Coumadin
Generic name: warfarin (oral)
Brand names: Coumadin, Jantoven
Drug class: Coumarins and indandiones
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Coumadin?
Coumadin is prescription medicine used to treat blood clots and to lower the chance of blood clots forming in your body. Blood clots can cause a stroke, heart attack, or other serious conditions if they form in the legs or lungs.
Description
COUMADIN (warfarin sodium) is an anticoagulant that acts by inhibiting vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors. Chemically, it is 3-(α-acetonylbenzyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin and is a racemic mixture of the R– and S-enantiomers. Crystalline warfarin sodium is an isopropanol clathrate. Its empirical formula is C19H15NaO4, and its structural formula is represented by the following:
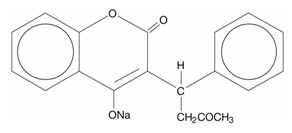
Crystalline warfarin sodium occurs as a white, odorless, crystalline powder that is discolored by light. It is very soluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol, and very slightly soluble in chloroform and ether.
COUMADIN tablets for oral use also contain:
| All strengths: | Lactose, starch, and magnesium stearate | |
| 1 mg: | D&C Red No. 6 Barium Lake | |
| 2 mg: | FD&C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake and FD&C Red No. 40 Aluminum Lake |
|
| 2-1/2 mg: | D&C Yellow No. 10 Aluminum Lake and FD&C Blue No. 1 Aluminum Lake |
|
| 3 mg: | FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake, and FD&C Red No. 40 Aluminum Lake |
|
| 4 mg: | FD&C Blue No. 1 Aluminum Lake | |
| 5 mg: | FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake | |
| 6 mg: | FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake and FD&C Blue No. 1 Aluminum Lake |
|
| 7-1/2 mg: | D&C Yellow No. 10 Aluminum Lake and FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake |
|
| 10 mg: | Dye-free |
COUMADIN for injection for intravenous use is supplied as a sterile, lyophilized powder, which, after reconstitution with 2.7 mL Sterile Water for Injection, contains:
| Warfarin sodium | 2 mg per mL | |
| Sodium phosphate, dibasic, heptahydrate | 4.98 mg per mL | |
| Sodium phosphate, monobasic, monohydrate | 0.194 mg per mL | |
| Sodium chloride | 0.1 mg per mL | |
| Mannitol | 38.0 mg per mL | |
| Sodium hydroxide, as needed for pH adjustment to 8.1 to 8.3 | ||
Mechanism of Action
Warfarin acts by inhibiting the synthesis of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors, which include Factors II, VII, IX, and X, and the anticoagulant proteins C and S. Vitamin K is an essential cofactor for the post ribosomal synthesis of the vitamin K-dependent clotting factors. Vitamin K promotes the biosynthesis of γ-carboxyglutamic acid residues in the proteins that are essential for biological activity. Warfarin is thought to interfere with clotting factor synthesis by inhibition of the C1 subunit of vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKORC1) enzyme complex, thereby reducing the regeneration of vitamin K1 epoxide
What is the most important information I should know about Coumadin?
Coumadin can cause bleeding which can be serious and sometimes lead to death. This is because Coumadin is a blood thinner medicine that lowers the chance of blood clots forming in your body.
You may have a higher risk of bleeding if you take Coumadin and:
- are 65 years of age or older
- have a history of stomach or intestinal bleeding
- have high blood pressure (hypertension)
- have a history of stroke, or “mini-stroke” (transient ischemic attack or TIA)
- have serious heart disease
- have a low blood count or cancer
- have had trauma, such as an accident or surgery
- have kidney problems
- take other medicines that increase your risk of bleeding, including:
- a medicine that contains heparin
- other medicines to prevent or treat blood clots
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- take warfarin sodium for a long time. Warfarin sodium is the active ingredient in Coumadin.
Tell your healthcare provider if you take any of these medicines. Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if your medicine is one listed above.
Many other medicines can interact with Coumadin and affect the dose you need or increase Coumadin side effects. Do not change or stop any of your medicines or start any new medicines before you talk to your healthcare provider.
Do not take other medicines that contain warfarin sodium while taking Coumadin.
- Get your regular blood test to check for your response to Coumadin. This blood test is called an INR test. The INR test checks to see how fast your blood clots. Your healthcare provider will decide what INR numbers are best for you. Your dose of Coumadin will be adjusted to keep your INR in a target range for you.
- Call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following signs or symptoms of bleeding problems:
- pain, swelling, or discomfort
- headaches, dizziness, or weakness
- unusual bruising (bruises that develop without known cause or grow in size)
- nosebleeds
- bleeding gums
- bleeding from cuts takes a long time to stop
- menstrual bleeding or vaginal bleeding that is heavier than normal
- pink or brown urine
- red or black stools
- coughing up blood
- vomiting blood or material that looks like coffee grounds
- Some foods and beverages can interact with Coumadin and affect your treatment and dose.
