Fosamax Plus D
Generic name: alendronate and cholecalciferol
Drug class: Bisphosphonates
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Fosamax Plus D?
Fosamax Plus D is a prescription medicine used to treat osteoporosis in women after menopause. Fosamax Plus D helps increase bone mass and reduces the chance of having a hip or spinal fracture (break), increases bone mass in men with osteoporosis.
Fosamax Plus D should not be used to treat vitamin D deficiency.
It is not known how long Fosamax Plus D works for the treatment of osteoporosis. You should see your doctor regularly to determine if Fosamax Plus D is still right for you.
Fosamax Plus D is not for use in children.
Description
FOSAMAX PLUS D contains alendronate sodium, a bisphosphonate, and cholecalciferol (vitamin D3).
Alendronate sodium is a bisphosphonate that acts as a specific inhibitor of osteoclast-mediated bone resorption. Bisphosphonates are synthetic analogs of pyrophosphate that bind to the hydroxyapatite found in bone.
Alendronate sodium is chemically described as (4-amino-1-hydroxybutylidene) bisphosphonic acid monosodium salt trihydrate.
The empirical formula of alendronate sodium is C4H12NNaO7P2•3H2O and its formula weight is 325.12. The structural formula is:
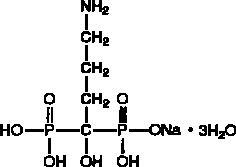
Alendronate sodium is a white, crystalline, nonhygroscopic powder. It is soluble in water, very slightly soluble in alcohol, and practically insoluble in chloroform.
Cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) is a secosterol that is the natural precursor of the calcium-regulating hormone calcitriol (1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3).
The chemical name of cholecalciferol is (3β,5Z,7E)-9,10-secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-trien-3-ol. The empirical formula of cholecalciferol is C27H44O and its molecular weight is 384.6. The structural formula is:
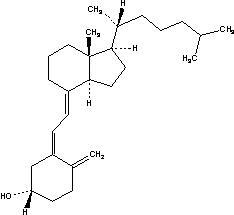
Cholecalciferol is a white, crystalline, odorless powder. Cholecalciferol is practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in usual organic solvents, and slightly soluble in vegetable oils.
FOSAMAX PLUS D for oral administration contains 91.37 mg of alendronate monosodium salt trihydrate, the molar equivalent of 70 mg of free acid, and 70 or 140 mcg of cholecalciferol, equivalent to 2800 or 5600 international units vitamin D, respectively. Each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, lactose anhydrous, medium chain triglycerides, gelatin, croscarmellose sodium, sucrose, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, butylated hydroxytoluene, modified food starch, and sodium aluminum silicate.
Mechanism of Action
Alendronate Sodium
Animal studies have indicated the following mode of action. At the cellular level, alendronate shows preferential localization to sites of bone resorption, specifically under osteoclasts. The osteoclasts adhere normally to the bone surface but lack the ruffled border that is indicative of active resorption. Alendronate does not interfere with osteoclast recruitment or attachment, but it does inhibit osteoclast activity. Studies in mice on the localization of radioactive [3H]alendronate in bone showed about 10-fold higher uptake on osteoclast surfaces than on osteoblast surfaces. Bones examined 6 and 49 days after [3H]alendronate administration in rats and mice, respectively, showed that normal bone was formed on top of the alendronate, which was incorporated inside the matrix. While incorporated in bone matrix, alendronate is not pharmacologically active. Thus, alendronate must be continuously administered to suppress osteoclasts on newly formed resorption surfaces. Histomorphometry in baboons and rats showed that alendronate treatment reduces bone turnover (i.e., the number of sites at which bone is remodeled). In addition, bone formation exceeds bone resorption at these remodeling sites, leading to progressive gains in bone mass.
Cholecalciferol
Vitamin D3 is produced in the skin by photochemical conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to previtamin D3 by ultraviolet light. This is followed by non-enzymatic isomerization to vitamin D3. In the absence of adequate sunlight exposure, vitamin D3 is an essential dietary nutrient. Vitamin D3 in skin and dietary vitamin D3 (absorbed into chylomicrons) is converted to 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 in the liver. Conversion to the active calcium-mobilizing hormone 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol) in the kidney is stimulated by both parathyroid hormone and hypophosphatemia. The principal action of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is to increase intestinal absorption of both calcium and phosphate as well as regulate serum calcium, renal calcium and phosphate excretion, bone formation and bone resorption.
Vitamin D is required for normal bone formation. Vitamin D insufficiency develops when both sunlight exposure and dietary intake are inadequate. Insufficiency is associated with negative calcium balance, increased parathyroid hormone levels, bone loss, and increased risk of skeletal fracture. In severe cases, deficiency results in more severe hyperparathyroidism, hypophosphatemia, proximal muscle weakness, bone pain and osteomalacia.
What is the most important information I should know about Fosamax Plus D?
