Femring
Generic name: estradiol vaginal (systemic)
Drug class: Estrogens
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Femring?
Femring is a prescription vaginal ring that contains estradiol (an estrogen hormone). Femring should be removed after 90 days of continuous use. If you and your healthcare provider decide you should continue using Femring, a new ring can be inserted in your vagina.
Femring is used after menopause to reduce moderate to severe hot flushes
Estrogens are hormones made by a woman’s ovaries. The ovaries normally stop making estrogens when a woman is between 45 and 55 years old. This drop in body estrogen levels causes the “change of life” or menopause, the end of monthly menstrual periods. Sometimes both ovaries are removed during an operation before natural menopause takes place. The sudden drop in estrogen levels causes “surgical menopause”.
When estrogen levels begin dropping, some women get very uncomfortable symptoms, such as feelings of warmth in the face, neck, and chest, or sudden intense episodes of heat and sweating (“hot flashes” or “hot flushes”). In some women the symptoms are mild, and they will not need to take estrogens. In other women, symptoms can be more severe.
It is also used to treat moderate to severe menopausal changes in and around the vagina
You and your healthcare provider should talk regularly about whether you still need treatment with Femring to control these problems. If you use Femring only to treat your menopausal changes in and around your vagina, talk with your healthcare provider about whether a topical vaginal product would be better for you.
You and your healthcare provider should talk regularly about whether you still need treatment with Femring.
Description
Femring (estradiol acetate vaginal ring) is an off-white, soft, flexible ring with a central core containing estradiol acetate.
Femring is made of cured silicone elastomer composed of dimethyl polysiloxane silanol, silica (diatomaceous earth), normal propyl orthosilicate, stannous octoate; barium sulfate and estradiol acetate. The rings have the following dimensions: outer diameter 56 mm, cross-sectional diameter 7.6 mm, core diameter 2 mm.
Femring is available in two strengths: Femring 0.05 mg/day has a central core that contains 12.4 mg of estradiol acetate, which releases at a rate equivalent to 0.05 mg of estradiol per day for 3 months. Femring 0.10 mg/day has a central core that contains 24.8 mg of estradiol acetate, which releases at a rate equivalent to 0.10 mg of estradiol per day for 3 months.
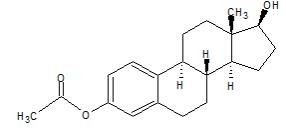
Estradiol acetate is chemically described as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol-3-acetate. The molecular formula of estradiol acetate is C 20H 26O 3 and the molecular weight of estradiol acetate is 314.42.
Mechanism of Action
Endogenous estrogens are largely responsible for the development and maintenance of the female reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics. Although circulating estrogens exist in a dynamic equilibrium of metabolic interconversions, estradiol is the principal intracellular human estrogen and is substantially more potent than its metabolites, estrone and estriol, at the receptor level.
The primary source of estrogen in normally cycling adult women is the ovarian follicle, which secretes 70 to 500 mcg of estradiol daily, depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. After menopause, most endogenous estrogen is produced by conversion of androstenedione, which is secreted by the adrenal cortex, to estrone in the peripheral tissues. Thus, estrone and the sulfate conjugated form, estrone sulfate, are the most abundant circulating estrogens in postmenopausal women.
Estrogens act through binding to nuclear receptors in estrogen-responsive tissues. To date, two estrogen receptors have been identified. These vary in proportion from tissue to tissue.
Circulating estrogens modulate the pituitary secretion of the gonadotropins, luteinizing hormone (LH) and FSH through a negative feedback mechanism. Estrogens act to reduce the elevated levels of these hormones seen in postmenopausal women.
What is the most important information I should know about Femring?
- Using estrogen-alone may increase your chance of getting cancer of the uterus (womb). Report any unusual vaginal bleeding right away while you are using Femring. Vaginal bleeding after menopause may be a warning sign of cancer of the uterus (womb). Your healthcare provider should check any unusual vaginal bleeding to find out the cause.
- Do not use estrogen-alone to prevent heart disease, heart attacks, strokes or dementia (decline in brain function).
- Using estrogen-alone may increase your chances of getting strokes or blood clots.
- Using estrogen-alone may increase your chance of getting dementia, based on a study of women 65 years of age or older.
- Do not use estrogens with progestins to prevent heart disease, heart attacks, strokes or dementia.
- Using estrogens with progestins may increase your chances of getting heart attacks, strokes, breast cancer, or blood clots.
- Using estrogens with progestins may increase your chance of getting dementia, based on a study of women 65 years of age or older.
- You and your healthcare provider should talk regularly about whether you still need treatment with Femring.
Who should not use Femring?
Do not start using Femring if you:
- have unusual vaginal bleeding
Vaginal bleeding after menopause may be a warning sign of cancer of the uterus (womb). Your healthcare provider should check any unusual vaginal bleeding to find out the cause.
- currently have or have had certain cancers
Estrogens may increase the chances of getting certain types of cancers, including cancer of the breast and uterus. If you have or have had cancer, talk with your healthcare provider about whether you should use Femring.
