Symtuza
Generic name: cobicistat, darunavir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir
Drug class: Antiviral combinations
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Symtuza?
Symtuza is a prescription medicine that is used without other antiretroviral medicines to treat Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) infection in adults and in children who weigh at least 88 pounds (40 kg) who have not received anti-HIV-1 medicines in the past, or when their healthcare provider determines that they meet certain requirements.
HIV-1 is the virus that causes Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS).
Symtuza contains the prescription medicines darunavir, cobicistat, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide.
It is not known if Symtuza is safe and effective in children weighing less than 88 pounds (40 kg).
Description
SYMTUZA® (darunavir, cobicistat, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide) is a fixed-dose combination tablet.
- Darunavir is an inhibitor of the HIV-1 protease.
- Cobicistat is a mechanism-based inhibitor of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes of the CYP3A family.
- Emtricitabine, a synthetic nucleoside analog of cytidine, is an HIV nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor (HIV NRTI).
- Tenofovir alafenamide, an HIV NRTI, is converted in vivo to tenofovir, an acyclic nucleoside phosphonate (nucleotide) analog of adenosine 5′-monophosphate.
SYMTUZA tablets are for oral administration. Each tablet contains darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 800 mg of darunavir, 150 mg of cobicistat, 200 mg of emtricitabine, and 11.2 mg of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate equivalent to 10 mg of tenofovir alafenamide. The tablets include the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. The tablets are film-coated with a coating material containing polyethylene glycol (macrogol), polyvinyl alcohol (partially hydrolyzed), talc, titanium dioxide, and yellow ferric oxide.
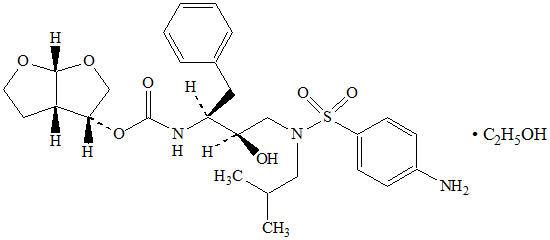
Darunavir: Darunavir, in the form of darunavir ethanolate, has the following chemical name: [(1S,2R)-3-[[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]-2-hydroxy-1-(phenylmethyl)propyl]-carbamic acid (3R,3aS,6aR)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl ester monoethanolate. Its molecular formula is C27H37N3O7S ∙ C2H5OH and its molecular weight is 593.73. Darunavir ethanolate has the following structural formula:
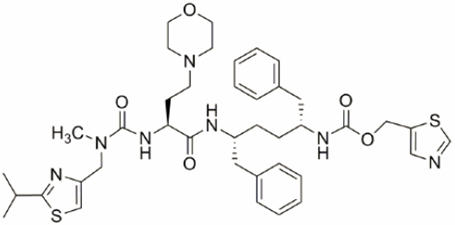
Cobicistat: Cobicistat is adsorbed onto silicon dioxide. The chemical name for cobicistat is 1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethyl[(2R,5R)-5-{[(2S)-2-[(methyl{[2-(propan-2-yl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methyl}carbamoyl)amino]-4-(morpholin-4yl)butanoyl]amino}-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl]carbamate. It has a molecular formula of C40H53N7O5S2 and a molecular weight of 776.02. It has the following structural formula:
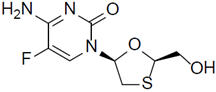
Emtricitabine: The chemical name of emtricitabine is 4-amino-5-fluoro-1-(2R-hydroxymethyl-[1,3]-oxathiolan-5S-yl)-(1H)-pyrimidin-2-one. Emtricitabine is the (-)enantiomer of a thio analog of cytidine, which differs from other cytidine analogs in that it has a fluorine in the 5 position. Emtricitabine has a molecular formula of C8H10FN3O3S and a molecular weight of 247.24. It has the following structural formula:
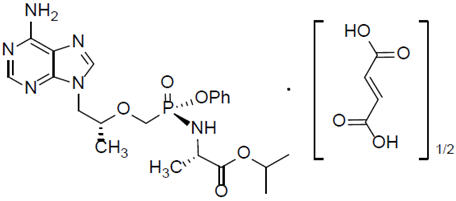
Tenofovir alafenamide: The chemical name of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate drug substance is L-alanine, N-[(S)-[[(1R)-2-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-1-methylethoxy]methyl]phenoxyphosphinyl]-,1-methylethyl ester, (2E)-2-butenedioate (2:1). Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate has a molecular formula of C21H29O5N6P∙½(C4H4O4) and a formula weight of 534.50. It has the following structural formula:
Mechanism of Action
SYMTUZA is a fixed-dose combination of antiretroviral drugs darunavir (plus the CYP3A inhibitor cobicistat), emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide
What is the most important information I should know about Symtuza?
