Acetazolamide
Generic name: acetazolamide
The brand name is Diamox, Diamox Sequels
Forms of dosage: oral capsule, extended-release (500 mg) oral tablet (125 mg 250 mg)
Class of drug: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
What is Acetazolamide?
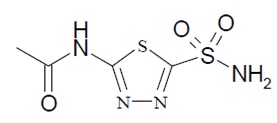
Acetazolamide decreases the activity of a protein found in the body known as carbonic anhydrase. The blockage of this protein may help to reduce the accumulation of specific fluids within the body.
Acetazolamide can be used by those with specific types of Glaucoma to lower amounts of fluid inside the eye, thereby reducing pressure in the eye.
Acetazolamide can also be used as a diuretic (“water pill”) for people suffering from constricted heart disease in order to limit the amount of fluid that builds up in the body. This accumulation is known as edema.¶
What is t53 pill
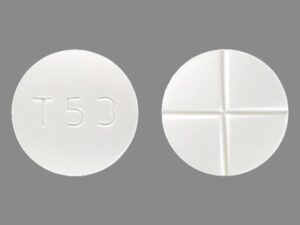 t53 pill Is a white round pill that is identified as acetazolamide 250 mg. It is supplied by Taro Pharmaceuticals, USA
t53 pill Is a white round pill that is identified as acetazolamide 250 mg. It is supplied by Taro Pharmaceuticals, USA
t53 pill can also be used to treat certain kinds of seizures as well as to prevent or treat altitude sickness.
Acetazolamide is also employed for other purposes that are not covered in this guideline for medication.
Pill identifier
What is t52 pill
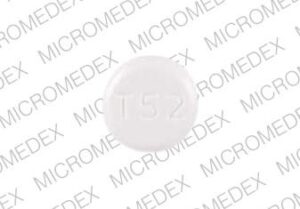
- Acetazolamide 125 mg
- Made available by Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A
S572 pill
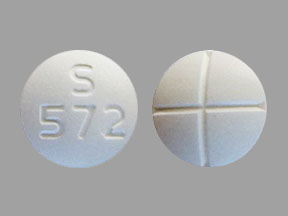
- Acetazolamide 250 mg
- pill imprint S572
- Round shape with white color
N34 pill

- Acetazolamide 250 mg
- Pill Imprint: N34
- white color and round shape
Warning and precautions
It is not recommended to use acetazolamide in the case of cirrhosis or kidney or liver disease, an imbalance in electrolytes or adrenal gland failure as well as an allergic reaction to acetazolamide, or sulfa medications.
General
- The dose increase does not cause diuresis to increase and can increase the likelihood of paresthesia or drowsiness. In most cases, increasing the dose causes an increase in diuresis. However, in certain instances, high doses of diuretics are administered in conjunction with diuretics to maintain diuresis an irreparable failure.
Information for Patients
- Common adverse reactions to all sulfonamide derivatives can result in fever, anaphylaxis, and anaphylaxis. rash (including Steven-Johnson syndrome neurotoxic epidermal necrosis) and crystalluria. They can also cause renal calculus bone marrow depression hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenic purpura pancytopenia, leukopenia, and Agranulocytosis. It is recommended to be cautious for the early detection of reactions, and the medication should be stopped and appropriate treatment implemented.
- In patients suffering from emphysema or pulmonary obstruction where breathing through the alveoli is compromised, extended-release capsules of acetazolamide that may cause or aggravate acidosis should be utilized with cautiousness. A gradual ascent is recommended in order to avoid the onset of mountain sickness.
- In the event that rapid climbing is attempted and acetazolamide extended-release capsules are employed, it is observed that this method doesn’t eliminate the necessity of a rapid descent in the event that severe forms of high altitude illness occur, i.e., high altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) as well as high altitude cerebral swelling.
- A cautious approach is advised for those taking concomitant high-dose aspirin and acetazolamide extended-release capsules, since anorexia, lethargy, tachypnea, metabolic acidosis, coma, as well as deaths have been documented.
- Both decreases and increases in blood glucose levels have been reported in patients by Acetazolamide. This is something to take into account in patients suffering from an impaired tolerance to glucose or with diabetes.
- Acetazolamide treatment could result in electrolyte imbalances, such as hypokalemia and hyponatremia, and metabolic acidosis. Therefore, regular surveillance of electrolytes in the serum is advised. Particular caution is advised for patients suffering from conditions related to or may cause acid/base imbalances and electrolytes like those with impaired kidney function and patients suffering from diabetes mellitus, or with impaired alveolar venting.
