Adoxa
Generic name: Doxycycline Capsules
Brand name: Adoxa
Drug class: Tetracyclines
What is Adoxa
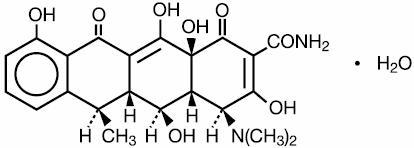 Adoxa(Doxycycline Monohydrate) is equivalent to 100 mg, 75 mg, or 50 mg of doxycycline for oral administration. The light-yellow crystalline powder’s chemical name is alpha-6-deoxy-5-oxytetracycline.
Adoxa(Doxycycline Monohydrate) is equivalent to 100 mg, 75 mg, or 50 mg of doxycycline for oral administration. The light-yellow crystalline powder’s chemical name is alpha-6-deoxy-5-oxytetracycline.
Uses of Adoxa:

- Rickettsial infections are illnesses caused by Rickettsia ricket
- Infections that are spread by sexual contact
- Infections of the respiratory tract
- Bacterial infections that are specific
- Infections of the eyes
- Anthrax, especially anthrax inhaled (post-exposure)
- When penicillin is contraindicated, there are other options for treating some illnesses.
- Adjunctive treatment for severe acne and acute intestinal amebiasis
- Malaria prophylaxis
 The Rickettsial Infections
The Rickettsial Infections - Transmission of sexually transmitted diseases
- Infections of the respiratory tract
- Specific bacteria-related infection
- Ophthalmic diseases
- Anthrax Inhalational Anthrax (post-exposure)
- Alternative treatment for specific infections where penicillin is not recommended
- Adjunctive treatment to treat acute intestinal amebiasis as well as extremely skin acne
- Malaria prevention
What to tell my doctor before I take Adoxa?
- If you are allergic to Adoxa (doxycycline capsules); any part of Adoxa; or any other drugs, foods, or substances. Tell your doctor about the allergy and what signs you had.
- If you are taking any of these drugs: Acitretin, isotretinoin, or penicillin.
This is not a list of all drugs or health problems that interact with Adoxa
Tell your doctor and pharmacist about all of your drugs (prescription or OTC, natural products, vitamins) and your health problems. You must check to make sure that it is safe for you to take Adoxa with all of your drugs and health problems. Do not start, stop, or change the dose of any drug without checking with your doctor.¶
Warnings and precautions
Tooth Development
- Use of the drugs in the tetracycline-class in the period of the development of teeth (last part of pregnancy, from infancy to childhood until the age of 8 years) could cause permanent discoloration of teeth (yellow-gray-brown). This type of reaction is more prevalent when the use is long-term. drugs, however, it has also been noticed following repeated short-term treatments. The condition of enamel hypoplasia is also documented. Use Adoxa for pediatric patients aged 8 years or less age or less, only if there are benefits that could be believed to outweigh the risk for life-threatening or severe circumstances (e.g. anthrax and Rocky Mountain spotted fever) in particular when there is no alternative treatment options.
Clostridium difficile Associated Diarrhea
- Clostridium difficile-related diarrhea (CDAD) has been identified by using nearly all antibacterial medications such as Adoxa. The condition can be mild diarrhea to death from colitis. The treatment with antibacterial drugs alters the colon’s normal flora which can lead to an increase in C. difficile.
- C. difficile is a bacterium that produces toxin B and A that aid in developing CDAD. C. difficile that produces hyper toxin-producing strains C. difficile are associated with increased mortality and morbidity as the infections may be resistant to treatment with antibacterials and could necessitate colectomy. CDAD should be considered in any patient who presents with diarrhea after antibacterial treatment. A thorough medical history is required because CDAD is reported to develop over a period of two months following the treatment with antibacterial agents.
- In the event that CDAD can be confirmed as a possibility, any treatment with antibacterials that are not targeted at C. difficile might have to be stopped. The appropriate management of electrolytes and fluids, as well as protein supplementation for treatment for antibacterial infections of C. difficile as well as the need for surgical evaluation, must be implemented according to the clinical indications.
Photosensitivity
- The over-exaggerated sunburn reaction was observed in some people who are taking tetracyclines. Patients who are exposed to ultraviolet or direct sunlight must be aware that this reaction may be caused by tetracycline medications and should be stopped at the first indication for skin erythema.
Possibility of Microbial Overgrowth
- Adoxa may result in the overgrowth of non-susceptible bacteria, such as fungi. If you notice any of these infections stop use and implement appropriate treatment.