Fosamax Plus D can cause serious side effects including:
- Esophagus problems
- Low calcium levels in your blood (hypocalcemia)
- Bone, joint, or muscle pain
- Severe jaw bone problems (osteonecrosis)
- Unusual thigh bone fractures
1. Esophagus problems.
Some people who take Fosamax Plus D may develop problems in the esophagus (the tube that connects the mouth and the stomach). These problems include irritation, inflammation, or ulcers of the esophagus which may sometimes bleed.
- It is important that you take Fosamax Plus D exactly as prescribed to help lower your chance of getting esophagus problems. (See the section “How should I take Fosamax Plus D tablet?”)
- Stop taking Fosamax Plus D and call your doctor right away if you get chest pain, new or worsening heartburn, or have trouble or pain when you swallow.
2. Low calcium levels in your blood (hypocalcemia).
Fosamax Plus D may lower the calcium levels in your blood. If you have low blood calcium before you start taking Fosamax Plus D, it may get worse during treatment. Your low blood calcium must be treated before you take Fosamax Plus D. Most people with low blood calcium levels do not have symptoms, but some people may have symptoms. Call your doctor right away if you have symptoms of low blood calcium such as:
- Spasms, twitches, or cramps in your muscles
- Numbness or tingling in your fingers, toes, or around your mouth
Your doctor may prescribe calcium and vitamin D to help prevent low calcium levels in your blood, while you take Fosamax Plus D. Take calcium and vitamin D as your doctor tells you to.
3. Bone, joint, or muscle pain.
Some people who take Fosamax Plus D develop severe bone, joint, or muscle pain.
4. Severe jaw bone problems (osteonecrosis).
Severe jaw bone problems may happen when you take Fosamax Plus D. Your doctor should examine your mouth before you start Fosamax Plus D. Your doctor may tell you to see your dentist before you start Fosamax Plus D. It is important for you to practice good mouth care during treatment with Fosamax Plus D.
5. Unusual thigh bone fractures.
Some people have developed unusual fractures in their thigh bone. Symptoms of a fracture may include new or unusual pain in your hip, groin, or thigh.
Call your doctor right away if you have any of these side effects.
Who should not take Fosamax Plus D?
Do not take Fosamax Plus D if you:
- Have certain problems with your esophagus, the tube that connects your mouth with your stomach
- Cannot stand or sit upright for at least 30 minutes
- Have low levels of calcium in your blood
- Are allergic to Fosamax Plus D or any of its ingredients. A list of ingredients is at the end of this guide.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Fosamax Plus D?
Before you start Fosamax Plus D, be sure to talk to your doctor if you:
- Have problems with swallowing
- Have stomach or digestive problems
- Have low blood calcium
- Plan to have dental surgery or teeth removed
- Have kidney problems
- Have sarcoidosis, leukemia, lymphoma. These conditions may cause changes in vitamin D.
- Have been told you have trouble absorbing minerals in your stomach or intestines (malabsorption syndrome)
- Are pregnant, trying to become pregnant or suspect that you are pregnant. If you become pregnant while taking Fosamax Plus D, stop taking it and contact your doctor. It is not known if Fosamax Plus D can harm your unborn baby.
- Are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed. It is not known if Fosamax Plus D passes into your milk and may harm your baby.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- antacids
- aspirin
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory (NSAID) medicines
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Certain medicines may affect how Fosamax Plus D works.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your doctor and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine.
How should I take Fosamax Plus D?
- Take Fosamax Plus D exactly as your doctor tells you.
- Fosamax Plus D works only if taken on an empty stomach.
- Take 1 dose of Fosamax Plus D 1 time a week, after you get up for the day and before taking your first food, drink, or other medicine.
- Take Fosamax Plus D while you are sitting or standing.
- Take your Fosamax Plus D tablet with a full glass (6-8 oz) of plain water.
- Do not chew or suck on a tablet of Fosamax Plus D.
- Do not take Fosamax Plus D with mineral water, coffee, tea, soda, or juice.
- Do not take Fosamax Plus D at bedtime.
After swallowing Fosamax Plus D, wait at least 30 minutes:
- Before you lie down. You may sit, stand or walk, and do normal activities like reading.
- Before you take your first food or drink except for plain water.
- Before you take other medicines, including antacids, calcium, and other supplements and vitamins.
Do not lie down for at least 30 minutes after you take Fosamax Plus D and after you eat your first food of the day.
If you miss a dose of Fosamax Plus D, do not take it later in the day. Take your missed dose on the next morning after you remember and then return to your normal schedule. Do not take 2 doses on the same day.
If you take too much Fosamax Plus D, call your doctor. Do not try to vomit. Do not lie down.
What are the possible side effects of Fosamax Plus D?
Fosamax Plus D may cause serious side effects.
- See “What is the most important information I should know about Fosamax Plus D?”
The most common side effects of Fosamax Plus D are:
- Stomach area (abdominal) pain
- Heartburn
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Upset stomach
- Pain in your bones, joints, or muscles
- Nausea
You may get allergic reactions, such as hives or swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Worsening of asthma has been reported.