- Eat a normal, balanced diet. Talk to your healthcare provider before you make any diet changes. Do not eat large amounts of leafy, green vegetables. Leafy, green vegetables contain vitamin K. Certain vegetable oils also contain large amounts of vitamin K. Too much vitamin K can lower the effect of Coumadin.
- Always tell all of your healthcare providers that you take Coumadin.
- Wear or carry information that you take Coumadin.
See “What are the possible side effects of Coumadin?” below for more information about side effects.
Who should not take Coumadin?
Do not take Coumadin if:
- your risk of having bleeding problems is higher than the possible benefit of treatment. Your healthcare provider will decide if Coumadin is right for you.
- you are pregnant unless you have a mechanical heart valve. Coumadin may cause birth defects, miscarriage, or death of your unborn baby.
- you are allergic to warfarin or any of the other ingredients in Coumadin. See “What are the ingredients in Coumadin?” for a complete list of ingredients in Coumadin.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Coumadin?
Before taking Coumadin, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have bleeding problems
- fall often
- have liver problems
- have kidney problems or are undergoing dialysis
- have high blood pressure
- have a heart problem called congestive heart failure
- have diabetes
- plan to have any surgery or a dental procedure
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. See “Who should not take Coumadin?”above. Your healthcare provider will do a pregnancy test before you start treatment with Coumadin. Females who can become pregnant should use effective birth control during treatment, and for at least 1 month after the last dose of Coumadin.
- are breastfeeding. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take Coumadin and breastfeed. Check your baby for bruising or bleeding if you take Coumadin and breastfeed.
Tell all of your healthcare providers and dentists that you are taking Coumadin. They should talk to the healthcare provider who prescribed Coumadin for you before you have any surgery or dental procedure. Your Coumadin may need to be stopped for a short time or you may need your dose adjusted.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Some of your other medicines may affect the way Coumadin works. Certain medicines may increase your risk of bleeding. See “What is the most important information I should know about Coumadin?”.
How should I take Coumadin?
- Take Coumadin exactly as prescribed. Your healthcare provider will adjust your dose from time to time depending on your response to Coumadin.
- You must have regular blood tests and visits with your healthcare provider to monitor your condition.
- If you miss a dose of Coumadin, call your healthcare provider. Take the dose as soon as possible on the same day. Do not take a double dose of Coumadin the next day to make up for a missed dose.
- Call your healthcare provider right away if you:
- take too much Coumadin
- are sick with diarrhea, an infection, or have a fever
- fall or injure yourself, especially if you hit your head. Your healthcare provider may need to check you.
What should I avoid while taking Coumadin?
Do not do any activity or sport that may cause a serious injury.
What are the possible side effects of Coumadin?
Coumadin may cause serious side effects including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about Coumadin?”
- Death of skin tissue (skin necrosis or gangrene). This can happen soon after starting Coumadin. It happens because blood clots form and block blood flow to an area of your body. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have pain, color, or temperature change to any area of your body. You may need medical care right away to prevent death or loss (amputation) of your affected body part.
- Kidney problems. Kidney injury may happen in people who take Coumadin. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop blood in your urine.Your healthcare provider may do tests more often during treatment with Coumadin to check for bleeding if you already have kidney problems.
- “Purple toes syndrome.” Call your healthcare provider right away if you have pain in your toes and they look purple in color or dark in color.
These are not all of the side effects of Coumadin. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1‑800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Coumadin.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Coumadin for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Coumadin to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about Coumadin that is written for health professionals.
How should I store Coumadin?
- Store Coumadin at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep Coumadin in a tightly closed container
- Keep Coumadin out of the light and moisture.
- Follow your healthcare provider or pharmacist instructions about the right way to throw away outdated or unused Coumadin.
- Females who are pregnant should not handle crushed or broken Coumadin tablets.
Keep Coumadin and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Coumadin tablets?
Active ingredient: warfarin sodium
Inactive ingredients: lactose, starch, and magnesium stearate, in addition:
- 1 mg: D&C Red No. 6 Barium Lake
- 2 mg: FD&C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake and FD&C Red No. 40 Aluminum Lake
- 2.5 mg: D&C Yellow No. 10 Aluminum Lake and FD&C Blue No. 1 Aluminum Lake
- 3 mg: FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake, and FD&C Red No. 40 Aluminum Lake
- 4 mg: FD&C Blue No. 1 Aluminum Lake
- 5 mg: FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake
- 6 mg: FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake and FD&C Blue No. 1 Aluminum Lake
- 7.5 mg: D&C Yellow No. 10 Aluminum Lake and FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake
- 10 mg: Dye-free
Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 43353-493
Warfarin Na (Coumadin®) 1mg
Rx Only

- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 43353-494
Warfarin Na (Coumadin®) 7.5mg
Rx Only

- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL


