Stavudine
Generic : stavudine
What is stavudine?
Stavudine is a prescription medicine used in combination with other drugs to treat adults and children who are infected with HIV (the human immunodeficiency virus), the virus that causes AIDS. Stavudine belongs to a class of drugs called nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs). By reducing the growth of HIV, stavudine helps your body maintain its supply of CD4 cells, which are important for fighting HIV and other infections.
Stavudine will not cure your HIV infection. At present, there is no cure for HIV infection. Even while taking stavudine, you may continue to have HIV-related illnesses, including infections caused by other disease-producing organisms. Continue to see your doctor regularly and report any medical problems that occur.
Stavudine does not prevent a person infected with HIV from passing the virus to other people. To protect others, you must continue to practice safe sex and take precautions to prevent others from coming in contact with your blood and other body fluids.
There is limited information on the long-term use of stavudine.
Description
Stavudine (d4T), a synthetic thymidine nucleoside analogue, active against the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
Stavudine Capsules are supplied for oral administration in strengths of 15, 20, 30, and 40 mg of stavudine. Each capsule also contains inactive ingredients microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, lactose anhydrous, and magnesium stearate. The hard gelatin shell consists of gelatin, sodium lauryl sulfate, titanium dioxide, and iron oxides.The capsules are printed with Black ink containing black iron oxide E172 dye.
The chemical name for stavudine is 2′,3′-didehydro-3′-deoxythymidine. Stavudine has the following structural formula:

Stavudine is a white to off-white crystalline solid with the molecular formula C10 H12 N2 O4 and a molecular weight of 224.2. The solubility of stavudine at 23° C is approximately 83 mg/mL in water and 30 mg/mL in propylene glycol. The n-octanol/water partition coefficient of stavudine at 23° C is 0.144.
What is the most important information I should know about stavudine?
Stavudine capsules can cause serious side effects, including:
- Build-up of an acid in your blood (lactic acidosis). Lactic acidosis can happen in some people who take stavudine capsules or similar medicines (nucleoside analogues). Lactic acidosis is a serious medical emergency that can lead to death. Do not take stavudine capsules with didanosine.
- Call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms which could be signs of lactic acidosis:
- Severe liver problems. Severe liver problems, including liver failure can happen in people who take stavudine capsules. In some cases, these liver problems can lead to death. Your liver may become large (hepatomegaly) and you may develop fat in your liver (steatosis). Taking stavudine capsules with medicines that contain didanosine or hydroxyurea may increase your risk for liver problems.
- Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms of liver problems:
- your skin or the white part of your eyes turns yellow (jaundice)
- nausea
- light colored stools (bowel movements)
- loss of appetite
- dark or “tea-colored” urine
- pain, aching, or tenderness on the right side of your stomach area
- Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms of liver problems:
You may be more likely to get lactic acidosis or severe liver problems if you are female, are very overweight (obese), or have been taking nucleoside analogue medicines for a long time.
- Neurologic problems including weakness of your legs, feet, arms, or hands (motor weakness) and numbness, tingling or pain in your hands or feet (peripheral neuropathy). Peripheral neuropathy can be common and severe and happens more often in people who have advanced HIV-1 disease, have a history of peripheral neuropathy, or in people who take other medicines that can cause peripheral neuropathy. In some cases, symptoms of neurologic problems may continue, worsen or temporarily worsen after you stop treatment with stavudine capsules.
Neurologic problems can be difficult to notice in children who take stavudine capsules. Ask your child’s healthcare provider for the signs and symptoms of neurologic problems in children.
- Inflammation of your pancreas (pancreatitis) can happen in people who take stavudine capsules in combination with didanosine and can lead to death. Do not take stavudine capsules with didanosine.
- Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms of pancreatitis:
- severe stomach (abdomen) pain
- swelling of your stomach
- nausea and vomiting
- fever
- Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms of pancreatitis:
For more information about side effects, see “What are the possible side effects of stavudine?”
Who should not take stavudine?
Do not take stavudine capsules if you:
- are allergic to stavudine or any of the ingredients in stavudine capsules. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of the ingredients in stavudine capsules.
- take a medicine that contains didanosine.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking stavudine?
Before taking stavudine capsules, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have or had liver problems, including hepatitis C virus infection
- have or had problems with your pancreas
- have or had kidney problems
- are receiving dialysis
- have or had numbness, tingling, or pain in the hands or feet (peripheral neuropathy)
- drink alcoholic beverages
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if stavudine capsules will harm your unborn baby.Pregnancy Registry: There is a pregnancy registry for women who take antiretroviral medicines, including stavudine capsules during pregnancy. The purpose of the registry is to collect information about the health of you and your baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about how you can take part in this registry.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Do not breastfeed if you take stavudine capsules.
- You should not breastfeed if you have HIV-1 because of the risk of passing HIV-1 to your baby.
- Stavudine can pass into your breast milk and it could harm your baby.Talk with your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines that you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, or herbal supplements. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take a medicine called hydroxyurea.
Some medicines interact with stavudine capsules. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
- You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of medicines that interact with stavudine capsules.
- Do not start taking a new medicine without telling your healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider can tell you if it is safe to take stavudine capsules with other medicines.
How should I take stavudine?
- Take stavudine capsules exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you how much stavudine capsules to take and when to take it.
- Stavudine capsules may be taken with or without food.
- Stavudine capsules should be taken every 12 hours.
- Your child’s healthcare provider should give you instructions on how to give stavudine capsules to your child.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose. Do not change your dose of stavudine capsules without talking to your healthcare provider.
- Do not miss a dose of stavudine capsules. If you miss a dose of stavudine capsules, take it as soon as possible.
- It is important to take stavudine capsules on a regular schedule. The virus in your blood may increase and the virus may become harder to treat if you miss doses.
- If you take too much stavudine capsules, contact a poison control center or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking stavudine?
- Avoid drinking alcohol while taking stavudine capsules. Alcohol may increase your risk of side effects during treatment with stavudine capsules.
What are the possible side effects of stavudine?
Stavudine capsules can cause serious side effects including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about stavudine?”
- Loss of body fat (lipoatrophy) from the arms, legs, or face. Loss of body fat (lipoatrophy) happens more often in people who take stavudine capsules than in people who take other similar HIV-1 medicines. Your healthcare provider will monitor you for changes in your body fat. It is important to tell your healthcare provider if you notice any changes.
- Changes in your immune system (immune reconstitution syndrome) can happen when you start taking HIV-1 medicines. Your immune system may get stronger and begin to fight infections that have been hidden in your body for a long time. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you start having new symptoms after starting your HIV-1 medicine.
The most common side effects of stavudine capsules include:
These are not all the possible side effects of stavudine capsules.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Package Label
!5 mg label

