mice and rabbits, respectively) the FTC exposure and at exposure equal to or 53 times (rats and rabbits, respectively) the TAF exposure at the recommended daily dose of Descovy (see Data). Likewise, no adverse developmental effects were seen when FTC was administered to mice through lactation at exposures up to approximately 60 times the exposure at the recommended daily dose of Descovy. No adverse effects were observed in the offspring when TDF was administered through lactation at tenofovir exposures of approximately 14 times the exposure at the recommended daily dosage of Descovy.
Data
Human Data
Prospective reports from the APR of overall major birth defects in pregnancies exposed to the components of Descovy are compared with a U.S. background major birth defect rate. Methodological limitations of the APR include the use of MACDP as the external comparator group. The MACDP population is not disease-specific, evaluates women and infants from a limited geographic area, and does not include outcomes for births that occurred at less than 20 weeks gestation.
Emtricitabine (FTC)
Based on prospective reports to the APR of over 5,400 exposures to FTC-containing regimens during pregnancy resulting in live births (including over 3,900 exposed in the first trimester and over 1,500 exposed in the second/third trimester), the prevalence of birth defects in live births was 2.6% (95% CI: 2.2% to 3.2%) and 2.7% (95% CI: 1.9% to 3.7%) following first and second/third trimester exposure, respectively, to FTC-containing regimens.
Tenofovir Alafenamide (TAF)
Based on prospective reports to the APR of over 660 exposures to TAF-containing regimens during pregnancy resulting in live births (including over 520 exposed in the first trimester and over 130 exposed in the second/third trimester), the prevalence of birth defects in live births was 4.2 % (95% CI: 2.6 % to 6.3 %) and 3.0% (95% CI: 0.8% to 7.5 %) following first and second/third trimester exposure, respectively, to TAF-containing regimens.
Animal Data
Emtricitabine: FTC was administered orally to pregnant mice (250, 500, or 1000 mg/kg/day) and rabbits (100, 300, or 1000 mg/kg/day) through organogenesis (on gestation days 6 through 15, and 7 through 19, respectively). No significant toxicological effects were observed in embryo-fetal toxicity studies performed with FTC in mice at exposures (area under the curve [AUC]) approximately 60 times higher and in rabbits at approximately 108 times higher than human exposures at the recommended daily dose. In a pre/postnatal development study with FTC, mice were administered doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day; no significant adverse effects directly related to drug were observed in the offspring exposed daily from before birth (in utero) through sexual maturity at daily exposures (AUC) of approximately 60-fold higher than human exposures at the recommended daily dose.
Tenofovir Alafenamide: TAF was administered orally to pregnant rats (25, 100, or 250 mg/kg/day) and rabbits (10, 30, or 100 mg/kg/day) through organogenesis (on gestation days 6 through 17, and 7 through 20, respectively). No adverse embryo-fetal effects were observed in rats and rabbits at TAF exposures approximately similar to (rats) and 53 (rabbits) times higher than the exposure in humans at the recommended daily dose of Descovy. TAF is rapidly converted to tenofovir; the observed tenofovir exposures in rats and rabbits were 59 (rats) and 93 (rabbits) times higher than human tenofovir exposures at the recommended daily dose. Since TAF is rapidly converted to tenofovir and a lower tenofovir exposure in rats and mice was observed after TAF administration compared to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF, another prodrug for tenofovir) administration, a pre/postnatal development study in rats was conducted only with TDF. Doses up to 600 mg/kg/day were administered through lactation; no adverse effects were observed in the offspring on gestation day 7 (and lactation day 20) at tenofovir exposures of approximately 14 (21) times higher than the exposures in humans at the recommended daily dose of Descovy.
Lactation
Risk Summary
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that HIV-infected mothers not breastfeed their infants, to avoid risking postnatal transmission of HIV-1.
Based on limited data, FTC has been shown to be present in human breast milk; it is not known if TAF is present in human breast milk. Tenofovir has been shown to be present in the milk of lactating rats and rhesus monkeys after administration of TDF (see Data). It is not known if TAF is present in animal milk.
It is not known if Descovy affects milk production or has effects on the breastfed child.
Because of the potential for: 1) HIV transmission (in HIV-negative infants); 2) developing viral resistance (in HIV-positive infants); and 3) adverse reactions in a breastfed infant similar to those seen in adults, instruct mothers not to breastfeed if they are taking Descovy for the treatment of HIV-1 (see Data).
Data
Animal Data
Tenofovir Alafenamide: Studies in rats and monkeys have demonstrated that tenofovir is secreted in milk. Tenofovir was excreted into the milk of lactating rats following oral administration of TDF (up to 600 mg/kg/day) at up to approximately 24% of the median plasma concentration in the highest dosed animals at lactation day 11. Tenofovir was excreted into the milk of lactating monkeys following a single subcutaneous (30 mg/kg) dose of tenofovir at concentrations up to approximately 4% of plasma concentration, resulting in exposure (AUC) of approximately 20% of plasma exposure.
Pediatric Use
Treatment of HIV-1 Infection
The safety and effectiveness of Descovy, in combination with other antiretroviral agents, for the treatment of HIV-1 infection was established in pediatric patients with body weight greater than or equal to 14 kg [see Indication and Usage (1.1) and Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)].
