Feraheme
Generic name: ferumoxytol
Drug class: Iron products
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Feraheme?
Feraheme is a prescription medicine used to treat iron deficiency anemia in adults who have intolerance to oral iron or who have not responded well to treatment with oral iron or chronic kidney disease (CKD).
It is not known if Feraheme is safe and effective in children less than 18 years of age.
Description
Feraheme is an iron replacement product containing ferumoxytol for intravenous infusion. Ferumoxytol is a non-stoichiometric magnetite (superparamagnetic iron oxide) coated with polyglucose sorbitol carboxymethylether. The overall colloidal particle size is 17-31 nm in diameter. The chemical formula of Feraheme is Fe5874O8752-C11719H18682O9933Na414 with an apparent molecular weight of 750 kDa.
Feraheme Injection is a sterile aqueous colloidal product that is formulated with mannitol. It is a black to reddish brown liquid, and is provided in single-dose vials containing 510 mg of elemental iron. Each mL of the sterile colloidal solution of Feraheme Injection contains 30 mg of elemental iron, 30 mg polyglucose sorbitol carboxymethylether, and 44 mg of mannitol. The formulation is isotonic with an osmolality of 270-330 mOsm/kg. The product contains no preservatives, and has a pH of 6 to 8.
Mechanism of Action
Feraheme consists of a superparamagnetic iron oxide that is coated with a carbohydrate shell, which helps to isolate the bioactive iron from plasma components until the iron-carbohydrate complex enters the reticuloendothelial system macrophages of the liver, spleen and bone marrow. The iron is released from the iron-carbohydrate complex within vesicles in the macrophages. Iron then either enters the intracellular storage iron pool (e.g., ferritin) or is transferred to plasma transferrin for transport to erythroid precursor cells for incorporation into hemoglobin.
What is the most important information I should know about Feraheme?
Feraheme may cause serious side effects including:
- Serious allergic reactions that can lead to death. Serious allergic reactions have happened in people after receiving the first dose of Feraheme or after receiving additional doses in people who did not previously have an allergic reaction. If you have a history of allergies to many different medicines, you may have an increased risk of serious allergic reactions to Feraheme. Tell your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you get any of these signs or symptoms:
- rash
- itching
- dizziness or lightheadedness
- swelling of the tongue or throat
- wheezing or trouble breathing
See “What are the possible side effects of Feraheme?” for more information about side effects.
Who should not use Feraheme?
Do not receive Feraheme if you:
- are allergic to Feraheme or any of the ingredients in Feraheme. See the end of this guide for a complete list of ingredients in Feraheme.
- have had an allergic reaction to any iron medicine given into your vein by intravenous (IV) infusion.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before using Feraheme?
Before receiving Feraheme, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have allergies to many different medicines
- have iron overload
- have low blood pressure (hypotension).
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Feraheme will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Feraheme passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will receive Feraheme or breastfeed.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
How should I use Feraheme?
- Feraheme will be given to you into your vein by intravenous (IV) infusion over at least 15 minutes by your healthcare provider. You will receive Feraheme in 2 doses 3 to 8 days apart.
- Your healthcare provider will watch you during and for at least 30 minutes after you receive Feraheme.
What are the possible side effects of Feraheme?
Feraheme can cause serious side effects, including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about Feraheme?”
- Low blood pressure (hypotension) is a common side effect of Feraheme and can sometimes be serious. Your healthcare provider will check you for signs and symptoms of hypotension after each Feraheme infusion.
- Iron overload. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check your iron levels during treatment with Feraheme.
The most common side effects of Feraheme include: diarrhea, headache, nausea, dizziness, constipation, and swelling of your legs, feet, arms, or hands.
These are not all of the possible side effects of Feraheme. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Feraheme
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. If you would like more information, talk to your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Feraheme that is written for health professionals.
How should I store Feraheme?
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). Excursions permitted to 15° – 30°C (59° – 86°F).
What are the ingredients in Feraheme?
Active ingredient: ferumoxytol
Inactive ingredient: mannitol
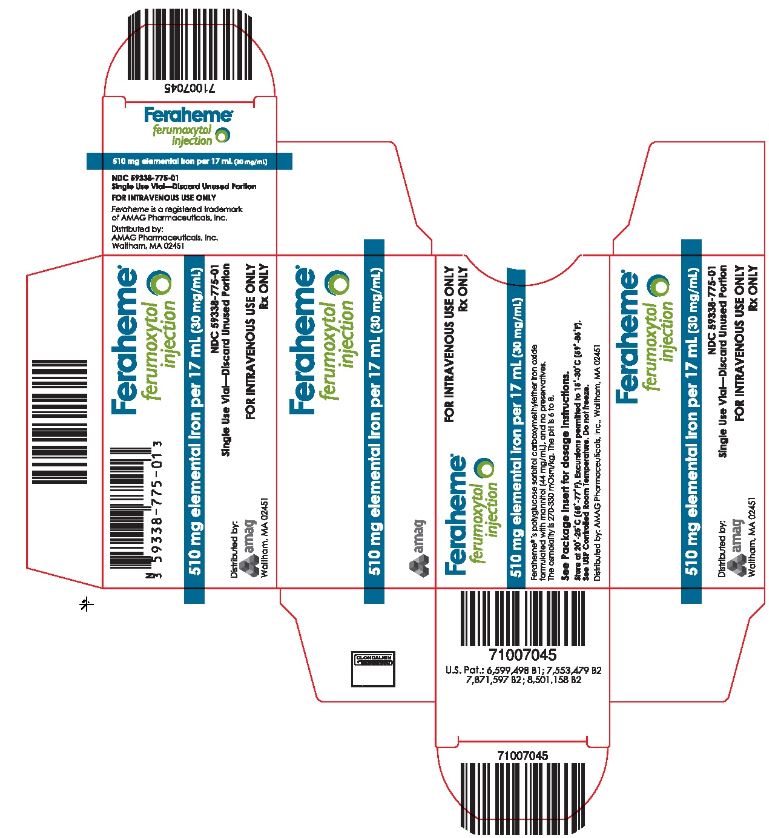
Label
Package Label – Principal Display Panel – 17 mL Vial, Feraheme Injection

Package Label – Principal Display Panel – Carton for Single Use Vial, Feraheme Injection
SRC: NLM .
