Opsumit
Generic name: macitentan
Drug class: Agents for pulmonary hypertension
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Opsumit?
Opsumit is a prescription medicine used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), which is high blood pressure in the arteries of your lungs. Opsumit can improve your ability to exercise, improve some of your symptoms, and help slow down the progression of your disease. Opsumit can also lower your chance of being hospitalized for PAH. It is not known if Opsumit is safe and effective in children.
Description
OPSUMIT® (macitentan) is an endothelin receptor antagonist. The chemical name of macitentan is N-[5-(4-Bromophenyl)-6-[2-[(5-bromo-2-pyrimidinyl)oxy]ethoxy]-4-pyrimidinyl]-N’-propylsulfamide. It has a molecular formula of C19H20Br2N6O4S and a molecular weight of 588.27. Macitentan is achiral and has the following structural formula:
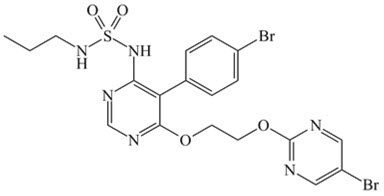
Macitentan is a crystalline powder that is insoluble in water. In the solid state macitentan is very stable, is not hygroscopic, and is not light sensitive.
OPSUMIT is available as a 10 mg film-coated tablet for once daily oral administration. The tablets include the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polysorbate 80, povidone, and sodium starch glycolate Type A. The tablets are film-coated with a coating material containing polyvinyl alcohol, soya lecithin, talc, titanium dioxide, and xanthan gum.
Mechanism of Action
Endothelin (ET)-1 and its receptors (ETA and ETB) mediate a variety of deleterious effects, such as vasoconstriction, fibrosis, proliferation, hypertrophy, and inflammation. In disease conditions such as PAH, the local ET system is upregulated and is involved in vascular hypertrophy and in organ damage.
Macitentan is an endothelin receptor antagonist that inhibits the binding of ET-1 to both ETA and ETB receptors. Macitentan displays high affinity and sustained occupancy of the ET receptors in human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. One of the metabolites of macitentan is also pharmacologically active at the ET receptors and is estimated to be about 20% as potent as the parent drug in vitro. The clinical impact of dual endothelin blockage is unknown.
What is the most important information I should know about Opsumit?
- Serious birth defects.
Opsumit can cause serious birth defects if taken during pregnancy.- Females must not be pregnant when they start taking Opsumit or become pregnant during treatment with Opsumit.
- Females who are able to get pregnant must have a negative pregnancy test before beginning treatment with Opsumit, each month during treatment with Opsumit and 1 month after stopping Opsumit. Talk to your healthcare provider about your menstrual cycle. Your healthcare provider will decide when to do the pregnancy test, and will order a pregnancy test for you depending on your menstrual cycle.
- Females who are able to get pregnant are females who:
- have entered puberty, even if they have not started their menstrual period, and
- have a uterus, and
- have not gone through menopause. Menopause means that you have not had a menstrual period for at least 12 months for natural reasons, or that you have had your ovaries removed.
- Females who are not able to get pregnant are females who:
- have not yet entered puberty, or
- do not have a uterus, or
- have gone through menopause. Menopause means that you have not had a menstrual period for at least 12 months for natural reasons, or that you have had your ovaries removed, or
- are infertile for other medical reasons and this infertility is permanent and cannot be reversed.
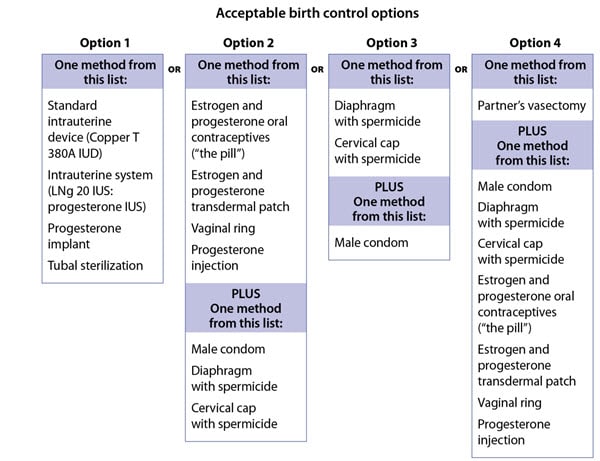
Females who are able to get pregnant must use two acceptable forms of birth control during treatment with Opsumit, and for one month after stopping Opsumit because the medicine may still be in the body.
