Depakote
Generic name: divalproex sodium
Drug class: Fatty acid derivative anticonvulsants
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Depakote?
Depakote comes in different dosage forms with different usages.
Depakote Tablets are a prescription medicine used to treat manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder alone or with other medicines to treat complex partial seizures in adults and children 10 years of age and older, simple and complex absence seizures, with or without other seizure types to prevent migraine headaches
Description
Divalproex sodium is a stable co-ordination compound comprised of sodium valproate and valproic acid in a 1:1 molar relationship and formed during the partial neutralization of valproic acid with 0.5 equivalent of sodium hydroxide. Chemically it is designated as sodium hydrogen bis(2-propylpentanoate). Divalproex sodium has the following structure:
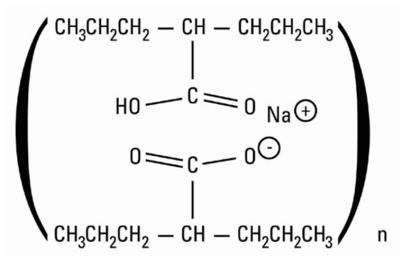
Divalproex sodium occurs as a white powder with a characteristic odor.
Depakote tablets are for oral administration. Depakote tablets are supplied in three dosage strengths containing divalproex sodium equivalent to 125 mg, 250 mg, or 500 mg of valproic acid.
Inactive Ingredients
Depakote tablets: cellulosic polymers, diacetylated monoglycerides, povidone, pregelatinized starch (contains corn starch), silica gel, talc, titanium dioxide, and vanillin.
In addition, individual tablets contain:
125 mg tablets: FD&C Blue No. 1 and FD&C Red No. 40.
250 mg tablets: FD&C Yellow No. 6 and iron oxide.
500 mg tablets: D&C Red No. 30, FD&C Blue No. 2, and iron oxide.
Mechanism of Action
Divalproex sodium dissociates to the valproate ion in the gastrointestinal tract. The mechanisms by which valproate exerts its therapeutic effects have not been established. It has been suggested that its activity in epilepsy is related to increased brain concentrations of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
What is the most important information I should know about Depakote?
Do not stop taking Depakote without first talking to your healthcare provider.
Stopping Depakote suddenly can cause serious problems.
Depakote can cause serious side effects, including:
1. Serious liver damage that can cause death, especially in children younger than 2 years old. The risk of getting this serious liver damage is more likely to happen within the first 6 months of treatment.
Call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms:
In some cases, liver damage may continue despite stopping the drug.
- nausea or vomiting that does not go away
- loss of appetite
- pain on the right side of your stomach (abdomen)
- dark urine
- swelling of your face
- yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes
2. Depakote may harm your unborn baby.
- If you take Depakote during pregnancy for any medical condition, your baby is at risk for serious birth defects that affect the brain and spinal cord and are called spina bifida or neural tube defects. These defects occur in 1 to 2 out of every 100 babies born to mothers who use this medicine during pregnancy. These defects can begin in the first month, even before you know you are pregnant. Other birth defects that affect the structures of the heart, head, arms, legs, and the opening where the urine comes out (urethra) on the bottom of the penis can also happen. Decreased hearing or hearing loss can also happen.
- Birth defects may occur even in children born to women who are not taking any medicines and do not have other risk factors.
- Taking folic acid supplements before getting pregnant and during early pregnancy can lower the chance of having a baby with a neural tube defect.
- If you take Depakote during pregnancy for any medical condition, your child is at risk for having lower IQ and may be at risk for developing autism or attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
- There may be other medicines to treat your condition that have a lower chance of causing birth defects, decreased IQ, or other disorders in your child.
- Women who are pregnant must not take Depakote to prevent migraine headaches.
- All women of childbearing age (including girls from the start of puberty) should talk to their healthcare provider about using other possible treatments instead of Depakote. If the decision is made to use Depakote, you should use effective birth control (contraception).
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant while taking Depakote. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will continue to take Depakote while you are pregnant.
- Pregnancy Registry: If you become pregnant while taking Depakote, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the North American Antiepileptic Drug Pregnancy Registry. You can enroll in this registry by calling toll-free 1-888-233-2334 or by visiting the website, http://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org/. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy.
3. Inflammation of your pancreas that can cause death.
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms:
- severe stomach pain that you may also feel in your back
- nausea or vomiting that does not go away
4. Like other antiepileptic drugs, Depakote may cause suicidal thoughts or actions in a very small number of people, about 1 in 500.
Call a healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- attempts to commit suicide
- new or worse depression
- new or worse anxiety
- feeling agitated or restless
- panic attacks
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- new or worse irritability
- acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- acting on dangerous impulses
- an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
How can I watch for early symptoms of suicidal thoughts and actions?
- Pay attention to any changes, especially sudden changes in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings.
- Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider as scheduled.
Call your healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you are worried about symptoms.
Do not stop Depakote without first talking to a healthcare provider. Stopping Depakote suddenly can cause serious problems. Stopping a seizure medicine suddenly in a patient who has epilepsy can cause seizures that will not stop (status epilepticus).