Use of Descovy in pediatric patients between 6 to less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 25 kg is supported by adequate and well controlled studies of FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI in adults and by an open-label trial in antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected pediatric subjects aged 12 to less than 18 years and weighing at least 35 kg through Week 48 (N=50; cohort 1) and in virologically-suppressed pediatric subjects aged 6 to less than 12 years and weighing at least 25 kg through Week 48 (N=52; cohort 2). The safety and efficacy of FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI in adolescent subjects was similar to that in adults on this regimen. The safety and efficacy of FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI in subjects 6 to 12 years of age weighing at least 25 kg was similar to that in antiretroviral treatment-naïve adults and adolescents on this regimen, with the exception of a decrease from baseline in CD4+ cell count [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Use of Descovy in pediatric patients between 2 to less than 6 years of age and weighing at least 14 to less than 25 kg is supported by adequate and well controlled studies of FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI in adults and by a separate open-label trial of FTC+TAF with bictegravir in virologically-suppressed pediatric patients at least 2 years of age and weighing at least 14 to less than 25 kg through Week 24 (N=22; cohort 3). The safety and efficacy of FTC+TAF in these pediatric subjects were similar to that observed in adults who received FTC+TAF with bictegravir [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Safety and effectiveness of Descovy coadministered with an HIV-1 protease inhibitor that is administered with either ritonavir or cobicistat have not been established in pediatric patients weighing less than 35 kg [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Safety and effectiveness of Descovy for treatment of HIV-1 infection in pediatric patients weighing less than 14 kg have not been established.
HIV-1 PrEP
Safety and effectiveness of Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP in at-risk adolescents weighing at least 35 kg, excluding individuals at risk from receptive vaginal sex, is supported by data from an adequate and well-controlled trial of Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP in adults with additional data from safety and pharmacokinetic studies in previously conducted trials with the individual drug products, FTC and TAF, with EVG+COBI, in HIV-1 infected adults and pediatric subjects [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 and 12.4), and Clinical Studies (14)].
While using Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP, HIV-1 testing should be repeated at least every 3 months, and upon diagnosis of any other STIs. Previous studies in at-risk adolescents indicated waning adherence to a daily oral PrEP regimen once visits were switched from monthly to quarterly visits. Adolescents may therefore benefit from more frequent visits and counseling [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Safety and effectiveness of Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP in pediatric patients weighing less than 35 kg have not been established.
Geriatric Use
In clinical trials of an FTC+TAF-containing regimen for treatment of HIV-1, 80 of the 97 subjects enrolled aged 65 years and over received FTC+TAF and EVG+COBI. No differences in safety or efficacy have been observed between elderly subjects and adults between 18 and less than 65 years of age.
Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment of Descovy is recommended in individuals with estimated creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 30 mL per minute, or in adults with ESRD (estimated creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute) who are receiving chronic hemodialysis. On days of hemodialysis, administer the daily dose of Descovy after completion of hemodialysis treatment.
Safety and effectiveness of Descovy coadministered with an HIV-1 protease inhibitor that is administered with either ritonavir or cobicistat have not been established in patients with ESRD [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Descovy is not recommended in individuals with severe renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance of 15 to below 30 mL per minute), or in individuals with ESRD who are not receiving chronic hemodialysis, as the safety of Descovy has not been established in these populations [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) and Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of Descovy is recommended in individuals with mild (Child-Pugh Class A) or moderate (Child-Pugh Class B) hepatic impairment. Descovy has not been studied in individuals with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Overdosage
No data are available on overdose of Descovy in patients. If overdose occurs, monitor the individual for evidence of toxicity. Treatment of overdose with Descovy consists of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs as well as observation of the clinical status of the individual.
Emtricitabine (FTC): Limited clinical experience is available at doses higher than the recommended dose of FTC in Descovy. In one clinical pharmacology study, single doses of FTC 1200 mg (6 times the FTC dose in Descovy) were administered to 11 subjects. No severe adverse reactions were reported. The effects of higher doses are not known.
Hemodialysis treatment removes approximately 30% of the FTC dose over a 3-hour dialysis period starting within 1.5 hours of FTC dosing (blood flow rate of 400 mL per minute and a dialysate flow rate of 600 mL per minute). It is not known whether FTC can be removed by peritoneal dialysis.
Tenofovir Alafenamide (TAF): Limited clinical experience is available at doses higher than the recommended dose of TAF. A single dose of 125 mg TAF (5 times the TAF dose in 200/25 mg Descovy) was administered to 48 healthy subjects; no serious adverse reactions were reported. The effects of higher doses are unknown. Tenofovir is efficiently removed by hemodialysis with an extraction coefficient of approximately 54%.
Descovy Description
Descovy (emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide) is a fixed dose combination tablet containing emtricitabine (FTC) and tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) for oral administration.
- FTC, a synthetic nucleoside analog of cytidine, is an HIV nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor (HIV NRTI).
- TAF, an HIV NRTI, is converted in vivo to tenofovir, an acyclic nucleoside phosphonate (nucleotide) analog of adenosine 5′-monophosphate.
Descovy tablets are available in two dose strengths:
- 200 mg/25 mg tablets: 200 mg of FTC and 25 mg of TAF (equivalent to 28 mg of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate).
- 120 mg/15 mg tablets: 120 mg of FTC and 15 mg of TAF (equivalent to 16.8 mg of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate).
Both dose strengths of Descovy tablets include the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. The 200 mg/ 25 mg tablets are film-coated with a coating material containing indigo carmine aluminum lake, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide. The 120 mg/15 mg tablets are film-coated with a coating material containing polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol, and talc.
Emtricitabine: The chemical name of FTC is 4-amino-5-fluoro-1-(2R-hydroxymethyl-1,3-oxathiolan-5S-yl)-(1H)-pyrimidin-2-one. FTC is the (-)enantiomer of a thio analog of cytidine, which differs from other cytidine analogs in that it has a fluorine in the 5 position.
FTC has a molecular formula of C8H10FN3O3S and a molecular weight of 247.24 and has the following structural formula:
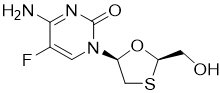
FTC is a white to off-white powder with a solubility of approximately 112 mg per mL in water at 25 °C.