- A few adverse reactions associated with Acetazolamide, including fatigue, drowsiness, and myopia, could hinder the ability to operate and drive machines.
Laboratory Tests
- To detect Hematologic reactions that are common to all sulfonamides it is suggested to conduct an initial CBC as well as a platelet count is taken on patients prior to starting extended-release acetazolamide capsules and every few weeks during treatment. If there are significant changes the prompt discontinuation and implementation of the correct therapy is essential. Regular monitoring of electrolytes in serum is suggested.
Before you start taking this medication
Acetazolamide should not be used when you are allergic to the substance or suffer from:
- severe liver disease that is severe or cirrhosis
- chronic kidney illness;
- An unbalanced electrolyte (such as acidosis, or low levels of sodium or potassium within your blood);
- adrenal glands fail and
- An allergy to sulfa-containing drugs.
To ensure that acetazolamide is suitable for you, inform your doctor if:
- respiratory problems that are severe;
- Close angle glaucoma;
- If you take aspirin in large doses.
It is unclear if this medication will cause harm to a baby who is not yet born. Inform your doctor if are expecting or planning to be pregnant.
Acetazolamide may be absorbed into breast milk and could cause harm to nursing babies. It is not recommended to breastfeed during the course of taking this medication.
Acetazolamide is not permitted for use by anyone less than 18 years old.
How to take acetazolamide?
Follow the directions on the label of your prescription. Your doctor might alter the dosage to ensure you are getting the best outcomes. Avoid using acetazolamide at higher or lower amounts or for longer periods than suggested.
The dosage of this medication will be determined by the illness you’re treating. If you’re taking acetazolamide in the treatment of chronic heart disease, your physician might advise you to stop taking the medication for a few days. Follow the doctor’s instructions for dosing with care.
Consume this medicine along with a glass full of water.
If you take acetazolamide you might require regular blood tests.
Acetazolamide could be a part of a comprehensive treatment plan which may include other medicines. Follow your doctor’s prescriptions precisely.
Store at room temperature, away from heat and moisture. Close the bottle when not being used.
What If I miss a dose?
You should take the dose missed as soon as you can remember. Do not take any missed doses if it’s close to the time of the next dose. Don’t take any extra medication to make up for the missed dose.
If I take too much?
For medical emergencies, seek emergency medical attention or contact toll-free the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222.
What to avoid while taking Acetazolamide?
Acetazolamide can affect your reactions or thinking. Be aware when you drive or perform things that require you to be aware.
Avoid exposure to sun and tanning bed. Acetazolamide can cause sunburn more quickly. Protect yourself with protective clothing and sunblock (SPF 30 or more) while you’re outdoors.
Acetazolamide side effects
See a doctor immediately If you are experiencing symptoms warning signs of an allergic reaction: hives and breathing difficulties and swelling of your lips, face, and tongue.
Consult your physician immediately If you are suffering from:
- Blood in urine or stools;
- a seizure (convulsions);
- the loss from movement on any body part;
- a blood cell disorder: sudden weakness or feeling of ill-health such as chills, fever, tension in the throat mouth sores pale skin and fatigue or shortness of breath fast heartbeat, nasal bleeding, or bleeding gums
- liver disorders(e.g. nausea, stomach pain or swelling, tiredness nausea, lack of appetite dark urine, stools that are clay-colored, jaundice (yellowing of the eyes or skin);
- indications that suggest metabolic acidosis–confusion, vomiting and energy loss, irregular heartbeats,
- symptoms of kidney stones: pain in your lower back or lower back, blood in your urine painful or difficult urination;
- extreme skin reaction – fever or sore throat, swelling of your tongue or face burning in your eyes, pain in your skin, that is followed by an irritated or red or purple rash that can spread (especially in the face and the upper part of the body) and leads to blisters and peeling.
Common side effects can be:
- Nausea, vomiting, loss in appetite nausea, vomiting and loss of appetite;
- the sensation of numbness or tingling in your legs and arms;
- drowsiness, confusion;
- hearing loss, ringing in your ears;
- an increase in urination; or
- Taste perception is altered.
This is not a comprehensive list of possible side effects, and other side effects could be present. Consult your physician for advice regarding medical adverse effects. You can report any adverse reactions to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
What other medications can alter the effects of Acetazolamide?
Other medications can be incompatible with acetazolamide, such as medications that are prescribed and available over the counter, vitamins, and herbal products. Inform your health professionals about any medications you take in the present and any medication you stop or start using.
Additional details
Keep all medicines away from the reach of children. Never divulge your medications to others and only use the medication in the prescribed indication.
Always consult your doctor to confirm that the information provided on this site is appropriate to your particular situation.
