Naratriptan
Generic name: naratriptan
Brand name: Amerge
Dosage form: oral tablet (1 mg; 2.5 mg)
Drug class: Antimigraine agents
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is naratriptan used for?
Naratriptan is a prescription medicine that is used to treat migraine headaches.
Description
Naratriptan tablets, USP contain naratriptan hydrochloride USP, a selective 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonist. Naratriptan hydrochloride, USP is chemically designated as N-methyl-3-(1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)-1H-indole-5-ethanesulfonamide monohydrochloride, and it has the following structure:
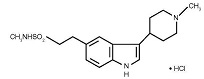
The empirical formula is C17H25N3O2S•HCl, representing a molecular weight of 371.93. Naratriptan hydrochloride, USP is a white to pale yellow powder that is sparingly soluble in water.
Each naratriptan tablet, USP for oral administration contains 1.11 or 2.78 mg of naratriptan hydrochloride USP, equivalent to 1 or 2.5 mg of naratriptan, respectively. Each tablet also contains the inactive ingredients croscarmellose sodium, anhydrous lactose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, opadry white (1 mg tablet) and opadry green (2.5 mg tablet). The components of opadry white are hypromellose, triacetin, and titanium dioxide. The components of opadry green are hypromellose, triacetin, titanium dioxide, iron oxide yellow, and FD&C Blue No. 2.
Mechanism of Action
Naratriptan binds with high affinity to human cloned 5-HT1B/1D receptors. Migraines are likely due to local cranial vasodilatation and/or to the release of sensory neuropeptides (including substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide) through nerve endings in the trigeminal system. The therapeutic activity of naratriptan tablets for the treatment of migraine headache is thought to be due to the agonist effects at the 5-HT1B/1D receptors on intracranial blood vessels (including the arterio-venous anastomoses) and sensory nerves of the trigeminal system, which result in cranial vessel constriction and inhibition of pro-inflammatory neuropeptide release.
Before taking naratriptan, tell your doctor:
For all patients taking naratriptan:
- If you are allergic to naratriptan; any part of this medicine; or any other drugs, foods, or substances. Tell your doctor about the allergy and what signs you had.
- If you have any of these health problems: High blood pressure or some types of migraine headaches like hemiplegic or basilar migraine.
- If you have ever had any of these health problems: Chest pain or pressure; diseased arteries going to the legs or arms; heart attack; heart disease; poor blood flow in the heart, brain, bowel, or kidney; stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA); or a heartbeat that is not normal like Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
- If you have any of these health problems: Kidney disease or liver disease.
- If you have taken almotriptan, eletriptan, frovatriptan, rizatriptan, sumatriptan, or zolmitriptan in the last 24 hours.
- If you have taken ergotamine, methysergide, dihydroergotamine, or any drug like them in the last 24 hours.
Children:
- If the patient is a child. Do not give naratriptan to a child.
This is not a list of all drugs or health problems that interact with naratriptan.
Tell your doctor and pharmacist about all of your drugs (prescription or OTC, natural products, vitamins) and health problems. You must check to make sure that it is safe for you to take naratriptan with all of your drugs and health problems. Do not start, stop, or change the dose of any drug without checking with your doctor.
What are some things I need to know or do while I take naratriptan?
- Tell all of your health care providers that you take naratriptan. This includes your doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and dentists.
- Allergic reactions have happened with naratriptan. Rarely, some reactions can be very bad or life-threatening. Talk with the doctor.
- Avoid driving and doing other tasks or actions that call for you to be alert until you see how naratriptan affects you.
- This medicine is not meant to prevent or lower the number of migraine headaches you get.
- If you have a headache that is not like your usual migraine headaches, talk with your doctor before you take naratriptan.
- Use care if you have risks for heart disease (high blood pressure, high cholesterol, overweight, high blood sugar or diabetes, cigarette smoking, man older than 40 years of age, other family members with early heart disease, woman after change of life). Talk with your doctor.
- Taking more of naratriptan (a higher dose, more often) than your doctor told you to take may cause your headaches to become worse.
- High blood pressure has happened with naratriptan. Have your blood pressure checked as you have been told by your doctor.
- If you are 65 or older, use naratriptan with care. You could have more side effects.
- Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan on getting pregnant. You will need to talk about the benefits and risks of using naratriptan while you are pregnant.
