Duetact
Generic name: glimepiride and pioglitazone
Drug class: Antidiabetic combinations
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Duetact?
Duetact is a prescription medicine used with diet and exercise to improve blood sugar (glucose) control in adults with type 2 diabetes.
Duetact contains 2 prescription diabetes medicines called pioglitazone (ACTOS) and glimepiride, a sulfonylurea.
Duetact is not for people with type 1 diabetes.
Duetact is not for people with diabetic ketoacidosis (increased ketones in your blood or urine).
It is not known if Duetact is safe and effective in children under the age of 18. Duetact is not recommended for use in children.
Description
DUETACT tablets are a thiazolidinedione and a sulfonylurea combination product that contains two oral antihyperglycemic agents: pioglitazone and glimepiride. The concomitant use of pioglitazone and a sulfonylurea, the class of drugs that includes glimepiride, has been previously approved based on clinical trials in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on a sulfonylurea. Additional efficacy and safety information about pioglitazone and glimepiride monotherapies may be found in the prescribing information for each individual drug.
Pioglitazone is an oral antidiabetic medication.
Pioglitazone [(±)-5-[[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-2,4-] thiazolidinedione monohydrochloride contains one asymmetric carbon, and the compound is synthesized and used as the racemic mixture. The two enantiomers of pioglitazone interconvert in vivo. No differences were found in the pharmacologic activity between the two enantiomers. The structural formula is as shown:
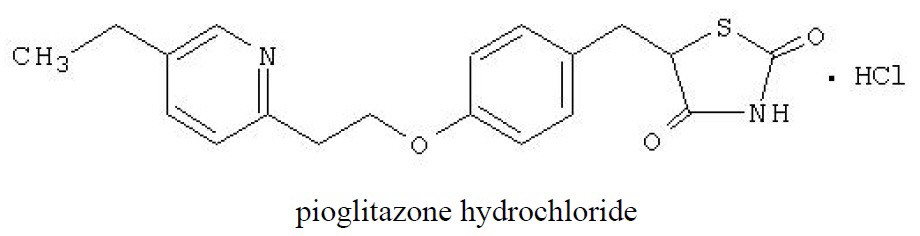
Pioglitazone hydrochloride is an odorless, white crystalline powder that has a molecular formula of C19H20N2O3S•HCl and a molecular weight of 392.90 daltons. It is soluble in N,N‑dimethylformamide, slightly soluble in anhydrous ethanol, very slightly soluble in acetone and acetonitrile, practically insoluble in water, and insoluble in ether.
Glimepiride is an oral sulfonylurea chemically identified as 1-[[p-[2-(3-ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-3-pyrroline-1-carboxamido)ethyl]phenyl]sulfonyl]-3-(trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)-urea (C24H34N4O5S) with a molecular weight of 490.62. Glimepiride is a white to yellowish-white, crystalline, odorless to practically odorless powder and is practically insoluble in water. The structural formula is:
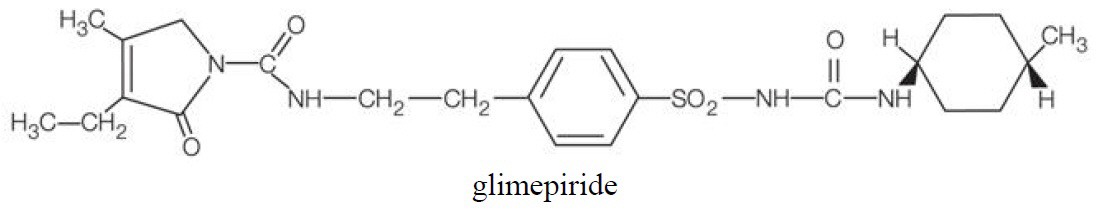
DUETACT is available as a tablet for oral administration containing 30 mg pioglitazone (as the base) with 2 mg glimepiride (30 mg/2 mg) or 30 mg pioglitazone (as the base) with 4 mg glimepiride (30 mg/4 mg) formulated with the following excipients: croscarmellose sodium NF, lactose monohydrate NF, magnesium stearate NF, hydroxypropyl cellulose NF, polysorbate 80 NF, and microcrystalline cellulose NF.
Mechanism of Action
DUETACT combines 2 antihyperglycemic agents with different mechanisms of action to improve glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: pioglitazone, a member of the thiazolidinedione class, and glimepiride, a member of the sulfonylurea class. Thiazolidinediones are insulin-sensitizing agents that act primarily by enhancing peripheral glucose utilization, whereas sulfonylureas are insulin secretagogues that act primarily by stimulating release of insulin from functioning pancreatic beta cells.
What is the most important information I should know about Duetact?
Duetact can cause serious side effects, including new or worse heart failure.
- Pioglitazone, one of the medicines in Duetact, can cause your body to keep extra fluid (fluid retention), which leads to swelling (edema) and weight gain. Extra body fluid can make some heart problems worse or lead to heart failure. Heart failure means your heart does not pump blood well enough
- Do not take Duetact if you have severe heart failure
- If you have heart failure with symptoms (such as shortness of breath or swelling), even if these symptoms are not severe, Duetact may not be right for you
Call your doctor right away if you have any of the following:
- swelling or fluid retention, especially in the ankles or legs
- shortness of breath or trouble breathing, especially when you lie down
- an unusually fast increase in weight
- unusual tiredness
Duetact can have other serious side effects. See “What are the possible side effects of Duetact?”
Who should not take Duetact?
