Qualaquin
Generic name: quinine
Drug class: Antimalarial quinolines
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Qualaquin?
Qualaquin is a prescription medicine used to treat uncomplicated malaria caused by the parasite Plasmodium falciparum.
Qualaquin is not approved to:
- Prevent malaria
- Treat severe or complicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria
- Prevent or treat night-time leg cramps
It is not known if Qualaquin is safe and effective in children under 16 years of age.
Description
QUALAQUIN (quinine sulfate) is a cinchona alkaloid chemically described as cinchonan-9-ol, 6′-methoxy-, (8α, 9R)-, sulfate (2:1) (salt), dihydrate with a molecular formula of (C20H24N2O2)2•H2SO4•2H2O and a molecular weight of 782.96.
The structural formula of quinine sulfate is:
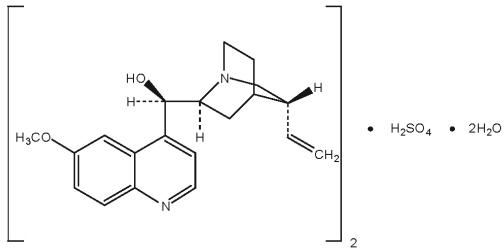
Quinine sulfate occurs as a white, crystalline powder that darkens on exposure to light. It is odorless and has a persistent very bitter taste. It is only slightly soluble in water, alcohol, chloroform, and ether.
QUALAQUIN is supplied for oral administration as capsules containing 324 mg of the active ingredient quinine sulfate USP, equivalent to 269 mg free base. Inactive ingredients: corn starch, magnesium stearate, and talc.
What is the most important information I should know about Qualaquin?
Qualaquin used to treat or prevent leg cramps may cause serious side effects or even death.
Qualaquin may cause:
- your blood cell (platelet) count to drop causing serious bleeding problems. In some people, serious kidney problems can happen.
- problems with your heart rhythm that can lead to death.
- serious allergic reactions.
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have:
Qualaquin can have other serious side effects. See “What are the possible side effects of Qualaquin?”
Who should not take Qualaquin?
Do not take Qualaquin if you have:
- changes in the electrical activity of your heart called QT prolongation.
- had allergic reactions to quinine (the active ingredient in Qualaquin), such as low platelets, which are necessary for your blood to clot.
- had allergic reactions to mefloquine (Lariam) or quinidine.
- an autoimmune disease (myasthenia gravis) that leads to muscle weakness.
- an inflammation of the nerve important for vision (optic neuritis).
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Qualaquin?
Before taking Qualaquin, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have heart problems.
- have kidney problems.
- have liver problems.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Treatment of malaria is important because it can be a serious disease for a pregnant woman and her unborn baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about the benefits and risks of taking Qualaquin during pregnancy. Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can happen in pregnant women while taking Qualaquin. Signs and symptoms of low blood sugar can include sweating, weakness, nausea, vomiting, and confusion. You and your healthcare provider can decide if Qualaquin is right for you.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Qualaquin can pass into your breast milk. You should talk with your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby while taking Qualaquin.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Qualaquin and other medicines may affect each other causing serious side effects. Certain medicines can cause the blood levels of Qualaquin to be too high or too low in your body.
Do not start taking a new medicine without telling your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Even medicines that you may take for a short period of time, such as antibiotics, can mix in your blood with Qualaquin and cause serious side effects or death.
How should I take Qualaquin?
- Take Qualaquin exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you how many Qualaquin capsules to take and when to take them.
- Take Qualaquin with food to lower your chance of having an upset stomach.
- Do not skip any doses or stop taking Qualaquin without first talking to your healthcare provider, even if you feel better.
- Do not take more Qualaquin than prescribed.
- If you miss a dose of Qualaquin, do not double the next dose to make up for a missed dose. If it has been more than& 4 hours since the missed dose, take your next dose at the next scheduled time. Call your healthcare provider if you are not sure what to do.
- If you take too much Qualaquin, call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest emergency room right away.
What are the possible side effects of Qualaquin?
Qualaquin may cause serious side effects, including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about Qualaquin?”.
- Heart rhythm problems atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter).
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Signs and symptoms of low blood sugar can include sweating, weakness, nausea, vomiting, and confusion.
The most common side effects of Qualaquin include:
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all of the possible side effects of Qualaquin. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Qualaquin
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Qualaquin for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Qualaquin to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about Qualaquin. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about Qualaquin that is written for health professionals.
How should I store Qualaquin?
- Keep the capsules in a tightly closed container.
- Store Qualaquin at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
Keep Qualaquin and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Qualaquin?
Active Ingredients: quinine sulfate, USP
Inactive Ingredients: corn starch, magnesium stearate, talc
Label
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 324 mg Capsule Bottle Label
- 100 CAPSULES
NDC 13310-153-01 - QUALAQUIN®
quinine sulfate
capsules USP - 324 mg
- DISPENSE THE ACCOMPANYING
MEDICATION GUIDE TO EACH PATIENT - AR
SCIENTIFIC - Rx only

SRC: NLM .