Symtuza can cause serious side effects, including:
- Worsening of Hepatitis B virus infection (HBV). Your healthcare provider will test you for HBV before starting treatment with Symtuza. If you have HBV infection and take Symtuza, your HBV may get worse (flare-up) if you stop taking Symtuza. A “flare-up” is when your HBV infection suddenly returns in a worse way than before.
- Do not stop taking Symtuza without first talking to your healthcare provider.
- Do not run out of Symtuza. Refill your prescription or talk to your healthcare provider before your Symtuza is all gone.
- If you stop taking Symtuza, your healthcare provider will need to check your health often and do blood tests regularly for several months to check your HBV infection, or give you a medicine to treat your HBV infection. Tell your healthcare provider about any new or unusual symptoms you may have after you stop taking Symtuza.
- Change in liver enzymes. People with a history of hepatitis B or C virus infection or who have certain liver enzyme changes may have an increased risk of developing new or worsening liver problems during treatment with Symtuza. Liver problems can also happen during treatment with Symtuza in people without a history of liver disease. Your healthcare provider may need to do tests to check your liver enzymes before and during treatment with Symtuza.
- Severe liver problems. In rare cases, severe liver problems can happen that can lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get these symptoms: skin or the white part of your eyes turns yellow, dark “tea-colored” urine, light-colored stools, loss of appetite for several days or longer, nausea, vomiting, or stomach-area pain.
- Symtuza may cause severe or life-threatening skin reactions or rash. Sometimes these skin reactions and skin rashes can become severe and require treatment in a hospital. Call your healthcare provider right away if you develop a rash. Stop taking Symtuza and call your healthcare provider right away if you develop any skin changes with symptoms below:
- fever
- tiredness
- muscle or joint pain
- blisters or skin lesions
- mouth sores or ulcers
- red or inflamed eyes, like “pink eye” (conjunctivitis)
See “What are the possible side effects of Symtuza?” for more information about side effects.
Who should not take Symtuza?
Do not take Symtuza with any of the following medicines:
- alfuzosin
- carbamazepine
- cisapride
- colchicine, if you have liver or kidney problems
- dronedarone
- elbasvir and grazoprevir
- ergot-containing medicines, such as:
- dihydroergotamine
- ergotamine tartrate
- methylergonovine
- ivabradine
- lomitapide
- lovastatin or a product that contains lovastatin
- lurasidone
- midazolam, when taken by mouth
- naloxegol
- phenobarbital
- phenytoin
- pimozide
- ranolazine
- rifampin
- sildenafil, when used for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH)
- simvastatin or a product that contains simvastatin
- St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum), or a product that contains St. John’s wort
- triazolam
Serious problems can happen if you take any of these medicines with Symtuza.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Symtuza?
Before taking Symtuza, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have liver problems, including hepatitis B or hepatitis C
- have kidney problems
- are allergic to sulfa (sulfonamide)
- have diabetes
- have hemophilia
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- It is not known if Symtuza will harm your unborn baby.
- Symtuza should not be used during pregnancy because you may not have enough Symtuza in your body during pregnancy.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you become pregnant while taking Symtuza. Your healthcare provider will prescribe different medicines if you become pregnant while taking Symtuza.
Pregnancy Registry: There is a pregnancy registry for those who take antiretroviral medicines during pregnancy. The purpose of the registry is to collect information about the health of you and your baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about how you can take part in this registry.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Do not breastfeed if you take Symtuza.