- If you have had a tubal sterilization, have a progesterone implant, or have an IUD (intrauterine device), these methods can be used alone and no other form of birth control is needed.
- Talk with your healthcare provider or gynecologist (a doctor who specializes in female reproduction) to find out about options for acceptable birth control that you may use to prevent pregnancy during treatment with Opsumit.
- If you decide that you want to change the form of birth control that you use, talk with your healthcare provider or gynecologist to be sure that you choose another acceptable form of birth control.
See the chart below for Acceptable Birth Control Options during treatment with Opsumit.
- Do not have unprotected sex. Talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist right away if you have unprotected sex or if you think your birth control has failed. Your healthcare provider may talk with you about using emergency birth control.
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you miss a menstrual period or think you may be pregnant.
If you are the parent or caregiver of a female child who started taking Opsumit before reaching puberty, you should check your child regularly to see if she is developing signs of puberty. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you notice that she is developing breast buds or any pubic hair. Your healthcare provider should decide if your child has reached puberty. Your child may reach puberty before having her first menstrual period.
Females can only receive Opsumit through a restricted program called the Opsumit Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) Program. If you are a female who can get pregnant, you must talk to your healthcare provider, understand the benefits and risks of Opsumit, and agree to all of the instructions in the Opsumit REMS Program.
Males can receive Opsumit without taking part in the Opsumit REMS Program.
Who should not take Opsumit?
Do not take Opsumit if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or become pregnant during treatment with Opsumit. Opsumit can cause serious birth defects (see the Medication Guide section above called “What is the most important information I should know about Opsumit?”).
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Opsumit?
Tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions and all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Opsumit and other medicines may affect each other causing side effects. Do not start any new medicine until you check with your healthcare provider.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take an HIV medicine.
How should I take Opsumit?
Opsumit will be mailed to you by a specialty pharmacy. Your healthcare provider will give you complete details.
- Take Opsumit exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it. Do not stop taking Opsumit unless your healthcare provider tells you.
- You can take Opsumit with or without food.
- Do not split, crush, or chew Opsumit tablets.
- If you take too much Opsumit, call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
- If you miss a dose of Opsumit, take it as soon as you remember that day. Take the next dose at your regular time. Do not take 2 doses at the same time to make up for a missed dose.
What should I avoid while taking Opsumit?
- Do not get pregnant while taking Opsumit. See the serious birth defects section of the Medication Guide above called “What is the most important information I should know about Opsumit?” If you miss a menstrual period, or think you might be pregnant, call your healthcare provider right away.
- It is not known if Opsumit passes into your breastmilk. You should not breastfeed if you take Opsumit. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you take Opsumit.
What are the possible side effects of Opsumit?
Opsumit can cause serious side effects, including:
- Serious birth defects. See “What is the most important information I should know about Opsumit?”
- Some medicines that are like Opsumit can cause liver problems. Your healthcare provider should do blood tests to check your liver before you start taking Opsumit. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any of the following symptoms of liver problems while taking Opsumit.
- Fluid retention can happen within weeks after starting Opsumit. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any unusual weight gain or swelling of your ankles or legs. Your healthcare provider will look for the cause of any fluid retention.
- Low red blood cell levels (anemia) can occur with Opsumit treatment, usually during the first weeks after starting therapy. In some cases a blood transfusion may be needed, but this is not common. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check your red blood cells before starting Opsumit. Your healthcare provider may also need to do these tests during treatment with Opsumit.
- Decreased sperm count. Opsumit, and other medicines like Opsumit, may cause decreased sperm counts in men who take these medicines. A decreased sperm count may affect the ability to father a child. Tell your healthcare provider if being able to have children is important to you.
The most common side effects of Opsumit are:
- Stuffy nose or sore throat
- Irritation of the airways (bronchitis)
- Headache
- Flu
- Urinary tract infection
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of Opsumit. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Opsumit
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Opsumit for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Opsumit to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about Opsumit. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Opsumit that is written for health professionals. For more information, call 1-866-228-3546, or visit www.OPSUMIT.com.
How should I store Opsumit?
- Store Opsumit tablets at room temperature between 68°F and 77°F (20°C and 25°C).