Tenofovir Alafenamide: The chemical name of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate drug substance is L-alanine, N-[(S)-[[(1R)-2-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-1-methylethoxy]methyl]phenoxyphosphinyl]-, 1-methylethyl ester, (2E)-2-butenedioate (2:1).
Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate has an empirical formula of C21H29O5N6P∙½(C4H4O4) and a formula weight of 534.50 and has the following structural formula:
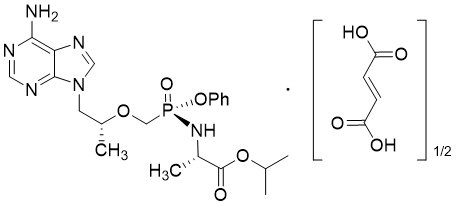
Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate is a white to off-white or tan powder with a solubility of 4.7 mg per mL in water at 20 °C.
Descovy – Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Descovy is a fixed dose combination of antiretroviral drugs emtricitabine (FTC) and tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) [see Microbiology (12.4)].
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
In a thorough QT/QTc study in 48 healthy subjects, TAF at the recommended dose or at a dose approximately 5 times the recommended dose, did not affect the QT/QTc interval and did not prolong the PR interval. The effect of the other component of Descovy, FTC, or the combination of FTC and TAF on the QT interval is not known.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion
The pharmacokinetic (PK) properties of the components of Descovy are provided in Table 7. The multiple dose PK parameters of FTC and TAF and its metabolite tenofovir are provided in Table 8. HIV status has no effect on the pharmacokinetics of FTC and TAF in adults.
| Emtricitabine | Tenofovir Alafenamide | |
|---|---|---|
| PBMCs=peripheral blood mononuclear cells; CES1=carboxylesterase 1 | ||
|
||
| Absorption | ||
| Tmax (h) | 3 | 1 |
| Effect of high fat meal (relative to fasting)* | AUC Ratio = 0.91 (0.89, 0.93) Cmax Ratio = 0.74 (0.69, 0.78) |
AUC Ratio = 1.75 (1.64, 1.88) Cmax Ratio= 0.85 (0.75, 0.95) |
| Distribution | ||
| % Bound to human plasma proteins | <4 | ~80 |
| Source of protein binding data | In vitro | Ex vivo |
| Blood-to-plasma ratio | 0.6 | 1.0 |
| Metabolism | ||
| Metabolism | Not significantly metabolized | Cathepsin A† (PBMCs) CES1 (hepatocytes) CYP3A (minimal) |
| Elimination | ||
| Major route of elimination | Glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion | Metabolism (>80% of oral dose) |
| t1/2 (h)‡ | 10 | 0.51 |
| % Of dose excreted in urine§ | 70 | <1 |
| % Of dose excreted in feces§ | 13.7 | 31.7 |
| Parameter Mean (CV%) | Emtricitabine* | Tenofovir Alafenamide† | Tenofovir‡ |
|---|---|---|---|
| CV=Coefficient of Variation; NA=Not Applicable | |||
|
|||
| Cmax (microgram per mL) |
2.1 (20.2) | 0.16 (51.1) | 0.02 (26.1) |
| AUCtau (microgram∙hour per mL) |
11.7 (16.6) | 0.21 (71.8) | 0.29 (27.4) |
| Ctrough (microgram per mL) |
0.10 (46.7) | NA | 0.01 (28.5) |
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
Pharmacokinetics of FTC and TAF have not been fully evaluated in the elderly (65 years of age and older). Population pharmacokinetics analysis of HIV-infected subjects in Phase 2 and Phase 3 trials of FTC+TAF and EVG+COBI showed that age did not have a clinically relevant effect on exposures of TAF up to 75 years of age [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Pediatric Patients
Treatment of HIV-1 Infection: Mean exposures of TAF in 24 pediatric subjects aged 12 to less than 18 years who received FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI were decreased (23% for AUC) and FTC exposures were similar compared to exposures achieved in treatment-naïve adults following administration of this dosage regimen. The TAF exposure differences are not thought to be clinically significant based on exposure-response relationships (Table 9).
| Parameter Mean (CV%) | Emtricitabine | Tenofovir Alafenamide | Tenofovir |
|---|---|---|---|
| CV = Coefficient of Variation; NA = Not Applicable | |||
|
|||
| Cmax (microgram per mL) |
2.3 (22.5) |
0.17 (64.4) |
0.02 (23.7) |
| AUCtau (microgram∙hour per mL) |
14.4 (23.9) |
0.20† (50.0) |
0.29† (18.8) |
| Ctrough (microgram per mL) |
0.10† (38.9) |
NA | 0.01 (21.4) |
Exposures of FTC and TAF achieved in 23 pediatric subjects between the ages of 6 to less than 12 years and weighing at least 25 kg (55 lbs) who received FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI were higher (20% to 80% for AUC) than exposures achieved in adults receiving this same dosage regimen; the increases were not considered clinically significant (Table 10) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
| Parameter Mean (CV%) | Emtricitabine | Tenofovir Alafenamide | Tenofovir |
|---|---|---|---|
| CV = Coefficient of Variation; NA = Not Applicable | |||
|
|||
| Cmax (microgram per mL) |
3.4 (27.0) |
0.31 (61.2) |
0.03 (20.8) |
| AUCtau (microgram∙hour per mL) |
20.6† (18.9) |
0.33 (44.8) |
0.44 (20.9) |
| Ctrough (microgram per mL) |
0.11 (24.1) |
NA | 0.02 (24.9) |
Exposures of FTC and TAF (AUCtau and Cmax) achieved in 22 pediatric patients at least 2 years of age and weighing from 14 to less than 25 kg who received FTC+TAF with bictegravir were higher than exposures in adults; the increases were not considered clinically significant as the safety profiles were similar in adult and pediatric patients (Table 11) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
| Parameter Mean (CV%) |
Emtricitabine† | Tenofovir Alafenamide† |
|---|---|---|
| CV = Coefficient of Variation; NA = Not Applicable | ||
|
||
| Cmax (microgram per mL) |
3.85 (34.7) | 0.414 (31.0) |
| AUCtau (microgram•h per mL) |
15.0 (21.9) | 0.305 (42.6) |
| Ctrough (microgram per mL) |
0.210 (243) | NA |
HIV-1 PrEP: The pharmacokinetic data for FTC and TAF following administration of Descovy in HIV-1 uninfected adolescents weighing 35 kg and above are not available. The dosage recommendations of Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP in this population are based on known pharmacokinetic information in HIV-infected adolescents taking FTC and TAF for treatment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Race and Gender
Based on population pharmacokinetic analyses, there are no clinically meaningful differences based on race or gender.