See “What is the most important information I should know about Duetact?”
Do not take Duetact if you:
- have severe heart failure
- are allergic to any of the ingredients in Duetact. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in Duetact
- have a condition called diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetic ketoacidosis should be treated with insulin
Talk to your doctor before taking Duetact if you have any of these conditions.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Duetact?
Before you take Duetact, tell your doctor if you:
- have heart failure
- have kidney problems
- have type 1 (“juvenile”) diabetes or had diabetic ketoacidosis
- have a type of diabetic eye disease that causes swelling in the back of the eye (macular edema)
- have liver problems
- have or have had cancer of the bladder
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Duetact can harm your unborn baby. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant about the best way to control your blood glucose levels while pregnant
- are a premenopausal woman (before the “change of life”), who does not have periods regularly or at all. Duetact may increase your chance of becoming pregnant. Talk to your doctor about birth control choices while taking Duetact. Tell your doctor right away if you become pregnant while taking Duetact
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Duetact passes into your milk and if it can harm your baby. Talk to your doctor about the best way to control your blood glucose levels while breastfeeding
- have G6PD deficiency (an inherited condition where you don’t produce enough of the enzyme (G6PD). Taking glimepiride, one of the medicines in Duetact, with this condition may cause your red blood cells to be destroyed too quickly (hemolytic anemia)
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take including prescription and over the counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Duetact and some of your other medicines can affect each other. You may need to have your dose of Duetact or certain other medicines changed.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your doctor and pharmacist before you start a new medicine. They will tell you if it is okay to take Duetact with other medicines.
How should I take Duetact?
- Take Duetact exactly as your doctor tells you to take it
- Your doctor may change your dose of Duetact. Do not change your dose unless your doctor tells you to
- Duetact may be prescribed alone or with other diabetes medicines. This will depend on how well your blood sugar is controlled
- Take Duetact one time each day with the first main meal
- If you take colesevelam, a medicine used to lower your cholesterol, take your Duetact at least 4 hours before you take your colesevelam.
- If you miss a dose of Duetact, take your next dose as prescribed unless your doctor tells you differently. Do not take two doses at one time the next day
- If you take too much Duetact, call your doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away
- If your body is under stress such as from a fever, infection, accident, or surgery, the dose of your diabetes medicines may need to be changed. Call your doctor right away
- Stay on your diet and exercise programs and test your blood sugar regularly while taking Duetact
- Your doctor should do certain blood tests before you start and while you take Duetact
- Your doctor should also do hemoglobin A1C testing to check how well your blood sugar is controlled with Duetact
- Your doctor should check your eyes regularly while you take Duetact
What are the possible side effects of Duetact?
Duetact may cause serious side effects including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about Duetact?”
- low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). This can happen if you skip meals, if you also use another medicine that lowers blood sugar, or if you have certain medical problems. Lightheadedness, dizziness, shakiness, or hunger may happen if your blood sugar is too low. Severe low blood sugar can cause unconsciousness (passing out), seizures, and death. Call your doctor if low blood sugar levels are a problem for you
- liver problems. Call your doctor right away if you have:
- bladder cancer. There may be an increased chance of having bladder cancer when you take Duetact. You should not take Duetact if you are receiving treatment for bladder cancer. Tell your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms of bladder cancer:
- blood or a red color in your urine
- an increased need to urinate
- pain while you urinate
- broken bones (fractures). Usually in the hand, upper arm, or foot in women. Talk to your doctor for advice on how to keep your bones healthy.
- diabetic eye disease with swelling in the back of the eye (macular edema). Tell your doctor right away if you have any changes in your vision. Your doctor should check your eyes regularly
- release of an egg from an ovary in a woman (ovulation) leading to pregnancy. Ovulation may happen when premenopausal women who do not have regular monthly periods take Duetact. This can increase your chance of getting pregnant
The most common side effects of Duetact include:
- cold-like symptoms (upper respiratory tract infection)
- headache
- sinus infection
- diarrhea
- nausea
- muscle pain
- sore throat
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the side effects of Duetact. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Duetact
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Duetact for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Duetact to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about Duetact. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about Duetact that is written for healthcare professionals. For more information, go to www.duetact.com or call 1-877-825-3327.
How should I store Duetact?
- Store Duetact at 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C). Keep Duetact in the original container to protect from light
- Keep the Duetact bottle tightly closed and keep tablets dry
- Keep Duetact and all medicines out of the reach of children
What are the ingredients in Duetact?
Active ingredients: pioglitazone and glimepiride
Inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, hydroxypropyl cellulose, polysorbate 80, and microcrystalline cellulose
Label
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 30 MG/2 MG TABLET BOTTLE LABEL
- NDC 64764-302-30
30 Tablets - duetact
pioglitazone 30 mg and
glimepiride 2 mg tablets - Each tablet contains pioglitazone
hydrochloride equivalent to 30 mg
pioglitazone and 2 mg glimepiride. - Dispense with Medication Guide
available in package insert or at
www.duetact.com - Takeda
Rx Only 
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 30 MG/4 MG TABLET BOTTLE LABEL
- NDC 64764-304-30
30 Tablets - duetact
pioglitazone 30 mg and
glimepiride 4 mg tablets - Each tablet contains pioglitazone
hydrochloride equivalent to 30 mg
pioglitazone and 4 mg glimepiride. - Dispense with Medication Guide
available in package insert or at
www.duetact.com - Takeda
Rx Only

SRC: NLM .
