Edarbyclor
Generic name: azilsartan and chlorthalidone
Drug class: Angiotensin II inhibitors with thiazides
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Edarbyclor?
Edarbyclor is a prescription medicine that contains azilsartan medoxomil, an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) and chlorthalidone, a water pill (diuretic).
Edarbyclor is used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) when one medicine to lower your high blood pressure is not enough, as the first medicine to lower your high blood pressure if your doctor decides you are likely to need more than one medicine.
It is not known if Edarbyclor is safe and effective in children under 18 years of age.
What is high blood pressure (hypertension)?
Blood pressure is the force in your blood vessels when your heart beats and when your heart rests. You have high blood pressure when the force is too great.
High blood pressure makes the heart work harder to pump blood through the body and causes damage to the blood vessels. Edarbyclor tablets can help your blood vessels relax so your blood pressure is lower. Medicines that lower your blood pressure may lower your chance of having a stroke or heart attack.
Description
Edarbyclor is a combination of azilsartan medoxomil (angiotensin II receptor blocker; as its potassium salt) and chlorthalidone (thiazide-like diuretic).
Azilsartan medoxomil, a prodrug, is hydrolyzed to azilsartan in the gastrointestinal tract during absorption. Azilsartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker. Chlorthalidone is a monosulfamyl thiazide-like diuretic that differs chemically from thiazide diuretics by the lack of a benzothiadiazine structure.
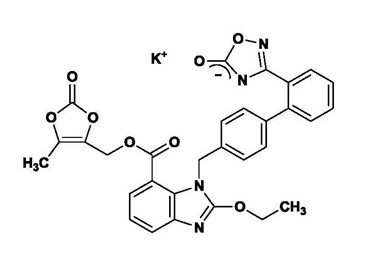
The potassium salt of azilsartan medoxomil, azilsartan kamedoxomil, is chemically described as (5-Methyl-2-oxo-1,3-dioxol-4-yl)methyl 2-ethoxy-1-{[2′-(5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl}-1H-benzimidazole-7-carboxylate monopotassium salt. Its empirical formula is C30H23KN4O8.
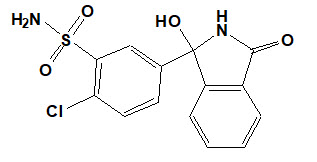
Chlorthalidone is chemically described as 2-chloro-5(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-1- isoindolinyl) benzenesulfonamide. Its empirical formula is C14H11ClN2O4S.
The structural formula for azilsartan medoxomil is
The structural formula for chlorthalidone is
Azilsartan kamedoxomil is a white to nearly white powder with a molecular weight of 606.62. It is practically insoluble in water and freely soluble in methanol.
Chlorthalidone is a white to yellowish white powder with a molecular weight of 338.76. Chlorthalidone is practically insoluble in water, in ether, and in chloroform; soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in ethanol.
Edarbyclor is available for oral use as tablets. The tablets have a characteristic odor. Each Edarbyclor tablet contains 42.68 mg of azilsartan kamedoxomil, which is equivalent to containing azilsartan medoxomil 40 mg plus 12.5 or 25 mg of chlorthalidone. Each tablet of Edarbyclor also contains the following inactive ingredients: mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, fumaric acid, sodium hydroxide, hydroxypropyl cellulose, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, hypromellose 2910, talc, titanium dioxide, ferric oxide red, polyethylene glycol 8000, and printing ink gray F1.
Mechanism of Action
The active ingredients of Edarbyclor target two separate mechanisms involved in blood pressure regulation.
Azilsartan medoxomil
Angiotensin II is formed from angiotensin I in a reaction catalyzed by angiotensin-converting enzymes (ACE, kinase II). Angiotensin II is the principle pressor agent of the renin-angiotensin system, with effects that include vasoconstriction, stimulation of synthesis and release of aldosterone, cardiac stimulation, and renal reabsorption of sodium. Azilsartan medoxomil is an orally administered prodrug that is rapidly converted by esterases during absorption to the active moiety, azilsartan. Azilsartan blocks the vasoconstrictor and aldosterone-secreting effects of angiotensin II by selectively blocking the binding of angiotensin II to the AT1 receptor in many tissues, such as vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal gland. Its action is, therefore, independent of the pathway for angiotensin II synthesis.