Patients with Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of FTC+TAF combined with EVG+COBI in HIV-1 infected subjects with renal impairment (eGFR 30 to 69 mL per minute by Cockcroft-Gault method), and in HIV-1 infected subjects with ESRD (eGFR less than 15 mL per minute by Cockcroft-Gault method) receiving chronic hemodialysis were evaluated in subsets of virologically-suppressed subjects in open-label trials. The pharmacokinetics of TAF were similar among healthy subjects, subjects with mild or moderate renal impairment, and subjects with ESRD receiving chronic hemodialysis; increases in FTC and TFV exposures in subjects with renal impairment were not considered clinically relevant (Table 12).
| AUCtau (microgram∙hour per mL) Mean (CV%) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimated Creatinine Clearance* | ≥90 mL per minute (N=18)† | 60–89 mL per minute (N=11)‡ | 30–59 mL per minute (N=18)§ | <15 mL per minute (N=12)¶ |
|
||||
| Emtricitabine | 11.4 (11.9) | 17.6 (18.2) | 23.0 (23.6) | 62.9 (48.0)# |
| Tenofovir | 0.32 (14.9) | 0.46 (31.5) | 0.61 (28.4) | 8.72 (39.4)Þ |
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Emtricitabine: The pharmacokinetics of FTC has not been studied in subjects with hepatic impairment; however, FTC is not significantly metabolized by liver enzymes, so the impact of hepatic impairment should be limited.
Tenofovir Alafenamide: Clinically relevant changes in tenofovir pharmacokinetics in subjects with hepatic impairment were not observed in subjects with mild to moderate (Child-Pugh Class A and B) hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Hepatitis B and/or Hepatitis C Virus Infection
The pharmacokinetics of FTC and TAF have not been fully evaluated in subjects infected with hepatitis B and/or C virus.
Drug Interaction Studies
The effects of coadministered drugs on the exposure of TAF are shown in Table 13 and the effects of Descovy or its components on the exposure of coadministered drugs are shown in Table 14 [these studies were conducted with Descovy or the components of Descovy (FTC or TAF) administered alone]. For information regarding clinical recommendations, see Drug Interactions (7).
| Coadministered Drug | Coadministered Drug(s) Dosage (once daily) (mg) |
Tenofovir Alafenamide Dosage (once daily) (mg) |
N | Mean Ratio of TAF PK Parameters (90% CI); No effect = 1.00 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax | AUC | Cmin | ||||
| NC=Not Calculated | ||||||
|
||||||
| Atazanavir | 300 (+100 ritonavir) | 10 | 10 | 1.77 (1.28, 2.44) |
1.91 (1.55, 2.35) |
NC |
| Cobicistat | 150 | 8 | 12 | 2.83 (2.20, 3.65) |
2.65 (2.29, 3.07) |
NC |
| Darunavir | 800 (+150 cobicistat) | 25† | 11 | 0.93 (0.72, 1.21) |
0.98 (0.80, 1.19) |
NC |
| Darunavir | 800 (+100 ritonavir) | 10 | 10 | 1.42 (0.96, 2.09) |
1.06 (0.84, 1.35) |
NC |
| Dolutegravir | 50 | 10 | 10 | 1.24 (0.88, 1.74) |
1.19 (0.96, 1.48) |
NC |
| Efavirenz | 600 | 40† | 11 | 0.78 (0.58, 1.05) |
0.86 (0.72, 1.02) |
NC |
| Lopinavir | 800 (+200 ritonavir) | 10 | 10 | 2.19 (1.72, 2.79) |
1.47 (1.17, 1.85) |
NC |
| Rilpivirine | 25 | 25 | 17 | 1.01 (0.84, 1.22) |
1.01 (0.94, 1.09) |
NC |
| Sertraline | 50 (dosed as a single dose) | 10‡ | 19 | 1.00 (0.86, 1.16) |
0.96 (0.89, 1.03) |
NC |
| Coadministered Drug | Coadministered Drug Dosage (once daily) (mg) |
Tenofovir Alafenamide Dosage (once daily) (mg) |
N | Mean Ratio of Coadministered Drug PK Parameters (90% CI); No effect = 1.00 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax | AUC | Cmin | ||||
| NC=Not Calculated | ||||||
|
||||||
| Atazanavir | 300 +100 ritonavir | 10 | 10 | 0.98 (0.89, 1.07) |
0.99 (0.96, 1.01) |
1.00 (0.96, 1.04) |
| Darunavir | 800 +150 cobicistat | 25† | 11 | 1.02 (0.96, 1.09) |
0.99 (0.92, 1.07) |
0.97 (0.82, 1.15) |
| Darunavir | 800 +100 ritonavir | 10 | 10 | 0.99 (0.91, 1.08) |
1.01 (0.96, 1.06) |
1.13 (0.95, 1.34) |
| Dolutegravir | 50 mg | 10 | 10 | 1.15 (1.04, 1.27) |
1.02 (0.97, 1.08) |
1.05 (0.97, 1.13) |
| Lopinavir | 800 +200 ritonavir | 10 | 10 | 1.00 (0.95, 1.06) |
1.00 (0.92, 1.09) |
0.98 (0.85, 1.12) |
| Midazolam‡ | 2.5 (single dose, orally) | 25 | 18 | 1.02 (0.92, 1.13) |
1.13 (1.04, 1.23) |
NC |
| 1 (single dose, intravenous) | 0.99 (0.89, 1.11) |
1.08 (1.04, 1.14) |
NC | |||
| Rilpivirine | 25 | 25 | 16 | 0.93 (0.87, 0.99) |
1.01 (0.96, 1.06) |
1.13 (1.04, 1.23) |
| Sertraline | 50 (single dose) | 10§ | 19 | 1.14 (0.94, 1.38) |
0.93 (0.77, 1.13) |
NC |
Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Emtricitabine: FTC, a synthetic nucleoside analog of cytidine, is phosphorylated by cellular enzymes to form emtricitabine 5′-triphosphate. Emtricitabine 5′-triphosphate inhibits the activity of the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase by competing with the natural substrate deoxycytidine 5′-triphosphate and by being incorporated into nascent viral DNA which results in chain termination. Emtricitabine 5′-triphosphate is a weak inhibitor of mammalian DNA polymerases α, β, Ɛ, and mitochondrial DNA polymerase γ.
Tenofovir Alafenamide: TAF is a phosphonoamidate prodrug of tenofovir (2′-deoxyadenosine monophosphate analog). Plasma exposure to TAF allows for permeation into cells and then TAF is intracellularly converted to tenofovir through hydrolysis by cathepsin A. Tenofovir is subsequently phosphorylated by cellular kinases to the active metabolite tenofovir diphosphate. Tenofovir diphosphate inhibits HIV-1 replication through incorporation into viral DNA by the HIV reverse transcriptase, which results in DNA chain-termination.
Tenofovir has activity against HIV-1. Cell culture studies have shown that both tenofovir and FTC can be fully phosphorylated when combined in cells. Tenofovir diphosphate is a weak inhibitor of mammalian DNA polymerases that include mitochondrial DNA polymerase γ and there is no evidence of toxicity to mitochondria in cell culture.
Antiviral Activity in Cell Culture
Emtricitabine: The antiviral activity of FTC against laboratory and clinical isolates of HIV-1 was assessed in T lymphoblastoid cell lines, the MAGI-CCR5 cell line, and primary peripheral blood mononuclear cells. The EC50 values for FTC were in the range of 1.3–640 nM. FTC displayed antiviral activity in cell culture against HIV-1 clades A, B, C, D, E, F, and G (EC50 values ranged from 7-75 nM) and showed strain specific activity against HIV-2 (EC50 values ranged from 7–1,500 nM).
In a study of FTC with a broad panel of representatives from the major classes of approved anti-HIV agents (NRTIs, non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors [NNRTIs], integrase strand transfer inhibitors [INSTIs], and PIs) no antagonism was observed for these combinations.
Tenofovir Alafenamide: The antiviral activity of TAF against laboratory and clinical isolates of HIV-1 subtype B was assessed in lymphoblastoid cell lines, PBMCs, primary monocyte/macrophage cells and CD4+-T lymphocytes. The EC50 values for TAF ranged from 2.0 to 14.7 nM.
TAF displayed antiviral activity in cell culture against all HIV-1 groups (M, N, O), including sub-types A, B, C, D, E, F, and G (EC50 values ranged from 0.10 to 12.0 nM) and strain specific activity against HIV-2 (EC50 values ranged from 0.91 to 2.63 nM).
In a study of TAF with a broad panel of representatives from the major classes of approved anti-HIV agents (NRTIs, NNRTIs, INSTIs, and PIs) no antagonism was observed for these combinations.
Prophylactic Activity in a Nonhuman Primate Model of HIV-1 Transmission
Emtricitabine and Tenofovir Alafenamide: The prophylactic activity of the combination of oral FTC and TAF was evaluated in a controlled study of macaques administered once weekly intra-rectal inoculations of chimeric simian/human immunodeficiency type 1 virus (SHIV) for up to 19 weeks (n=6). All 6 macaques that received FTC and TAF at doses resulting in PBMC exposures consistent with those achieved in humans administered a dose of FTC/TAF 200/25 mg remained SHIV uninfected.
Resistance
In Cell Culture
Emtricitabine: HIV-1 isolates with reduced susceptibility to FTC were selected in cell culture and in subjects treated with FTC. Reduced susceptibility to FTC was associated with M184V or I substitutions in HIV-1 RT.
Tenofovir Alafenamide: HIV-1 isolates with reduced susceptibility to TAF were selected in cell culture. HIV-1 isolates selected by TAF expressed a K65R substitution in HIV-1 RT, sometimes in the presence of S68N or L429I substitutions; in addition, a K70E substitution in HIV-1 RT was observed.
In Clinical Trials
Treatment of HIV-1
The resistance profile of Descovy in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection is based on studies of FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI in the treatment of HIV-1 infection. In a pooled analysis of antiretroviral-naïve subjects, genotyping was performed on plasma HIV-1 isolates from all subjects with HIV-1 RNA greater than 400 copies per mL at confirmed virologic failure, at Week 48, or at time of early study drug discontinuation. Genotypic resistance developed in 7 of 14 evaluable subjects. The resistance-associated substitutions that emerged were M184V/I (N=7) and K65R (N=1). Three subjects had virus with emergent R, H, or E at the polymorphic Q207 residue in reverse transcriptase.