- had a stroke or heart attack
- currently have or have had blood clots
- currently have or have had liver problems
- have been diagnosed with a bleeding disorder
- are allergic to Femring or any of its ingredients
See the list of ingredients in Femring at the end of this guide. - think you may be pregnant
Femring is not for pregnant women. If you think you may be pregnant, you should have a pregnancy test and know the results. Do not use Femring if the test is positive and talk to your healthcare provider.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before using Femring?
Before you use Femring, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have any unusual vaginal bleeding
Vaginal bleeding after menopause may be a warning sign of cancer of the uterus (womb). Your healthcare provider should check any unusual vaginal bleeding to find out the cause. - have any problems with your vagina or cervix (lower end of your womb)
Your healthcare provider may need to check you more carefully if your cervix, bladder, or rectum have fallen out of their normal position and into the vagina or through the opening of the vagina. This may make it more difficult for you to keep Femring in place in your vagina. - have any other medical conditions
Your healthcare provider may need to check you more carefully if you have certain conditions such as asthma (wheezing), epilepsy (seizures), diabetes, migraine, endometriosis, lupus, angioedema (swelling of face and tongue) or problems with your heart, liver, thyroid, kidneys, or have high calcium levels in your blood. - are going to have surgery or will be on bed rest
Your healthcare provider will let you know if you need to stop using Femring. - are breastfeeding
The hormones in Femring can pass into your breast milk.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Some medicines may affect how Femring works. Femring may also affect how your other medicines work. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use Femring?
For detailed instructions, see the step-by-step instructions that come with Femring.
- Use Femring exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Femring is inserted into your vagina by you.
- Femring should stay in your vagina for 90 days.
- After 90 days Femring should be removed. If you and your healthcare provider decide you should continue using Femring, a new Femring can be inserted.
- You and your healthcare provider should talk regularly (every 3 to 6 months) about the dose of medicine you are using and whether you still need treatment with Femring.
What are the possible problems you may have when using Femring?
- Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
Toxic shock syndrome is a rare but serious illness caused by a bacterial infection that may cause death. Remove your Femring immediately and call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms: - attachment to your vaginal wall
Contact your healthcare provider right away if you have difficulty removing Femring. - accidental placement in your bladder
What are the possible side effects of Femring?
Side effects are grouped by how serious they are and how often they happen when you are treated.
Serious, but less common side effects include:
- heart attack
- stroke
- blood clots
- dementia
- breast cancer
- cancer of the lining of the uterus (womb)
- cancer of the ovary
- high blood pressure
- high blood sugar
- gallbladder disease
- liver problems
- changes in your thyroid hormone levels
- enlargement of benign tumors of the uterus (“fibroids”)
Call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following warning signs, or any other unusual symptoms that concern you:
- new breast lumps
- unusual vaginal bleeding
- changes in vision or speech
- sudden new severe headaches
- severe pains in your chest or legs with or without shortness of breath, weakness and fatigue
Less serious, but common side effects include:
- headache
- breast tenderness or pain
- irregular vaginal bleeding or spotting
- stomach or abdominal cramps, bloating
- nausea and vomiting
- hair loss
- fluid retention
- vaginal yeast infection
- reactions from inserting Femring such as burning, irritation, and itching
These are not all the possible side effects of Femring. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effects that bother you or does not go away.
You may report side effects to Millicent at 1-877-810-2101 or to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
What can I do to lower my chances of a serious side effect with Femring?
- Talk with your healthcare provider regularly about whether you should continue using Femring.
- If you have a uterus, talk with your healthcare provider about whether the addition of a progestin is right for you. The addition of a progestin is generally recommended for a woman with a uterus to reduce the chance of getting cancer of the uterus (womb). See your healthcare provider right away if you develop vaginal bleeding while using Femring.
- Have a pelvic exam, breast exam and mammogram (breast x-ray) every year unless your healthcare provider tells you something else.
- If members of your family have had breast cancer or if you have ever had breast lumps or an abnormal mammogram (breast x-ray), you may need to have breast exams more often.
- If you have high blood pressure, high cholesterol (fat in the blood), diabetes, are overweight, or if you use tobacco, you may have a higher chance for getting heart disease.
Ask your healthcare provider for ways of lowering your chances for getting heart disease.
General information about the safe and effective use of Femring
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not use Femring for conditions for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Femring to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
Contact with blood may cause discoloration of Femring during use. This does not affect the way in which Femring releases medicine to control your menopausal symptoms. Call your health care provider right away if you have unusual vaginal bleeding.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about Femring. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider or pharmacist. You can ask for information about Femring that is written for health professionals. You can get more information by calling the toll free number 1-877-810-2101.
How should I store Femring?
- Store at room temperature 68º F to 77º F (20º C to 25º C).
Keep Femring and all other medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Femring?
Active ingredient: estradiol
Inactive ingredients: cured silicone elastomer composed of dimethyl polysiloxane silanol, silica (diatomaceous earth), normal propyl orthosilicate, stannous octoate; and barium sulfate. There are no coloring agents in Femring.
Label
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- NDC 72495-201-05
- Femring®(estradiol acetate vaginal ring)
0.05 mg/day
Rx only

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- NDC 72495-202-10
- Femring®
- (estradiol acetate vaginal ring)0.10 mg/day
Rx only

SRC: NLM .