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Fosamax Plus D. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Fosamax Plus D
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Fosamax Plus D for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Fosamax Plus D to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about Fosamax Plus D. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about Fosamax Plus D that is written for health professionals. For more information, go to: www.fosamaxplusd.com or call 1-800-622-4477 (toll-free).
How should I store Fosamax Plus D?
- Store Fosamax Plus D at room temperature, 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep Fosamax Plus D away from light.
- Keep Fosamax Plus D package and tablets dry.
- Store Fosamax Plus D in the original package.
Keep Fosamax Plus D and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Fosamax Plus D?
Active ingredients: alendronate sodium and cholecalciferol (vitamin D3).
Inactive ingredients: cellulose, lactose, medium chain triglycerides, gelatin, croscarmellose sodium, sucrose, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, butylated hydroxytoluene, modified food starch, and sodium aluminum silicate.
Label
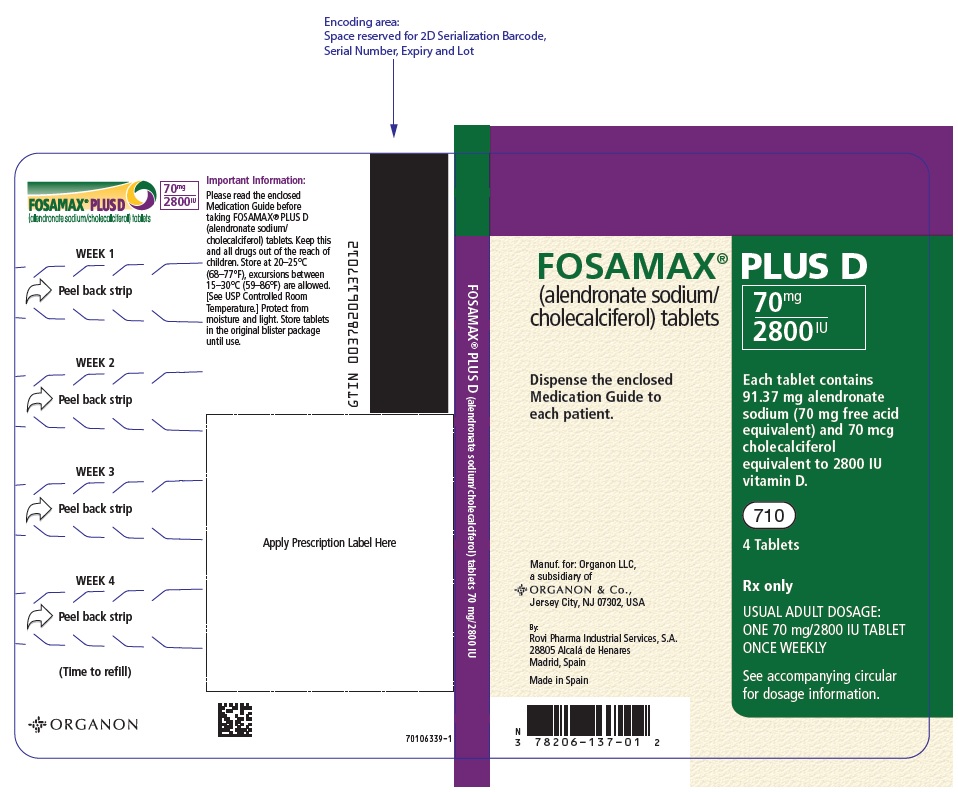
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 70 MG/2800 IU TABLET BLISTER PACK
- FOSAMAX® PLUS D
(alendronate sodium/
cholecalciferol) tablets - 70mg
2800IU - Dispense the enclosed
Medication Guide to
each patient. - Each tablet contains
91.37 mg alendronate
sodium (70 mg free acid
equivalent) and 70 mcg
cholecalciferol
equivalent to 2800 IU
vitamin D. - 710
- 4 Tablets
- Rx only
- USUAL ADULT DOSAGE:
ONE 70 mg/2800 IU TABLET
ONCE WEEKLY - See accompanying circular
for dosage information. - Manuf. for: Organon LLC,
a subsidiary of
ORGANON & Co.,
Jersey City, NJ 07302, USA - By:
Rovi Pharma Industrial Services, S.A.
28805 Alcalá de Henares
Madrid, Spain - Made in Spain
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 70 MG/5600 IU TABLET BLISTER PACK
- FOSAMAX® PLUS D
(alendronate sodium/
cholecalciferol) tablets - 70mg
5600IU - Dispense the enclosed
Medication Guide to
each patient. - Each tablet contains
91.37 mg alendronate
sodium (70 mg free acid
equivalent) and 140 mcg
cholecalciferol
equivalent to 5600 IU
vitamin D. - 270
- 4 Tablets
- Rx only
- USUAL ADULT DOSAGE:
ONE 70 mg/5600 IU
TABLET ONCE WEEKLY - See accompanying circular
for dosage information. - Manuf. for: Organon LLC,
a subsidiary of
ORGANON & Co.,
Jersey City, NJ 07302, USA - By:
Rovi Pharma Industrial Services, S.A.
28805 Alcalá de Henares
Madrid, Spain - Made in Spain

SRC: NLM .