- You should not breastfeed if you have HIV-1 because of the risk of passing HIV to your baby.
- One of the medicines in Symtuza called emtricitabine can pass into your breast milk. It is not known if the other medicines in Symtuza can pass into your breast milk.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Some medicines interact with Symtuza. Keep a list of your medicines to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist.
- You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of medicines that interact with Symtuza.
- Do not start taking a new medicine without telling your healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider can tell you if it is safe to take Symtuza with other medicines.
How should I take Symtuza?
- Take Symtuza exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
- Do not change your dose or stop taking Symtuza without talking to your healthcare provider.
- Take Symtuza 1 time a day with food.
- If you have difficulty swallowing, the tablet may be split using a tablet-cutter. After splitting the tablet, the entire dose (both halves) should then be taken right away.
- Do not miss a dose of Symtuza.
- When your Symtuza supply starts to run low, get more from your healthcare provider or pharmacy. This is very important because the amount of virus in your blood may increase if the medicine is stopped for even a short time. The virus may develop resistance to Symtuza and become harder to treat.
- If you take too much Symtuza, call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What are the possible side effects of Symtuza?
Symtuza may cause serious side effects, including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about Symtuza?”
- Changes in your immune system (Immune Reconstitution Syndrome) can happen when you start taking HIV-1 medicines. Your immune system may get stronger and begin to fight infections that have been hidden in your body for a long time. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you start having new symptoms after starting your HIV-1 medicine.
- New or worse kidney problems, including kidney failure. Your healthcare provider should do blood and urine tests to check your kidneys before you start and while you are taking Symtuza. Your healthcare provider may tell you to stop taking Symtuza if you develop new or worse kidney problems.
- Too much lactic acid in your blood (lactic acidosis). Too much lactic acid is a serious but rare medical emergency that can lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get these symptoms: weakness or being more tired than usual, unusual muscle pain, being short of breath or fast breathing, stomach pain with nausea and vomiting, cold or blue hands and feet, feel dizzy or lightheaded, or a fast or abnormal heartbeat.
- Diabetes and high blood sugar (hyperglycemia). Some people who take protease inhibitors including Symtuza can get high blood sugar, develop diabetes, or your diabetes can get worse. Tell your healthcare provider if you notice an increase in thirst or if you start urinating more often while taking Symtuza.
- Changes in body fat can happen in people who take HIV-1 medicines. The changes may include an increased amount of fat in the upper back and neck (“buffalo hump”), breast, and around the middle of your body (trunk). Loss of fat from the legs, arms, and face may also happen. The exact cause and long-term health effects of these conditions are not known.
- Increased bleeding for hemophiliacs. Some people with hemophilia have increased bleeding with protease inhibitors.
The most common side effects of Symtuza, include:
These are not all of the possible side effects of Symtuza.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Symtuza
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Symtuza for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Symtuza to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about Symtuza that is written for health professionals.
How should I store Symtuza?
- Store Symtuza tablets at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- The Symtuza bottle contains a desiccant and has a child-resistant cap.
- Keep the Symtuza container tightly closed with the desiccant inside of it to protect Symtuza from moisture.
Keep Symtuza out of reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Symtuza?
Active ingredient: darunavir, cobicistat, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. The tablets are film-coated with a coating material containing polyethylene glycol (macrogol), polyvinyl alcohol (partially hydrolyzed), talc, titanium dioxide, and yellow ferric oxide.
Label
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 30 TABLET BOTTLE LABEL
- NDC 59676-800-30
- Symtuza™
(darunavir, cobicistat,
emtricitabine, and tenofovir
alafenamide) tablets - 800 mg / 150 mg /
200 mg / 10 mg - Each tablet contains darunavir
ethanolate equivalent to 800 mg
of darunavir, 150 mg of cobicistat,
200 mg of emtricitabine, and
tenofovir alafenamide fumarate
equivalent to 10 mg of tenofovir
alafenamide. - Rx only
30 Tablets


SRC: NLM .