2o mg label
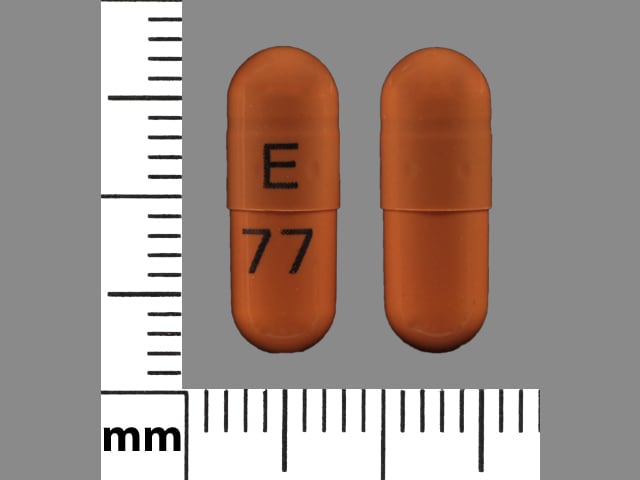


30 mg label

40 mg label
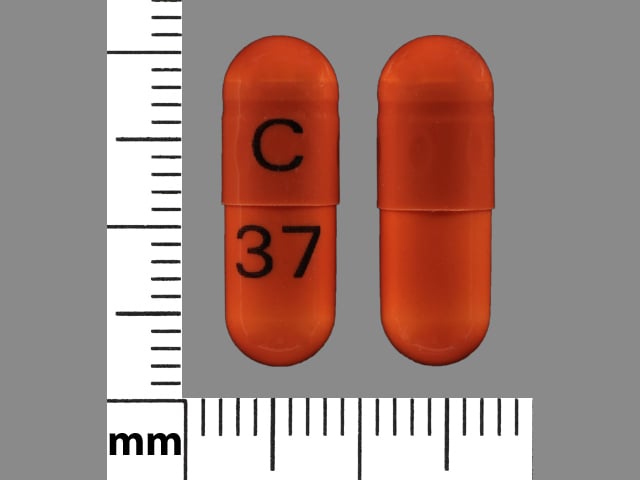


General information about the safe and effective use of stavudine
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use stavudine capsules for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give stavudine capsules to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about stavudine capsules that is written for health professionals.
How should I store stavudine?
Capsules:
- Store stavudine capsules in a tightly closed container at room temperature at 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F).
Keep stavudine capsules and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in stavudine?
Stavudine capsules manufactured by Aurobindo Pharma Ltd contain:
Active ingredient: stavudine
Inactive Ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, anhydrous lactose, and magnesium stearate. The hard gelatin shell consists of gelatin, sodium lauryl sulfate, titanium dioxide, yellow iron oxide, and red iron oxide. The capsules are printed with black ink containing black iron oxide.
Src:NLM.