An AT2 receptor is also found in many tissues, but this receptor is not known to be associated with cardiovascular homeostasis. Azilsartan has more than a 10,000-fold greater affinity for the AT1 receptor than for the AT2 receptor.
Blockade of the renin-angiotensin system with ACE inhibitors, which inhibit the biosynthesis of angiotensin II from angiotensin I, is widely used in the treatment of hypertension. ACE inhibitors also inhibit the degradation of bradykinin, a reaction catalyzed by ACE. Because azilsartan does not inhibit ACE (kinase II), it should not affect bradykinin levels. Whether this difference has clinical relevance is not yet known. Azilsartan does not bind to or block other receptors or ion channels known to be important in cardiovascular regulation.
Blockade of the angiotensin II receptor inhibits the negative regulatory feedback of angiotensin II on renin secretion, but the resulting increased plasma renin activity and angiotensin II circulating levels do not overcome the effect of azilsartan on blood pressure.
Chlorthalidone
Chlorthalidone produces diuresis with increased excretion of sodium and chloride. The site of action appears to be the distal renal tubule (early convoluted part), inhibiting NaCl reabsorption (by antagonizing the Na+-Cl-cotransporter) and promoting Ca++ reabsorption (by an unknown mechanism). The enhanced delivery of Na+ and water to the cortical collecting tubule and/or the increased flow rate leads to increased secretion and elimination of K+ and H+. The diuretic effects of chlorthalildone lead to decreased extracellular fluid volume, plasma volume, cardiac output, total exchangeable sodium, glomerular filtration rate, and renal plasma flow. Although the mechanism of action of chlorthalidone and related drugs is not wholly clear, sodium and water depletion appear to provide a basis for its antihypertensive effect.
What is the most important information I should know about Edarbyclor?
- Edarbyclor can cause harm or death to your unborn baby.
- Talk to your doctor about other ways to lower your blood pressure if you plan to become pregnant.
- If you become pregnant while taking Edarbyclor, tell your doctor right away. Your doctor may switch you to a different medicine to treat your high blood pressure.
Who should not take Edarbyclor?
Do not take Edarbyclor if you:
- make less urine because of kidney problems
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Edarbyclor?
Before you take Edarbyclor, tell your doctor if you:
- have been told that you have abnormal body salt (electrolytes) levels in your blood
- have liver or kidney problems
- have heart problems or stroke
- are vomiting or have diarrhea
- have gout
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. See “What is the most important information I should know about Edarbyclor?”
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Edarbyclor passes into your breast milk. You and your doctor should decide if you will take Edarbyclor or breastfeed. You should not do both. Talk with your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take Edarbyclor.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- other medicines used to treat your high blood pressure or heart problem
- water pills (diuretics)
- lithium carbonate (Lithobid), lithium citrate
- digoxin (Lanoxin)
Ask your doctor if you are not sure if you are taking a medicine listed above.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your doctor or pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take Edarbyclor?
- Take Edarbyclor exactly as your doctor tells you to.
- Your doctor will tell you how much Edarbyclor to take and when to take it.
- Your doctor may prescribe other medicines for you to take along with Edarbyclor to treat your high blood pressure.
- Edarbyclor can be taken with or without food.
- If you miss a dose, take it later in the same day. Do not take more than 1 dose of Edarbyclor in a day.
- If you take too much Edarbyclor and have symptoms of low blood pressure (hypotension) and dizziness, call your doctor for advice. See “What are the possible side effects of Edarbyclor?”
What are the possible side effects of Edarbyclor?
Edarbyclor may cause serious side effects, including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about Edarbyclor?”
