Exforge
Generic name: amlodipine and valsartan
Drug class: Angiotensin II inhibitors with calcium channel blockers
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Exforge?
Exforge contains 2 prescription medicines amlodipine, a calcium channel blocker, valsartan, an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB).
Exforge may be used to lower high blood pressure (hypertension) in adults when 1 medicine to lower your high blood pressure is not enough, as the first medicine to lower high blood pressure if your doctor decides you are likely to need more than 1 medicine.
Exforge has not been studied in children under 18 years of age.
What is high blood pressure (hypertension)?
Blood pressure is the force of blood in your blood vessels when your heart beats and when your heart rests. You have high blood pressure when the force is too much. Exforge can help your blood vessels relax so your blood pressure is lower. Medicines that lower blood pressure lower your chance of having a stroke or heart attack.
High blood pressure makes the heart work harder to pump blood throughout the body and causes damage to blood vessels. If high blood pressure is not treated, it can lead to stroke, heart attack, heart failure, kidney failure, and vision problems.
Description
Exforge is a fixed combination of amlodipine and valsartan.
Exforge contains the besylate salt of amlodipine, a dihydropyridine calcium-channel blocker (CCB). Amlodipine besylate is a white to pale yellow crystalline powder, slightly soluble in water and sparingly soluble in ethanol. Amlodipine besylate’s chemical name is 3-Ethyl-5-methyl(4RS)-2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate benzenesulphonate; its structural formula is:
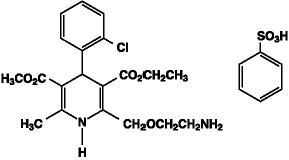
Its empirical formula is C20H25ClN2O5•C6H6O3S and its molecular weight is 567.1.
Valsartan is a nonpeptide, orally active, and specific angiotensin II antagonist acting on the AT1 receptor subtype. Valsartan is a white to practically white fine powder, soluble in ethanol and methanol and slightly soluble in water. Valsartan’s chemical name is N-(1-oxopentyl)-N-[[2’-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl) [1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-L-valine; its structural formula is:
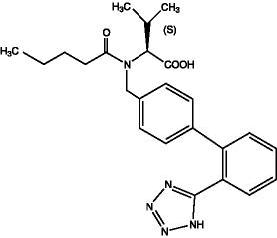
Its empirical formula is C24H29N5O3 and its molecular weight is 435.5.
Exforge tablets are formulated in 4 strengths for oral administration with a combination of amlodipine besylate (6.9 mg or 13.9 mg, equivalent to 5 mg or 10 mg of amlodipine respectively), with 160 mg, or 320 mg of valsartan providing for the following available combinations: 5/160 mg, 10/160 mg, 5/320 mg, and 10/320 mg.
The inactive ingredients for all strengths of the tablets are colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. Additionally the 5/320 mg and 10/320 mg strengths contain iron oxide yellow and sodium starch glycolate. The film coating contains hypromellose, iron oxides, polyethylene glycol, talc, and titanium dioxide.
Mechanism of Action
Amlodipine
Amlodipine is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker that inhibits the transmembrane influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle. Experimental data suggest that amlodipine binds to both dihydropyridine and nondihydropyridine binding sites. The contractile processes of cardiac muscle and vascular smooth muscle are dependent upon the movement of extracellular calcium ions into these cells through specific ion channels.
Amlodipine inhibits calcium ion influx across cell membranes selectively, with a greater effect on vascular smooth muscle cells than on cardiac muscle cells. Negative inotropic effects can be detected in vitro but such effects have not been seen in intact animals at therapeutic doses. Serum calcium concentration is not affected by amlodipine. Within the physiologic pH range, amlodipine is an ionized compound (pKa=8.6), and its kinetic interaction with the calcium channel receptor is characterized by a gradual rate of association and dissociation with the receptor binding site, resulting in a gradual onset of effect.