- Tell your doctor if you are breast-feeding. You will need to talk about any risks to your baby.
How is naratriptan best taken?
Use naratriptan as ordered by your doctor. Read all information given to you. Follow all instructions closely.
- Take with or without food.
- Swallow whole. Do not chew, break, or crush.
- Take with liquids as early as you can after the attack has started.
- If your headache comes back after the first dose, 1 more dose may be taken 4 hours after the first one.
What do I do if I miss a dose?
- This medicine is taken on an as needed basis. Do not take more often than told by the doctor.
What are the side effects of naratriptan that I need to call my doctor about immediately?
WARNING/CAUTION: Even though it may be rare, some people may have very bad and sometimes deadly side effects when taking a drug. Tell your doctor or get medical help right away if you have any of the following signs or symptoms that may be related to a very bad side effect:
- Signs of an allergic reaction, like rash; hives; itching; red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin with or without fever; wheezing; tightness in the chest or throat; trouble breathing, swallowing, or talking; unusual hoarseness; or swelling of the mouth, face, lips, tongue, or throat.
- Signs of high blood pressure like very bad headache or dizziness, passing out, or change in eyesight.
- Change in color of skin.
- Very bad headache or if headache is not better after the first dose.
- Loss of eyesight. This can be long-lasting.
- A burning, numbness, or tingling feeling that is not normal.
- Constipation.
- Diarrhea.
- Very upset stomach or throwing up.
- Severe stomach pain or bloody diarrhea.
- Fever.
- Weight loss.
- Leg cramps.
- Feeling of heaviness or tightness in the leg muscles.
- Feeling cold.
- Burning or aching pain in the feet or toes.
- Shortness of breath.
- A severe and sometimes deadly problem called serotonin syndrome may happen. The risk may be greater if you also take certain other drugs. Call your doctor right away if you have agitation; change in balance; confusion; hallucinations; fever; fast or abnormal heartbeat; flushing; muscle twitching or stiffness; seizures; shivering or shaking; sweating a lot; severe diarrhea, upset stomach, or throwing up; or very bad headache.
- Very bad and sometimes deadly heart problems like heart attack and a heartbeat that is not normal have rarely happened within a few hours of taking naratriptan. Call your doctor right away if you have chest, throat, neck, or jaw tightness, pain, pressure, or heaviness; break out in a cold sweat; shortness of breath; a fast heartbeat; a heartbeat that does not feel normal; or very bad dizziness or passing out.
- Very bad and sometimes deadly brain blood vessel problems like stroke have rarely happened with naratriptan. Call your doctor right away if you have weakness on 1 side of the body, trouble speaking or thinking, change in balance, drooping on 1 side of the face, or change in eyesight.
What are some other side effects of naratriptan?
All drugs may cause side effects. However, many people have no side effects or only have minor side effects. Call your doctor or get medical help if any of these side effects or any other side effects bother you or do not go away:
- Dizziness.
- Feeling sleepy.
- Feeling tired or weak.
- Flushing.
- Feeling of warmth.
- Upset stomach.
These are not all of the side effects that may occur. If you have questions about side effects, call your doctor. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.
You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-332-1088. You may also report side effects at https://www.fda.gov/medwatch.
If overdose is suspected:
If you think there has been an overdose, call your poison control center or get medical care right away. Be ready to tell or show what was taken, how much, and when it happened.
How do I store and/or throw out naratriptan?
- Store at room temperature.
- Store in a dry place. Do not store in a bathroom.
- Keep all drugs in a safe place. Keep all drugs out of the reach of children and pets.
- Throw away unused or expired drugs. Do not flush down a toilet or pour down a drain unless you are told to do so. Check with your pharmacist if you have questions about the best way to throw out drugs. There may be drug take-back programs in your area.
Label
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- NDC 69452-340-72
- Naratriptan Tablets, USP
- 1 mg
- PHARMACIST: Dispense the patient information leaflet provided separately to each patient.
- Rx only
- 9-Unit-of-Use Tablets
- BIONPHARMA

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- NDC 69452-341-72
- Naratriptan Tablets, USP
- 2.5 mg
- PHARMACIST: Dispense the patient information leaflet provided separately to each patient.
- Rx only
- 9-Unit-of-Use Tablets
- BIONPHARMA
![]()
SRC: NLM .