- Low blood pressure (hypotension) and dizziness is most likely to happen if you also:
- take water pills (diuretics)
- are on a low-salt diet
- take other medicines that affect your blood pressure
- sweat a lot
- get sick with vomiting or diarrhea
- do not drink enough fluids
If you feel faint or dizzy, lie down and call your doctor right away. If you pass out (faint) have someone call your doctor or get medical help. Stop taking Edarbyclor.
- Kidney problems. Kidney problems may become worse in people that already have kidney disease. Some people have changes in blood tests for kidney function and may need a lower dose of Edarbyclor or may need to stop treatment with Edarbyclor. During treatment with Edarbyclor, certain people who have severe heart failure, narrowing of the artery to the kidney, or who lose too much body fluid such as with nausea, vomiting, bleeding, or trauma, may develop sudden kidney failure and in rare instances, death.
- Fluid and body salt (electrolyte) problems. Tell your doctor if you get any of the following symptoms:
- dry mouth
- thirst
- lack of energy (lethargic)
- weakness
- drowsiness
- confusion
- seizures
- muscle pain or cramps
- restlessness
- muscle tiredness (fatigue)
- passing very little urine or passing large amounts of urine
- fast or abnormal heartbeat
- nausea and vomiting
- constipation
- Increased uric acid levels in the blood. People who have increased levels of uric acid in the blood may develop gout. If you already have gout, tell your doctor about worsening of your gout symptoms.
The most common side effects of Edarbyclor are:
- dizziness, and
- tiredness
These are not all the possible side effects with Edarbyclor. Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Edarbyclor
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in the Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Edarbyclor for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Edarbyclor to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about Edarbyclor. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about Edarbyclor that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to www.edarbyclor.com or call 1-866-516-4950.
How should I store Edarbyclor?
- Store Edarbyclor at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Store Edarbyclor in the original container that you received from your pharmacist or doctor. Do not put Edarbyclor into a different container.
- Keep the container closed tightly, and keep Edarbyclor out of the light.
Keep Edarbyclor and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Edarbyclor?
Active ingredients: azilsartan medoxomil and chlorthalidone
Inactive ingredients: mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, fumaric acid, sodium hydroxide, hydroxypropyl cellulose, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, hypromellose 2910, talc, titanium dioxide, ferric oxide red, polyethylene glycol 8000, and printing ink gray F1.
Label
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 40 MG/12.5 MG TABLET BOTTLE LABEL
- NDC 60631-412-30
30 Tablets - edarbyclor
- Azilsartan Medoxomil and
Chlorthalidone Tablets - 40 mg*/12.5 mg
- Rx Only
- *Each tablet contains:
42.68 mg azilsartan kamedoxomil
(equivalent to 40 mg
azilsartan medoxomil) and
12.5 mg chlorthalidone. - Dispense
and store
in original
container.

![]()
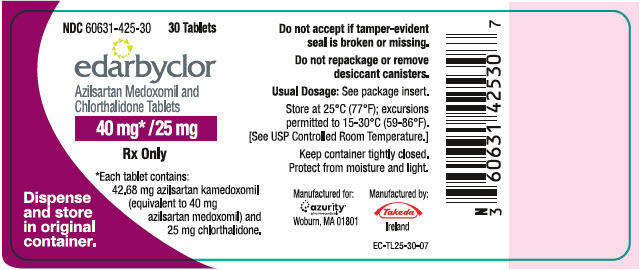
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 40 MG/25 MG TABLET BOTTLE LABEL
- NDC 60631-425-30
30 Tablets - edarbyclor
- Azilsartan Medoxomil and
Chlorthalidone Tablets - 40 mg* /25 mg
- Rx Only
- *Each tablet contains:
42.68 mg azilsartan kamedoxomil
(equivalent to 40 mg
azilsartan medoxomil) and
25 mg chlorthalidone. - Dispense
and store
in original
container.
SRC: NLM .