Amlodipine is a peripheral arterial vasodilator that acts directly on vascular smooth muscle to cause a reduction in peripheral vascular resistance and reduction in blood pressure.
Valsartan
Angiotensin II is formed from angiotensin I in a reaction catalyzed by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE, kininase II). Angiotensin II is the principal pressor agent of the renin-angiotensin system, with effects that include vasoconstriction, stimulation of synthesis and release of aldosterone, cardiac stimulation, and renal reabsorption of sodium. Valsartan blocks the vasoconstrictor and aldosterone-secreting effects of angiotensin II by selectively blocking the binding of angiotensin II to the AT1 receptor in many tissues, such as vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal gland. Its action is therefore independent of the pathways for angiotensin II synthesis.
There is also an AT2 receptor found in many tissues, but AT2 is not known to be associated with cardiovascular homeostasis. Valsartan has much greater affinity (about 20,000-fold) for the AT1 receptor than for the AT2 receptor. The increased plasma levels of angiotensin following AT1 receptor blockade with valsartan may stimulate the unblocked AT2 receptor. The primary metabolite of valsartan is essentially inactive with an affinity for the AT1 receptor about one-200th that of valsartan itself.
Blockade of the renin-angiotensin system with ACE inhibitors, which inhibit the biosynthesis of angiotensin II from angiotensin I, is widely used in the treatment of hypertension. ACE inhibitors also inhibit the degradation of bradykinin, a reaction also catalyzed by ACE. Because valsartan does not inhibit ACE (kininase II), it does not affect the response to bradykinin. Whether this difference has clinical relevance is not yet known. Valsartan does not bind to or block other hormone receptors or ion channels known to be important in cardiovascular regulation.
Blockade of the angiotensin II receptor inhibits the negative regulatory feedback of angiotensin II on renin secretion, but the resulting increased plasma renin activity and angiotensin II circulating levels do not overcome the effect of valsartan on blood pressure.
What is the most important information I should know about Exforge?
- Exforge can cause harm or death to an unborn baby.
- Talk to your doctor about other ways to lower your blood pressure if you plan to become pregnant.
- If you get pregnant while taking Exforge, tell your doctor right away.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Exforge?
Tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. See “What is the most important information I should know about Exforge?”
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Exforge is present in human milk. It is not known whether Exforge effects your breastfed baby or milk production. Do not breastfeed while you are taking Exforge.
- have heart problems
- have liver problems
- have kidney problems
- are vomiting or having a lot of diarrhea
- have ever had a reaction called angioedema, to another blood pressure medicine. Angioedema causes swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat, and may cause difficulty breathing.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Some of your other medicines and Exforge could affect each other, causing serious side effects.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- simvastatin or other cholesterol-lowering medicine
- other medicines for high blood pressure or a heart problem
- water pills (diuretics)
- potassium supplements. Your doctor may check the amount of potassium in your blood periodically.
- a salt substitute. Your doctor may check the amount of potassium in your blood periodically.
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (like ibuprofen or naproxen)
- medicines used to prevent and treat fungal skin infections (such as ketoconazole, itraconazole)
- medicines used to treat bacterial infections (such as clarithromycin, telithromycin)
- certain antibiotics (rifamycin group), a drug used to protect against transplant rejection (cyclosporine) or an antiretroviral drug used to treat HIV/AIDS infection (ritonavir). These drugs may increase the effect of valsartan.
- lithium, a medicine used in some types of depression
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your doctor or pharmacist when you get a new medicine. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before you start taking any new medicine. Your doctor or pharmacist will know what medicines are safe to take together.
How should I take Exforge?
- Take Exforge exactly as your doctor tells you.
- Take Exforge once each day.
- Exforge can be taken with or without food.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is close to your next dose, do not take the missed dose. Just take the next dose at your regular time.
- If you take too much Exforge, call your doctor or Poison Control Center, or go to the emergency room.
- Tell all your doctors or dentist you are taking Exforge if you:
- are going to have surgery
- go for kidney dialysis
What should I avoid while taking Exforge?