Extreme skin reactions
- Severe skin reactions like exfoliative dermatitis Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, erythema multiform and toxic epidermal necrolysis, and eosinophilia as a drug reaction and other manifestations (DRESS) are observed in patients who receive Doxycycline. If skin reactions are severe it is recommended to stop doxycycline immediately and the appropriate therapy is implemented.
Intracranial Hypertension
- Intracranial hypertension (IH also known as pseudotumor cerebri) is associated with treatment with tetracyclines such as Adoxa. Clinical signs of IH include blurred vision, headache diplopia, headache, and loss of vision; papilledema is seen on fundoscopy. Women that are obese or have a previous history of IH are at a higher risk of developing tetracycline-related IH. The use of isotretinoin in conjunction with Adoxa must be avoided as isotretinoin is also linked to the development of pseudotumor cerebri.
- While IH usually resolves following removal of treatment, the risk of permanent visual loss is present. If there is a visual disturbance in the course of treatment, an immediate ophthalmologic assessment is recommended. Because intracranial pressure is high for several weeks following discontinuation of medication, patients need to be observed until they settle.
Delayed Skeletal Growth
- All tetracyclines are stable calcium complexes within any bone-forming tissue. A reduction in the growth rate is observed in premature who are given oral tetracycline at amounts of around 25 mg/kilogram every 6 hours. The reaction was found to be reversible after the drug was removed.
- Studies on animals have shown that tetracyclines pass through the placenta and are found in the fetal tissues and may have harmful effects on the growing fetus (often due to a delay in the development of the skeletal system). Evidence of embryotoxicity has been observed when animals are treated early in pregnancy. Tetracycline-class medications can cause harm to the fetus if used on pregnant women however, the data on the drug doxycycline is insufficient. If any tetracycline drug is taken during pregnancy or if a patient is pregnant while taking these medications, they must be informed of the risk to the fetus.
Antianabolic Action
- The antianabolic effects of tetracyclines could result in an elevation in the number of BUN. Research has shown that this is not the case when doxycycline is used in patients suffering from impaired kidney function.
Complete Suppression of Malaria
- Doxycycline provides significant but not complete suppression of sexual Blood stages in Plasmodium strains.
- Doxycycline doesn’t suppress P. falciparum’s gametocytes of the sexual blood stage. People who take this regimen could still transmit the disease to mosquitoes that are not in the endemic zones.
The Development of Drug-resistant Bacteria
- Prescription of Adoxa without a documented or suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is not likely to bring benefits for the patient and may increase the chance of developing antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Laboratory Monitoring of Long-Term Therapy
- In the long-term treatment, regular examination of organ systems in the laboratory including hematopoietic and liver and renal studies must be conducted.
How is this medicine taken?
Use Adoxa as ordered by your doctor. Read all information given to you. Follow all instructions closely.
- Keep taking Adoxa as you have been told by your doctor or other health care provider, even if you feel well.
- Some drugs may need to be taken with food or on an empty stomach. For some drugs, it does not matter. Check with your pharmacist about how to take Adoxa.
- It is best to avoid taking Adoxa at the same time as milk, dairy, or other products with calcium. This medicine may not work as well. If you have questions, talk with the doctor or pharmacist.
- Drink lots of noncaffeine liquids unless told to drink less liquid by your doctor.
- Do not take bismuth (Pepto-Bismol®), calcium, iron, magnesium, zinc, multivitamins with minerals, colestipol, cholestyramine, didanosine, or antacids within 2 hours of Adoxa
- Take with a full glass of water.
- Do not lie down for at least 30 minutes after taking Adoxa
Dosage and administration
- Adults: The standard starting dose of oral doxycycline is 200 mg (given 100 mg every 12 hours or 50 mg every 6 hours), followed by a 100 mg/day maintenance dose. The maintenance dosage can be given in a single dose or in increments of 50 mg every 12 hours. 100 mg every 12 hours is suggested for the treatment of more severe infections (especially chronic infections of the urinary tract).
- For pediatric patients over the age of eight, the recommended dosage schedule is 2 mg/lb of body weight divided into two doses on the first day of treatment, followed by 1 mg/lb of body weight given as a single daily dose or divided into two doses on subsequent days for pediatric patients weighing 100 pounds or less. Up to 2 mg/lb of body weight may be administered for more severe illnesses. The regular adult dose should be administered for pediatric patients weighing more than 100 pounds.
- Adults with uncomplicated gonococcal infections (excluding anorectal infections in males) should take 100 mg twice a day for 7 days. As an alternative single-visit dosage, give 300 mg stat followed by a second 300 mg dose one hour later.
- If you have acute epididymo-orchitis caused by N. gonorrhoeae, take 100 mg twice a day by mouth for at least 10 days.
- For both primary and secondary syphilis, take 300 mg in split doses every day for at least 10 days.
- Adults with an uncomplicated urethral, endocervical, or rectal infection caused by Chlamydia trachomatis should take 100 mg twice day for at least 7 days.
- For nongonococcal urethritis caused by C. trachomatis and U. urealyticum, take 100 mg twice a day by mouth for at least 7 days.
- Acute epididymo-orchitis caused by C. trachomatis: take 100 mg twice a day by mouth for at least 10 days.
- Anthrax inhalation (post-exposure):
- ADULTS: Take 100 mg of doxycycline twice a day for 60 days by mouth.
- CHILDREN: take 1 mg/lb (2.2 mg/kg) of body weight twice a day for 60 days if they weigh less than 100 pounds (45 kg). The adult dose should be given to children weighing 100 pounds or more.
- In the case of streptococcal infections, treatment should be continued for a minimum of 10 days.
- To wash down tetracycline-class medications in capsule and tablet form and limit the danger of esophageal irritation and ulcers, it is suggested that you drink plenty of water when taking them. Doxycycline can be taken with meals if stomach discomfort occurs. The time to peak plasma concentrations is delayed by an average of one hour and 20 minutes after eating a high-fat meal.
What do I do if I miss a dose?
- Take a missed dose as soon as you think about it.
- If it is close to the time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your normal time.
- Do not take 2 doses at the same time or extra doses.
Adoxa side effects
- Signs of an allergic reaction, like rash; hives; itching; red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin with or without fever; wheezing; tightness in the chest or throat; trouble breathing, swallowing, or talking; unusual hoarseness; or swelling of the mouth, face, lips, tongue, or throat.
- Signs of liver problems like dark urine, feeling tired, not hungry, upset stomach or stomach pain, light-colored stools, throwing up, or yellow skin or eyes.
- Signs of a pancreas problem (pancreatitis) like very bad stomach pain, very bad back pain, or very bad upset stomach or throwing up.
- Chest pain or pressure or a fast heartbeat.
- Not able to pass urine or change in how much urine is passed.
- Fever, chills, or sore throat; any unexplained bruising or bleeding; or feeling very tired or weak.
- Throat irritation.
- Trouble swallowing.
- Muscle or joint pain.
- Fast breathing.
- Flushing.
- Very bad dizziness or passing out.
- Change in skin color.
- Swollen gland.
- Vaginal itching or discharge.
- Diarrhea is common with antibiotics. Rarely, a severe form called C diff–associated diarrhea (CDAD) may happen. Sometimes, this has led to a deadly bowel problem (colitis). CDAD may happen during or a few months after taking antibiotics. Call your doctor right away if you have stomach pain, cramps, or very loose, watery, or bloody stools. Check with your doctor before treating diarrhea.
- Raised pressure in the brain has happened with Adoxa Most of the time, this will go back to normal after Adoxa is stopped. Sometimes, loss of eyesight may happen and may not go away even after Acticlate (doxycycline tablets and capsules) is stopped. Call your doctor right away if you have a headache or eyesight problems like blurred eyesight, seeing double, or loss of eyesight.
All drugs may cause side effects. However, many people have no side effects or only have minor side effects. Call your doctor or get medical help if any of these side effects or any other side effects bother you or do not go away:
- Not hungry.
- Upset stomach or throwing up.
- Diarrhea.
These are not all of the side effects that may occur. If you have questions about side effects, call your doctor. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.
You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-332-1088. You may also report side effects at https://www.fda.gov/medwatch.
If I take too much
If you think there has been an overdose, call your poison control center or get medical care right away. Be ready to tell or show what was taken, how much, and when it happened.
Consumer information use
- If your symptoms or health problems do not get better or if they become worse, call your doctor.
- Do not share your drugs with others and do not take anyone else’s drugs.
- Some drugs may have another patient information leaflet. Check with your pharmacist. If you have any questions about Adoxa, please talk with your doctor, nurse, pharmacist, or other health care provider.
- If you think there has been an overdose, call your poison control center or get medical care right away. Be ready to tell or show what was taken, how much, and when it happened.
How is supplied
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