- Keep Opsumit and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Opsumit?
Active ingredient: macitentan
Inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polysorbate 80, povidone, and sodium starch glycolate Type A. The tablets are film-coated with a coating material containing polyvinyl alcohol, soya lecithin, talc, titanium dioxide, and xanthan gum.
Label
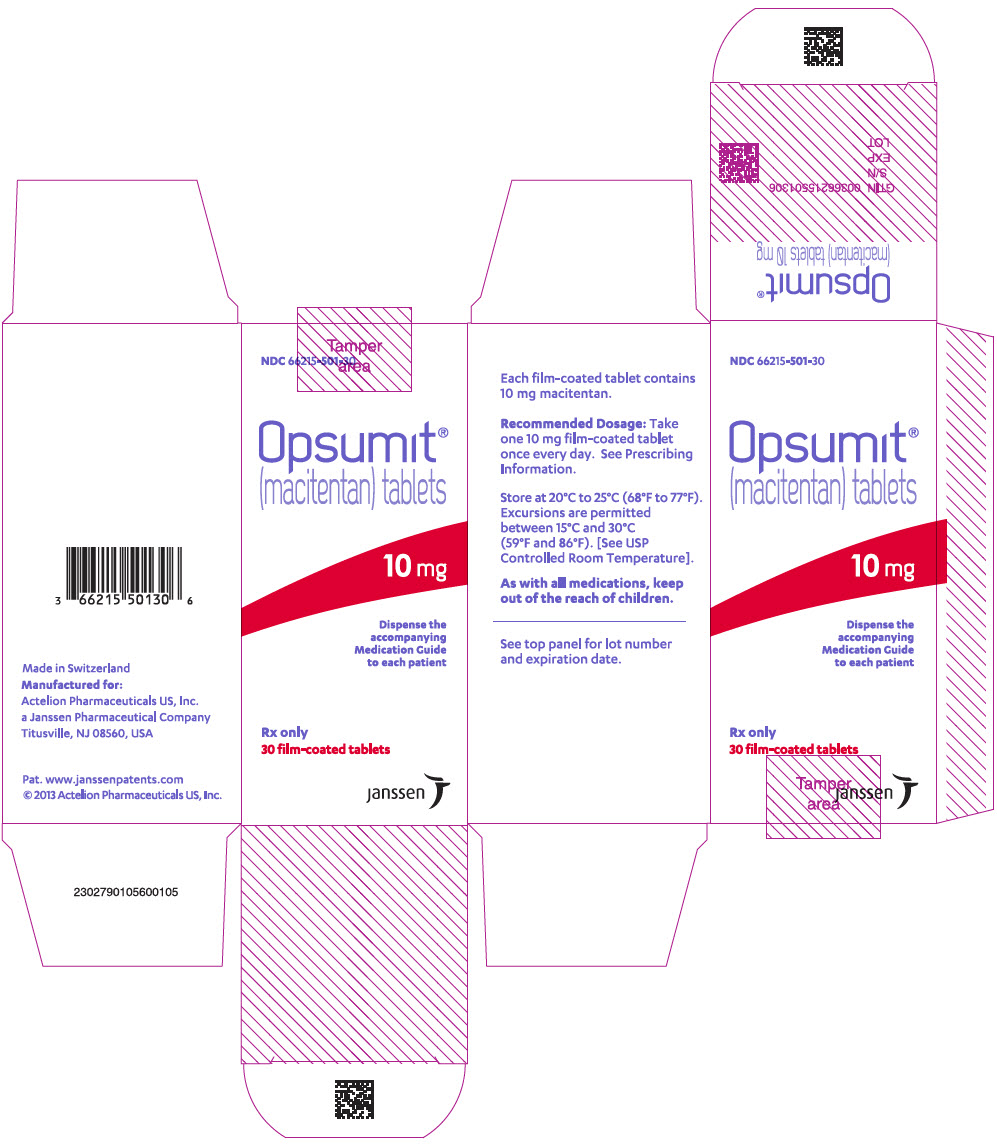
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 10 MG TABLET BOTTLE CARTON
- NDC 66215-501-30
- Opsumit®
(macitentan) tablets - 10 mg
- Dispense the
accompanying
Medication Guide
to each patient - Rx only
30 film-coated tablets - janssen

SRC: NLM .