One subject was identified with emergent resistance to FTC (M184M/I) out of 4 virologic failure subjects in a clinical study of virologically-suppressed subjects who switched from a regimen containing FTC+TDF to FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI (N=799).
HIV-1 PrEP
In the DISCOVER trial of HIV-1 uninfected men and transgender women who have sex with men and who are at risk of HIV-1 infection receiving Descovy or TRUVADA for HIV-1 PrEP, genotyping was performed on participants found to be infected during the trial who had HIV-1 RNA ≥400 copies/mL (6 of 7 participants receiving Descovy and 13 of 15 participants receiving TRUVADA). The development of FTC resistance-associated substitutions, M184I and/or M184V, was observed in 4 HIV-1 infected participants in the TRUVADA group who had suspected baseline infections.
Cross-Resistance
Emtricitabine: FTC-resistant viruses with the M184V or I substitution were cross-resistant to lamivudine, but retained sensitivity to didanosine, stavudine, tenofovir, and zidovudine.
Viruses harboring substitutions conferring reduced susceptibility to stavudine and zidovudine-thymidine analog substitutions (M41L, D67N, K70R, L210W, T215Y/F, K219Q/E) or didanosine (L74V) remained sensitive to FTC. HIV-1 containing the K103N substitution or other substitutions associated with resistance to NNRTIs was susceptible to FTC.
Tenofovir Alafenamide: Tenofovir resistance substitutions K65R and K70E result in reduced susceptibility to abacavir, didanosine, emtricitabine, lamivudine, and tenofovir.
HIV-1 with multiple thymidine analog substitutions (M41L, D67N, K70R, L210W, T215F/Y, K219Q/E/N/R), or multinucleoside resistant HIV-1 with a T69S double insertion mutation or with a Q151M substitution complex including K65R, showed reduced susceptibility to TAF in cell culture.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Emtricitabine
In long-term carcinogenicity studies of FTC, no drug-related increases in tumor incidence were found in mice at doses up to 750 mg per kg per day (23 times the human systemic exposure at the recommended dose of 200 mg per day in Descovy) or in rats at doses up to 600 mg per kg per day (28 times the human systemic exposure at the recommended dose in Descovy).
FTC was not genotoxic in the reverse mutation bacterial test (Ames test), mouse lymphoma or mouse micronucleus assays.
FTC did not affect fertility in male rats at approximately 140 times or in male and female mice at approximately 60 times higher exposures (AUC) than in humans given the recommended 200 mg daily dosage in Descovy. Fertility was normal in the offspring of mice exposed daily from before birth (in utero) through sexual maturity at daily exposures (AUC) of approximately 60 times higher than human exposures at the recommended 200 mg daily dosage in Descovy.
Tenofovir Alafenamide
Since TAF is rapidly converted to tenofovir and a lower tenofovir exposure in rats and mice was observed after TAF administration compared to TDF administration, carcinogenicity studies were conducted only with TDF. Long-term oral carcinogenicity studies of TDF in mice and rats were carried out at exposures up to approximately 10 times (mice) and 4 times (rats) those observed in humans at the recommended dose of TDF (300 mg) for HIV-1 infection. The tenofovir exposure in these studies was approximately 167 times (mice) and 55 times (rat) those observed in humans after administration of the daily recommended dose of Descovy. At the high dose in female mice, liver adenomas were increased at tenofovir exposures approximately 10 times (300 mg TDF) and 167 times (Descovy) the exposure observed in humans. In rats, the study was negative for carcinogenic findings.
TAF was not genotoxic in the reverse mutation bacterial test (Ames test), mouse lymphoma or rat micronucleus assays.
There were no effects on fertility, mating performance, or early embryonic development when TAF was administered to male rats at a dose equivalent to 62 times (25 mg TAF) the human dose based on body surface area comparisons for 28 days prior to mating and to female rats for 14 days prior to mating through Day 7 of gestation.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Minimal to slight infiltration of mononuclear cells in the posterior uvea was observed in dogs with similar severity after three- and nine-month administration of TAF; reversibility was seen after a three-month recovery period. No eye toxicity was observed in the dog at systemic exposures of 5 (TAF) and 15 (tenofovir) times the exposure seen in humans with the recommended daily TAF dose in Descovy.
Clinical Studies
Overview of Clinical Trials
The efficacy and safety of Descovy have been evaluated in the trials summarized in Table 15.
| Trial | Population | Study Arms (N) | Timepoint |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Study 104 * (NCT01780506) Study 111 * (NCT01797445) |
HIV-1 infected treatment-naïve adults | FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI † (866) FTC+TDF with EVG+COBI ‡ (867) |
48 Weeks |
| Study 109 § (NCT01815736) |
HIV-1 infected virologically–suppressed ¶ adults | FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI † (799) ATRIPLA® or TRUVADA®+atazanavir+cobicistat or ritonavir or FTC+TDF with EVG+COBI ‡ (397) |
48 Weeks |
| Study 112 # (NCT01818596) |
HIV-1 infected virologically-suppressed ¶ adults with renal impairment Þ | FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI † (242) | 24 Weeks |
| Study 1825 # (NCT02600819) |
HIV-1 infected virologically-suppressed ¶ adults with ESRD ß receiving chronic hemodialysis | FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI † (55) | 48 Weeks |
| Study 106 # (Cohort 1) (NCT01854775) |
HIV-1 infected treatment-naïve adolescents between the ages of 12 to less than 18 years (at least 35 kg) | FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI † (50) | 48 Weeks |
| Study 106 # (Cohort 2) (NCT01854775) |
HIV-1 infected, virologically suppressed ¶ children between the ages of 6 to less than 12 years (at least 25 kg) | FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI † (52) | 48 Weeks |
| Study 1474 # (Cohort 3) (NCT02881320) |
HIV-1 infected, virologically suppressed ¶ children at least 2 years (at least 14 kg and less than 25 kg) | FTC+TAF with bictegravir à (22) | 24 Weeks |
| DISCOVER * (NCT02842086) |
HIV-1 uninfected men or transgender women who have sex with men | Descovy (2,670) TRUVADA® (2,665) |
4,370 person-yearsè |
Clinical Trial Results for Treatment of HIV-1
Clinical Trials in Adults with HIV-1
In trials of FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI in HIV-1 infected adults as initial therapy in those with no antiretroviral treatment history (N=866) and to replace a stable antiretroviral regimen in those who were virologically-suppressed for at least 6 months with no known resistance substitutions (N=799), 92% and 96% of patients in the two populations, respectively, had HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL at Week 48.
Clinical Trials in Pediatric Patients with HIV-1
An open-label, single arm trial of FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI enrolled 50 treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected adolescents aged 12 to less than 18 years weighing at least 35 kg (cohort 1) and 52 virologically suppressed children aged 6 to less than 12 years weighing at least 25 kg (cohort 2). In cohort 1, the virologic response rate (i.e., HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL) was 92% (46/50) and the mean increase from baseline in CD4+ cell count was 224 cells per mm3 at Week 48. In cohort 2, 98% (51/52) of subjects remained virologically suppressed at Week 48. From a mean (SD) baseline CD4+ cell count of 961 (275.5) cells per mm3, the mean change from baseline in CD4+ cell count was -66 cells per mm3 and the mean (SD) change in CD4% was -0.6% (4.4%) at Week 48. All subjects maintained CD4+ cell counts above 400 cells/mm3 [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
In a separate open-label single arm trial of FTC+TAF with bictegravir that enrolled 24 virologically-suppressed children at least 2 years of age and weighing at least 14 to less than 25 kg (cohort 3), 91% (20/22) of subjects remained virologically suppressed at Week 24. From a mean (SD) baseline CD4+ count of 1104 (440), the mean (SD) change from baseline in CD4+ cell count was −126 (264) cells per mm3, and the mean (SD) change in CD4% was 0.2% (4.4%) at Week 24.
Clinical Trials in Adults with HIV-1 and Renal Insufficiency
In a trial in 248 HIV-1 infected adults with estimated creatinine clearance greater than 30 mL per minute but less than 70 mL per minute, 95% (235/248) of the combined population of treatment-naïve subjects began on FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI (N=6) and those previously virologically-suppressed on other regimens and switched to FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI (N=242) had HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL at Week 24.
In a trial in 55 HIV-1 infected virologically-suppressed adults with ESRD (estimated creatinine clearance of less than 15 mL per minute) receiving chronic hemodialysis for at least 6 months who switched to FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI, 82% (45/55) maintained HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL at Week 48. Two subjects had HIV-1 RNA ≥ 50 copies per mL by Week 48, 7 discontinued due to AE or other reasons while suppressed, and 1 did not have an HIV-1 RNA measurement at Week 48.
Clinical Trial Results for HIV-1 PrEP
The efficacy and safety of Descovy to reduce the risk of acquiring HIV-1 infection were evaluated in a randomized, double-blind multinational trial (DISCOVER) in HIV-seronegative men (N=5,262) or transgender women (N=73) who have sex with men and are at risk of HIV-1 infection, comparing once daily Descovy (N=2,670) to TRUVADA (FTC/TDF 200 mg/300 mg; N=2,665). Evidence of risk behavior at entry into the trial included at least one of the following: two or more unique condomless anal sex partners in the past 12 weeks or a diagnosis of rectal gonorrhea/chlamydia or syphilis in the past 24 weeks. The median age of participants was 34 years (range, 18-76); 84% were White, 9% Black/Mixed Black, 4% Asian, and 24% Hispanic/Latino. At baseline, 897 participants (17%) reported receiving TRUVADA for PrEP.
At weeks 4, 12, and every 12 weeks thereafter, all participants received local standard of care HIV-1 prevention services, including HIV-1 testing, evaluation of adherence, safety evaluations, risk-reduction counseling, condoms, management of sexually transmitted infections, and assessment of sexual behavior.
Trial participants maintained a high risk of sexual HIV-1 acquisition, with high rates of rectal gonorrhea (Descovy, 24%; TRUVADA, 25%), rectal chlamydia (Descovy, 30%; TRUVADA, 31%), and syphilis (14% in both treatment groups) during the trial.
The primary outcome was the incidence of documented HIV-1 infection per 100 person-years in participants randomized to Descovy and TRUVADA (with a minimum follow-up of 48 weeks and at least 50% of participants having 96 weeks of follow-up). Descovy was non-inferior to TRUVADA in reducing the risk of acquiring HIV-1 infection (Table 16). The results were similar across the subgroups of age, race, gender identity, and baseline TRUVADA for PrEP use.
| Descovy (N=2,670) |
TRUVADA (N=2,665) |
Rate Ratio (95% CI) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 4,370 person-years | 4,386 person-years | ||
| CI = Confidence interval. | |||
| HIV-1 infections, n | 7 | 15 | |
| Rate of HIV-1 infections per 100 person-years | 0.16 | 0.34 | 0.468 (0.19, 1.15) |
Of the 22 participants diagnosed with HIV-1 infection in the trial, five had suspected baseline infection prior to study entry (Descovy, 1; TRUVADA, 4). In a case-control substudy of intracellular drug levels and estimated number of daily doses as measured by dried blood spot testing, median intracellular tenofovir diphosphate concentrations were substantially lower in participants infected with HIV-1 at the time of diagnosis compared with uninfected matched control participants. For both Descovy and TRUVADA, efficacy was therefore strongly correlated to adherence to daily dosing.¶
How Supplied/Storage and Handling
Descovy tablets are available in bottles and blister packs containing 30 tablets:
Bottles
- 200 mg/25 mg tablets each contain 200 mg of emtricitabine (FTC) and 25 mg of tenofovir alafenamide (TAF). These tablets are blue, rectangular-shaped, and film-coated with “GSI” debossed on one side and “225” on the other side (NDC 61958-2002-1).
- 120 mg/15 mg tablets each contain 120 mg of FTC and 15 mg of TAF. These tablets are white, round-shaped, and film coated with “GSI” debossed on one side and “15” on the other side (NDC 61958-2005-1).
Bottles contain a silica gel desiccant, polyester coil, and child resistant closure.
Keep bottle tightly closed.
Blister Pack
- 200 mg/25 mg tablets each contain 200 mg of FTC and 25 mg of TAF. These tablets are blue, rectangular-shaped, and film-coated with “GSI” debossed on one side and “225” on the other side (NDC 61958-2002-2).
Blister packs are sealed with a child-resistant laminated foil lidding material (peel-push) and each blister cavity contains a die-cut desiccant film which is heat staked to the foil lidding material.
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) (see USP Controlled Room Temperature).
Dispense only in original container.
Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Important Information for Uninfected Individuals Taking Descovy for HIV-1 PrEP
Advise HIV-1 uninfected individuals about the following [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]:
- The need to confirm that they are HIV-negative before starting to take Descovy to reduce the risk of acquiring HIV-1.
- That HIV-1 resistance substitutions may emerge in individuals with undetected HIV-1 infection who are taking Descovy, because Descovy alone does not constitute a complete regimen for HIV-1 treatment.
- The importance of taking Descovy on a regular dosing schedule and strict adherence to the recommended dosing schedule to reduce the risk of acquiring HIV-1. Uninfected individuals who miss doses are at greater risk of acquiring HIV-1 than those who do not miss doses.
- That Descovy does not prevent other sexually acquired infections and should be used as part of a complete prevention strategy including other prevention measures.
- To use condoms consistently and correctly to lower the chances of sexual contact with any body fluids such as semen, vaginal secretions, or blood.
- The importance of knowing their HIV-1 status and the HIV-1 status of their partner(s).
- The importance of virologic suppression in their partner(s) with HIV-1.
- The need to get tested regularly for HIV-1 (at least every 3 months, or more frequently for some individuals such as adolescents) and to ask their partner(s) to get tested as well.
- To report any symptoms of acute HIV-1 infection (flu-like symptoms) to their healthcare provider immediately.
- That the signs and symptoms of acute infection include fever, headache, fatigue, arthralgia, vomiting, myalgia, diarrhea, pharyngitis, rash, night sweats, and adenopathy (cervical and inguinal).
- To get tested for other sexually transmitted infections, such as syphilis, chlamydia, and gonorrhea, that may facilitate HIV-1 transmission.
- To assess their sexual risk behavior and get support to help reduce sexual risk behavior.
Post-treatment Acute Exacerbation of Hepatitis B in Patients with HBV Infection
Inform individuals that severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B have been reported in patients who are infected with HBV and have discontinued products containing FTC and/or TDF and may likewise occur with discontinuation of Descovy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Advise HBV-infected individuals to not discontinue Descovy without first informing their healthcare provider.
Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Advise HIV-1 infected patients to inform their healthcare provider immediately of any symptoms of infection. In some patients with advanced HIV infection (AIDS), signs and symptoms of inflammation from previous infections may occur soon after anti-HIV treatment is started [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment
Advise HIV-1 infected patients and uninfected individuals to avoid taking Descovy with concurrent or recent use of nephrotoxic agents. Postmarketing cases of renal impairment, including acute renal failure, have been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Lactic Acidosis and Severe Hepatomegaly
Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with use of drugs similar to Descovy. Advise HIV-1 infected patients and uninfected individuals that they should stop Descovy if they develop clinical symptoms suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Dosage Recommendations for Treatment of HIV-1 Infection
Inform HIV-1 infected patients that it is important to take Descovy with other antiretroviral drugs for the treatment of HIV-1 on a regular dosing schedule with or without food and to avoid missing doses as it can result in development of resistance [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)].
Pregnancy Registry
Inform individuals using Descovy that there is an antiretroviral pregnancy registry to monitor fetal outcomes of pregnant women exposed to Descovy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Lactation
Instruct mothers with HIV-1 infection not to breastfeed because of the risk of passing the HIV-1 virus to the baby [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 200 mg/25 mg Tablet Bottle Label
- NDC 61958- 2002-1
- 30 tablets
- Descovy ®
- (emtricitabine and tenofovir
- alafenamide) Tablets
- 200 mg/25 mg
- Note to pharmacist: Do not cover ALERT box with pharmacy label.
- ALERT: Find out about medicines that
- should NOT be taken with Discovy ®
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 30 Tablet Blister Pack
- NDC 61958-2002-2
- 30 tablet blister pack
- Descovy®
- (emtricitabine and
- tenofovir alafenamide) tablets
- 200 mg / 25 mg
- Rx only
- Note to pharmacist:
- Do not cover ALERT box with pharmacy label.
- ALERT: Find out about medicines that
- should NOT be taken with Descovy

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 120 mg/15 mg Tablet Bottle Label
- NDC 61958-2005-1
30 tablets - Descovy®
(emtricitabine and
tenofovir alafenamide)
tablets - 120 mg/15 mg
- Note to pharmacist:
Do not cover ALERT box with pharmacy label. - ALERT: Find out about medicines that should NOT be taken with Descovy