Suicidal thoughts or actions can be caused by things other than medicines. If you have suicidal thoughts or actions, your healthcare provider may check for other causes.
Who should not take Depakote?
Do not take Depakote if you:
- have liver problems
- have or think you have a genetic liver problem caused by a mitochondrial disorder (e.g. Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome)
- are allergic to divalproex sodium, valproic acid, sodium valproate or any of the ingredients in Depakote. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in Depakote.
- have a genetic problem called urea cycle disorder
- are taking it to prevent migraine headaches and are either pregnant or may become pregnant because you are not using effective birth control (contraception)
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Depakote?
Before you take Depakote, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have a genetic liver problem caused by a mitochondrial disorder (e.g. Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome)
- drink alcohol
- are pregnant or breastfeeding. Depakote can pass into breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you take Depakote.
- have or have had depression, mood problems, or suicidal thoughts or behavior
- have any other medical conditions
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, herbal supplements and medicines that you take for a short period of time.
Taking Depakote with certain other medicines can cause side effects or affect how well they work. Do not start or stop other medicines without talking to your healthcare provider.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine.
How should I take Depakote?
- Take Depakote exactly as your healthcare provider tells you. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much Depakote to take and when to take it.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose.
- Do not change your dose of Depakote without talking to your healthcare provider.
- Do not stop taking Depakote without first talking to your healthcare provider. Stopping Depakote suddenly can cause serious problems.
- Swallow Depakote tablets whole. Do not crush or chew Depakote tablets. Tell your healthcare provider if you cannot swallow Depakote whole. You may need a different medicine.
- If you take too much Depakote call your healthcare provider or local Poison Control Center right away.
What should I avoid while taking Depakote?
- Depakote can cause drowsiness and dizziness. Do not drink alcohol or take other medicines that make you sleepy or dizzy while taking Depakote until you talk with your doctor. Taking Depakote with alcohol or drugs that cause sleepiness or dizziness may make your sleepiness or dizziness worse.
- Do not drive a car or operate dangerous machinery until you know how Depakote affects you. Depakote can slow your thinking and motor skills.
What are the possible side effects of Depakote?
- See “What is the most important information I should know about Depakote?”
Depakote can cause serious side effects including:
- Bleeding problems: red or purple spots on your skin, bruising, pain and swelling into your joints due to bleeding or bleeding from your mouth or nose.
- High ammonia levels in your blood: feeling tired, vomiting, changes in mental status.
- Low body temperature (hypothermia): drop in your body temperature to less than 95°F, feeling tired, confusion, coma.
- Allergic (hypersensitivity) reactions: fever, skin rash, hives, sores in your mouth, blistering and peeling of your skin, swelling of your lymph nodes, swelling of your face, eyes, lips, tongue, or throat, trouble swallowing or breathing.
- Drowsiness or sleepiness in the elderly. This extreme drowsiness may cause you to eat or drink less than you normally would. Tell your doctor if you are not able to eat or drink as you normally do. Your doctor may start you at a lower dose of Depakote.
Call your healthcare provider right away, if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The common side effects of Depakote include:
- nausea
- headache
- sleepiness
- vomiting
- weakness
- tremor
- dizziness
- stomach pain
- blurry vision
- double vision
- diarrhea
- increased appetite
- weight gain
- hair loss
- loss of appetite
- problems with walking or coordination
These are not all of the possible side effects of Depakote. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Depakote
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Depakote for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Depakote to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about Depakote. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Depakote that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to www.rxabbvie.com or call 1-800-633-9110.
How should I store Depakote?
- Store Depakote Delayed Release Tablets below 86°F (30°C).
Keep Depakote and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Depakote?
Active ingredient: divalproex sodium
Inactive ingredients: cellulosic polymers, diacetylated monoglycerides, povidone, pregelatinized starch (contains corn starch), silica gel, talc, titanium dioxide, and vanillin.
- Individual tablets also contain:
125 mg tablets: FD&C Blue No. 1 and FD&C Red No. 40,
250 mg tablets: FD&C Yellow No. 6 and iron oxide,
500 mg tablets: D&C Red No. 30, FD&C Blue No. 2, and iron oxide.
Label
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- NDC 0074-7325-13
- 100 Tablets
- DEPAKOTE®
- DIVALPROEX SODIUM DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS
- 125 mg Valproic Acid Activity
- Dispense the accompanying Medication Guide to each patient.
- Rx only abbvie


PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- NDC 0074-6214-53
- No image available
- NDC 0074-6214-13
- 100 Tablets
- DEPAKOTE®
- DIVALPROEX SODIUM DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS
- 250 mg Valproic Acid Activity
- Do not accept if seal over bottle opening is broken or missing.
- Dispense the accompanying Medication Guide to each patient.
- Rx only abbvie

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- NDC 0074-6215-13
- 100 Tablets
- DEPAKOTE®
- DIVALPROEX SODIUM DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS
- 500 mg Valproic Acid Activity
- Dispense the accompanying Medication Guide to each patient.
- Rx only abbvie


SRC: NLM .