You should not take Exforge during pregnancy. See “What is the most important information I should know about Exforge?”
What are the possible side effects of Exforge?
Exforge may cause serious side effects including:
- harm to an unborn baby causing injury and even death. See “What is the most important information I should know about Exforge?”
- low blood pressure (hypotension). Low blood pressure is most likely to happen if you:
- take water pills
- are on a low-salt diet
- get dialysis treatments
- have heart problems
- get sick with vomiting or diarrhea
- drink alcohol
Lie down if you feel faint or dizzy. Call your doctor right away.
- more heart attacks and chest pain (angina) in people that already have severe heart problems. This may happen when you start Exforge or when there is an increase in your dose of Exforge. Get emergency help if you get worse chest pain or chest pain that does not go away.
- kidney problems. Kidney problems may become worse in people that already have kidney disease. Some people will have changes in blood tests for kidney function and may need a lower dose of Exforge. Call your doctor if you have swelling in your feet, ankles, or hands or unexplained weight gain. If you have heart failure, your doctor should check your kidney function before prescribing Exforge.
- laboratory blood test changes in people with heart failure. Some people with heart failure who take valsartan, 1 of the medicines in Exforge, have changes in blood tests including increased potassium and decreased kidney function.
The most common side effects of Exforge include:
- swelling (edema) of the hands, ankles, or feet
- nasal congestion, sore throat, and discomfort when swallowing
- upper respiratory tract infection (head or chest cold)
- dizziness
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Exforge. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088
General information about the safe and effective use of Exforge
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in the patient information leaflet. Do not use Exforge for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Exforge to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This patient information leaflet summarizes the most important information about Exforge. If you would like more information about Exforge, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about Exforge that is written for health professionals. For more information go to www.pharma.us.novartis.com or call 1-888-839-3674.
How should I store Exforge?
- Store Exforge at room temperature between 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C).
- Keep Exforge dry (protect it from moisture).
Keep Exforge and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Exforge?
Active ingredients: Amlodipine besylate and valsartan
The inactive ingredients of all strengths of the tablets are colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. Additionally, the 5/320 mg and 10/320 mg strengths contain iron oxide yellow and sodium starch glycolate. The film coating contains hypromellose, iron oxides, polyethylene glycol, talc, and titanium dioxide.
Label
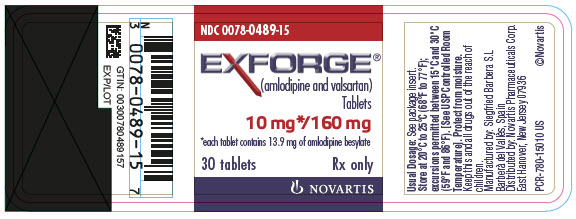
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- NDC 0078-0489-15
- EXFORGE®
(amlodipine and valsartan)
Tablets - 10 mg*/160 mg
- *each tablet contains 13.9 mg of amlodipine besylate
- 30 tablets
- Rx only
- NOVARTIS
![]()
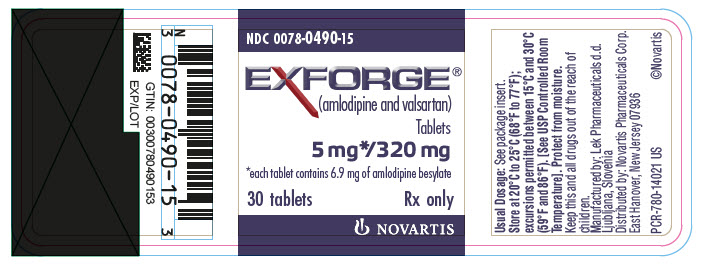
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- NDC 0078-0490-15
- EXFORGE®
(amlodipine and valsartan)
Tablets - 5 mg*/320 mg
- *each tablet contains 6.9 mg of amlodipine besylate
- 30 tablets
- Rx only
- NOVARTIS
![]()
SRC: NLM .
